File - The Envirothon
advertisement
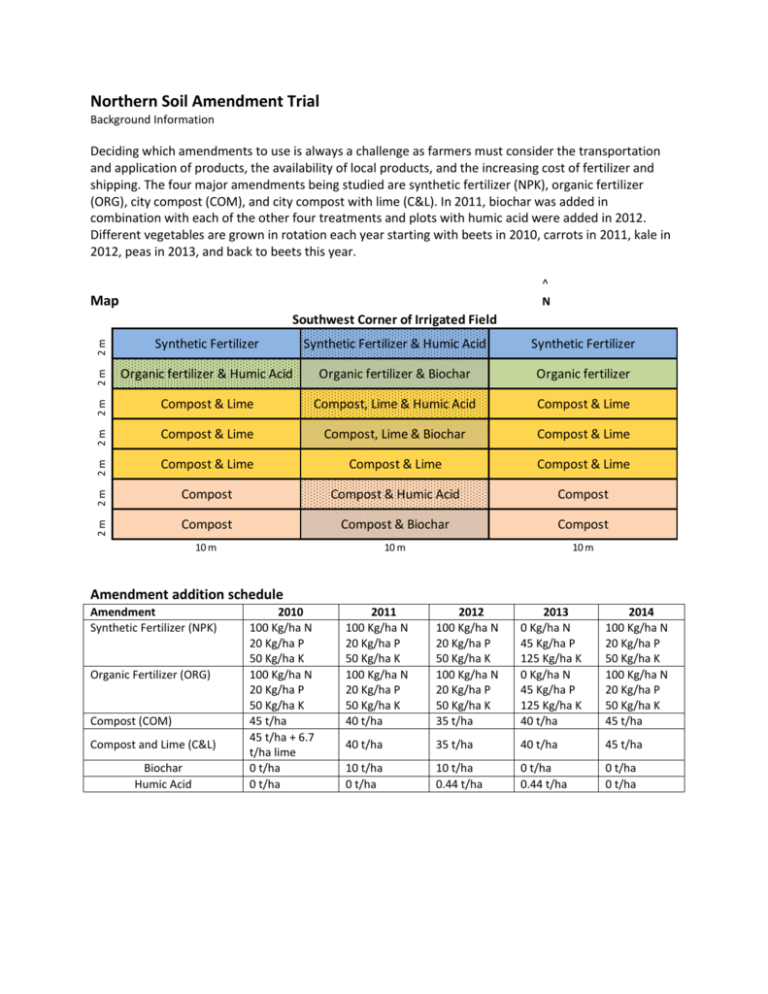
Northern Soil Amendment Trial Background Information Deciding which amendments to use is always a challenge as farmers must consider the transportation and application of products, the availability of local products, and the increasing cost of fertilizer and shipping. The four major amendments being studied are synthetic fertilizer (NPK), organic fertilizer (ORG), city compost (COM), and city compost with lime (C&L). In 2011, biochar was added in combination with each of the other four treatments and plots with humic acid were added in 2012. Different vegetables are grown in rotation each year starting with beets in 2010, carrots in 2011, kale in 2012, peas in 2013, and back to beets this year. ^ N Map 2m Synthetic Fertilizer Synthetic Fertilizer & Humic Acid Synthetic Fertilizer 2m Organic fertilizer & Humic Acid Organic fertilizer & Biochar Organic fertilizer 2m Compost & Lime Compost, Lime & Humic Acid Compost & Lime 2m Compost & Lime Compost, Lime & Biochar Compost & Lime 2m Compost & Lime Compost & Lime Compost & Lime 2m Compost Compost & Humic Acid Compost 2m Southwest Corner of Irrigated Field Compost Compost & Biochar Compost 10 m 10 m 10 m Amendment addition schedule Amendment Synthetic Fertilizer (NPK) Organic Fertilizer (ORG) Compost (COM) Compost and Lime (C&L) Biochar Humic Acid 2010 100 Kg/ha N 20 Kg/ha P 50 Kg/ha K 100 Kg/ha N 20 Kg/ha P 50 Kg/ha K 45 t/ha 45 t/ha + 6.7 t/ha lime 0 t/ha 0 t/ha 2011 100 Kg/ha N 20 Kg/ha P 50 Kg/ha K 100 Kg/ha N 20 Kg/ha P 50 Kg/ha K 40 t/ha 2012 100 Kg/ha N 20 Kg/ha P 50 Kg/ha K 100 Kg/ha N 20 Kg/ha P 50 Kg/ha K 35 t/ha 2013 0 Kg/ha N 45 Kg/ha P 125 Kg/ha K 0 Kg/ha N 45 Kg/ha P 125 Kg/ha K 40 t/ha 2014 100 Kg/ha N 20 Kg/ha P 50 Kg/ha K 100 Kg/ha N 20 Kg/ha P 50 Kg/ha K 45 t/ha 40 t/ha 35 t/ha 40 t/ha 45 t/ha 10 t/ha 0 t/ha 10 t/ha 0.44 t/ha 0 t/ha 0.44 t/ha 0 t/ha 0 t/ha Fertilizer background information The costs listed here are for commercial volumes and landed in the Yukon, costs of fertilizers vary every year, but with an upward trend over time. Synthetic Fertilizers Nitrogen (Urea 46-0-0) Phosphate (Triple Superphosphate 0-45-0) Potassium (Potassium sulphate 0-0-50) Supplier: Agrium Cost: $1 per kg Supplier: Agrium Cost: $1 per kg Supplier: Agrium Cost: $1.25 per kg Synthetically formulated Aka: NH2CONH2, CO(NH2)2, carbamide 95.5-97.5% Urea: nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen and carbon 1-1.5% Biuret (result of condensation of urea molecules - different organization of N, H, C and O) .1-.4% water Synthetically formulated Aka: GTSP, Concentrated superphosphate, calcium bis(dihydrogenorthophosphate) 58-95% Superphosphates, concentrated (P2O5) 1-20% Calcium sulphate (CaS04) 0.1-15% Calcium hydrogen orthophosphate (CaHPO4) 0.1-10% Fluorapatite (Ca5(PO4)3F) 0.1-5% Orthophosphoric acid (H3PO4) Mined Product Aka: K2SO4, sulphate of potash, SOP 10-15% Potassium hydrogen sulfate (KHSO 4) >85% Potassium sulphate (K2SO4) Organic Fertilizers Bloodmeal (12-0-0) Bone Meal (2-14-0) Potassium (Sulphate of potash 0-0-50) *This is both used in synthetic and organic fertilizer blends Supplier: Gaia Green Cost: $2.25 per kg Supplier: Agrium Cost:$2 per kg Supplier: Agrium Cost: $1.25 per kg Animal byproduct Components of Vertebrate Blood Proteins: made of amino acids o Carbon group, Hydrogen (-H), carboxyl group (-COOH), amino group (NH2) and unique side chain or R-group Fatty Acids: Chains of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen Urea: CO(NH2)2 Nutrients and vitamins in trace amounts including Ca, Fe, and P Glucose: C6H12O6 Hormones Electrolytes: Na+, K+, ClAnimal byproduct High in phosphorous and calcium Collagen - protein Carbonated hydroxyapatite Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 Mined Product Aka: K2SO4, potassium sulphate, SOP 10-15% Potassium hydrogen sulfate (KHSO 4) >85% Potassium sulphate (K2SO4) Compost City of Whitehorse Compost, from Boreal Compost Enterprises, LTD. Cost: 1 to 9 cubic yards: $45/yard, and 10 or more cubic yards: $25/yard. Note: One cubic yard = 3x3x3 feet = 1600 pounds ≈ one pick-up truck load. The composting produced at the Whitehorse compost facility is commonly known as hot aerobic composting. For more information: www.borealcompost.ca Lime Addition of Garden Green Lawn and Garden Lime, a pulverized limestone with a minimum 38% Ca and 97% CaCO3. Liming soils is common practice in other areas of the world where it counteracts acidification of soils. Our soils have a high pH and general sufficient Calcium, has the lime helped the garden grow? Cost is approximately $1 per kg. Humic Acid Humic acid is a naturally occurring component of soil that is formed by the microbial decomposition of organic matter. Once in this form, humic acid is very resistant to further chemical breakdown. In addition to naturally synthesized form, humic acid can also be extracted from mineral deposits similar to coal. The commercially mined humic acid is sold as a soil amendment product that has been linked with assisting the breakdown of compacted soils, helping the absorption and transfer of macro- and micronutrients, and encouraging the development of soil microbes. As compost is formed by the decomposition of organic matter, it already contains humic acid. There are concerns about the quality of compost in 2012 and this could have helped mitigate this problem. Humic acid will continue to be studied in 2013’s soil amendment trial and it will be interesting to see if humic acid increases yields even when the compost is better quality. Cost of humic acid varies dramatically, but expect to pay $10 or more per kg. Is the cost worth it? Biochar Biochar is essentially charcoal – the black, partially combusted remnants commonly found in a woodstove or after a campfire. Biochar is created when the heating of organic matter occurs with minimal oxygen – without the oxygen, carbon molecules cannot gas off as carbon dioxide and remain in solid form. The technical name for this process is pyrolysis. Cost of biochar varies dramatically, expect to pay about $2 per kg. Graph of results from previous years









