The Oceans of the Earth Article
advertisement

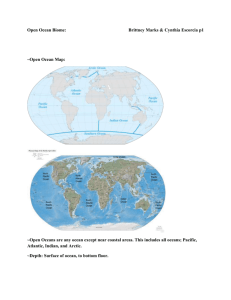
The Oceans of Earth More than 70% of the surface of Earth is covered with water. The ocean contains 97.6% of Earth’s water. The largest bodies of water are called oceans and are open to each other. Smaller bodies are called seas which are often enclosed 2 or more sides by land. Almost 2% of the water on Earth is in the ice of the icecaps of the North and South Pole. Less than 1% of water on Earth is fresh water. Fresh water is located in lakes and rivers. Why are the oceans salty? Fresh water in streams and rivers contains salts. Rivers flow into the ocean. It is estimated that about 4 billion tons of salts are carried by rivers and added to the ocean each year. Over time, more and more salts are added to the ocean. Also water evaporates out of the ocean leaving salts behind. Volcanoes, vents and other processes at the seafloor spew minerals from below Earth’s crust into the ocean. Particles, including minerals, can be carried by wind and deposited into the ocean. Salts remain dissolved in ocean water unless they become incorporated into sediments and rocks on the seafloor. We generally consider water to be salty or fresh. Water that is somewhere in between salty and fresh is referred to as brackish. Brackish water can be found in estuaries, ecosystems where rivers meet the seas. Estuaries are incredibly important to the ocean. They are sometimes called the “nurseries of the sea” because they are places where the young of many seabirds, fish, shellfish and other organisms can develop in a protected area. Many commercial fish species rely on estuaries as habitats for some portion of the life cycle. Migrating bird species often use estuaries as a resting place. Estuaries can filter and clean water before it travels to the ocean. Estuaries also protect coastlines by preventing erosion from large storms and storm surges. The measure of dissolved salts in water is known as salinity. Distilled water has no salinity. Fresh water and tap water have very low salinity. Water is considered fresh if it contains 1 part per thousand or less of salts. In contrast, the average salinity of the ocean is 35 parts per thousand (or 3.5% salty). Salinity is measured in “practical salinity units”, or PSU. One PSU is equal to one part per thousand. In general, the salinity of the ocean is greater in the equatorial region, especially at the surface where a lot of water evaporates into the atmosphere. Scientists who study the ocean are called oceanographers. They study waves that break on shore. They study the currents which are like rivers in the ocean. They study the salinity and physical makeup of the water. They study the temperature of the oceans and the topography of the ocean floor. Oceanographers have made a map of the currents in the ocean. The California Current flows off shore from San Diego. It begins near Alaska and follows the coastline south. It flows past California and Mexico. Because the water in the California Current has come from near Alaska (the north), the water is cold. Ocean salt water = 97.6% Ice sheets & glaciers = 1.9% Groundwater aquifers = 0.5% Rivers, lakes & inland seas = 0.02% Soil moisture = 0.01% Atmospheric water = 0.0001% *Only 0.4% of the water on Earth is accessible as fresh water. Answer each question in a complete sentence. Underline your answer in the text. 1) How much of the Earth’s water is fresh water? 2) Complete the table: Type of Water Distilled Tap Fresh Salt Average Salinity (PSU) 3. What is a PSU? 4. Name four things that oceanographers can study in the ocean. 5. If you were an oceanographer, which things would you like to study? Why? 6. Which current flows past California? 7. Describe the path of the California Current. 8. What is the difference between and ocean and a sea? 9. Where would you expect the ocean to be saltier, off the coast of Alaska or off the coast of Peru? Why? 10. Think about the solutions of sugar water that you prepared for the rainbow lab. Do you remember which solution was the densest? Which do you think is denser, salt water or fresh water? Which will provide more support for a floating body?