Phases of Matter
advertisement

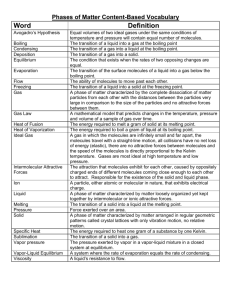
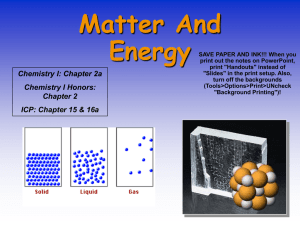
Phases of Matter 3.d. Students know the states of matter (solid, liquid, gas) depend on molecular motion. 1. Which of the following show the phases of matter in the order from LEAST to MOST molecular motion? a. Solid – Gas – Liquid b. Liquid – Solid – Gas c. Gas – Solid – Liquid d. Solid – Liquid – Gas 2. Which statement is true about the motions of solids, liquid and gases? a. Solid molecules has more motion than liquid b. Solid molecules has more motion than gas c. Liquid molecules has more motion than gas d. Gas molecules has more motion than liquid 3. When water evaporate from liquid to gas, the molecules: a. Spread out b. Split c. Combined with other molecules d. Form a new substance 4. What word describes the volume of a solid? a. Variable b. Fixed c. Definite d. Exact 5. Liquid has definite _____ and _____ shape. a. Shape, volume b. Pressure, density c. Volume, indefinite d. Distance, velocity 6. Phases of matter are dependent on the _____. a. Size b. Molecular motion/movement c. Elevation d. Location 7. Air a mixture of different elements and compounds in _______ form. a. Gas b. Aero c. Liquid vapor d. Solid 8. Which statement is true? a. The energy level of solids are greater than liquids b. The energy level of gases are greater than liquids c. The energy level of gases and liquids are the same d. The energy level of solids and liquids are the same 9. In which of the following do the molecules have the LEAST energy? a. A frozen popsicle b. A glass of lemonade c. A cup of warm coffee d. A pot of boiling water 10. Which object contains matter with the MOST energy? a. A science book b. A helium balloon c. A glass of water d. A scoop of ice cream 3.e. Students know that in solids the atoms are closely locked in position and can only vibrate; in liquids the atoms and molecules are more loosely connected and can collide with and move past one another; and in gases the atoms and molecules are free to move independently, colliding frequently. 11. Which of these statements best explains how molecules in a liquid act? a. Closely spaced molecules vibrate b. Closely spaced molecules slide past one another c. Molecules move independently of one another and collide often d. Molecules are bonded to form one large molecule Phases of Matter 12. Which of these statements best explains flowing liquids? a. Closely spaced molecules vibrate. b. Closely spaced molecules move past one another. c. Molecules move independently of one another. d. Molecules are bonded to form one large molecule. 13. Arnold knows from using a bicycle pump that gases can be compressed into a smaller volume. Which of these statements best explains why this is possible? a. Molecules in a gas are arranged in a set pattern. b. Molecules in a gas become smaller under pressure. c. Molecules in a gas have lots of space between them. d. Molecules in a gas are strongly attracted to one another. 14. Which of the following statements best describes why solids have definite shapes while liquids and gases do not? a. Atoms have more heat when in the solid state. b. Atoms vibrate slightly in position when in the solid state. c. Atoms are softer when in the liquid and gas states. d. Atoms are lighter when in the liquid and gas states. 15. What word describes the spreading out of gas molecules? a. Crystals b. Viscosity c. Diffusion d. Fart 16. Which liquid has the greatest viscosity? a. Honey b. Soda c. Water d. Carbon Dioxide 17. In which compound do molecules move freely and collide often? a. Solution of salt dissolved in water b. Solid sodium chloride c. Liquid sodium chloride d. Gaseous sodium chloride 18. The tiny particles that make up a solid a. Can move more easily than the particles in other phases. b. Can flow around each other. c. Are spread far apart. d. Are packed very close together. 19. Which phase is the densest? a. Solid b. Liquid c. Plasma d. Gas 20. Compressing is a term used to increase the pressure of a gas. What is the best example of a compressed gas? a. The air inside a bicycle tire b. The steam coming from a pot of boiling water c. The bubble produced by scuba divers under the water d. None of the above 5.d. Students know physical processes include freezing and boiling, in which a material changes form with no chemical reaction. 21. In order for a liquid to change into a solid, the object must ______________ thermal energy. a. Add b. Remove c. Constant d. Normal Phases of Matter 22. Matter changes state (phase) when a sufficient amount of thermal energy changes. a. True b. False c. Both d. Neither 23. On a hot sunny day, ice cream will transform from a solid to a liquid. What phase change did the ice cream experience? a. freezing b. melting c. condensation d. boiling 24. Which of the following describes a physical process for turning a solid into a gas? a. Baking a cake b. Heating ice until it melts, then boiling it c. Burning wood until it creates smoke and flames d. Blowing baby powder in the air 25. Which of the following involves a decrease in molecular motion? a. Freezing b. Melting c. Boiling d. Condensation 26. As an ice cube melts, its molecules a. Release heat energy and move closer together b. Release heat energy and move farther apart c. Absorb heat energy and from a crystal pattern d. Absorb heat energy and move farther apart 27. What phase change does dry ice undergo when it transforms from a solid to a gas, skipping the liquid phase entirely? a. Boiling b. Condensation c. Sublimation d. Deposition 28. Phase change is a form of _________. a. Chemical change b. Physical change c. Mixture d. Solution 29. The beads of sweat on the outside of your cup come from the water vapor in the air. What phase change did the water vapor have to undergo to become the dew drops on the outside of your cup? a. Deposition b. Condensation c. Evaporation d. Solidification 30. As matter cools, its particles ___________. a. Move farther apart b. Move closer together c. Stay the same d. Turn blue