ES11 U3 Asst 1 Rocks and Minerals
advertisement
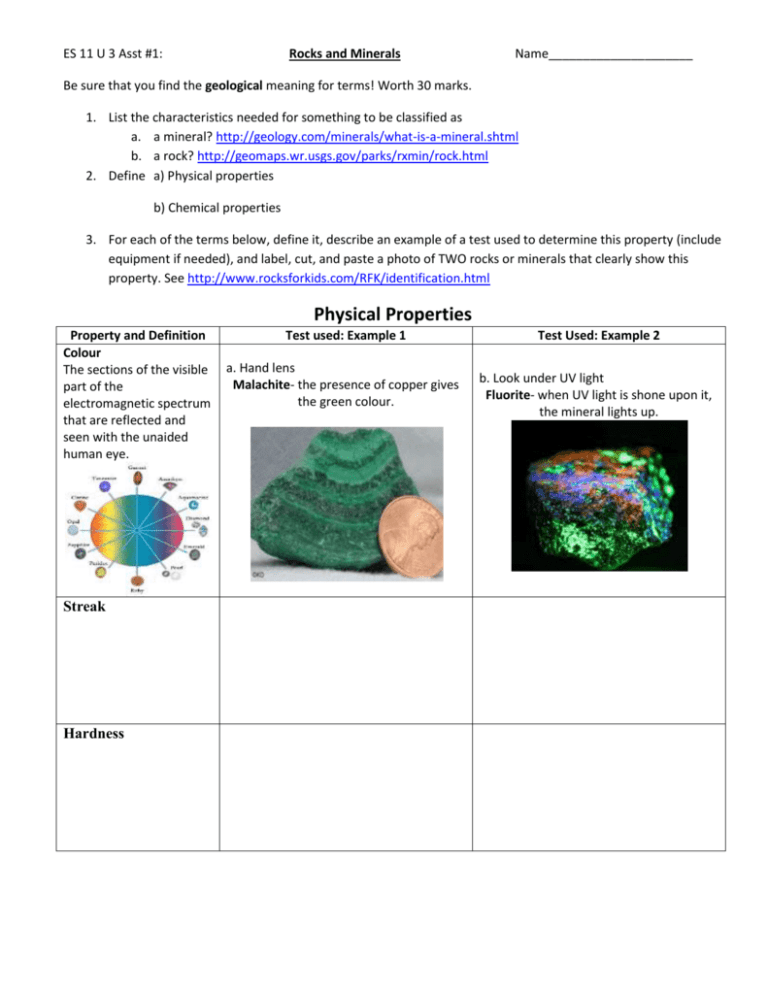
ES 11 U 3 Asst #1: Rocks and Minerals Name_____________________ Be sure that you find the geological meaning for terms! Worth 30 marks. 1. List the characteristics needed for something to be classified as a. a mineral? http://geology.com/minerals/what-is-a-mineral.shtml b. a rock? http://geomaps.wr.usgs.gov/parks/rxmin/rock.html 2. Define a) Physical properties b) Chemical properties 3. For each of the terms below, define it, describe an example of a test used to determine this property (include equipment if needed), and label, cut, and paste a photo of TWO rocks or minerals that clearly show this property. See http://www.rocksforkids.com/RFK/identification.html Physical Properties Property and Definition Colour The sections of the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum that are reflected and seen with the unaided human eye. Streak Hardness Test used: Example 1 a. Hand lens Malachite- the presence of copper gives the green colour. Test Used: Example 2 b. Look under UV light Fluorite- when UV light is shone upon it, the mineral lights up. Cleavage or Fracture Crystalline Structure Transparency Magnetism Lustre Sources: Chemical Properties Definition of This Property 1. Felsic Test used: Example 1 Test used: Example 2 2. Mafic 3. Formula Sources: 1. What is the Mohs scale? a. What is a 1 on this scale? Give 2 examples of substances that have this rating. b. What is a 10 on this scale? Give 2 examples of substances that have this rating. 2. Cut and paste a chart of the Mohs Scale. Sources: Rocks 3. Igneous Rocks = 4. How are igneous rocks formed? 5. Where on/in earth are they commonly found? 6. TWO TYPES OF IGNEOUS ROCKS a. Intrusive (plutonic) igneous rock is… b. Three examples are (provide labeled photos of each)… c. Describe their texture. d. e. f. g. Extrusive (volcanic)igneous rock is… Three examples are (provide labeled photos of each)… Describe their texture. describe the relationship between crystal size and cooling rate in igneous rocks Sources: 7. Sedimentary Rock= 8. How are sedimentary rocks formed? 9. Where on/in earth are they commonly found? 10. a. Three examples are (provide labeled photos of each)… b. Describe their texture. Sources: 11.Metamorphic Rock= 12. How are metamorphic rocks formed? 13. Where on/in earth are they commonly found? 14. a. Three examples are (provide labeled photos of each)… b. Describe their texture. Sources: The Rock Cycle 15. What is the rock cycle? 16. Label the rock cycle diagram below. Sources: 17. Using the rock cycle as a guide, describe what needs to happen to create: a. Sedimentary rock from metamorphic rock? b. Sedimentary rock from igneous rock? c. Metamorphic rock from sedimentary rock? d. Metamorphic rock from igneous rock? e. Igneous rock from sedimentary rock? f. Igneous rock from metamorphic rock?









