LEARNING TARGET:
advertisement
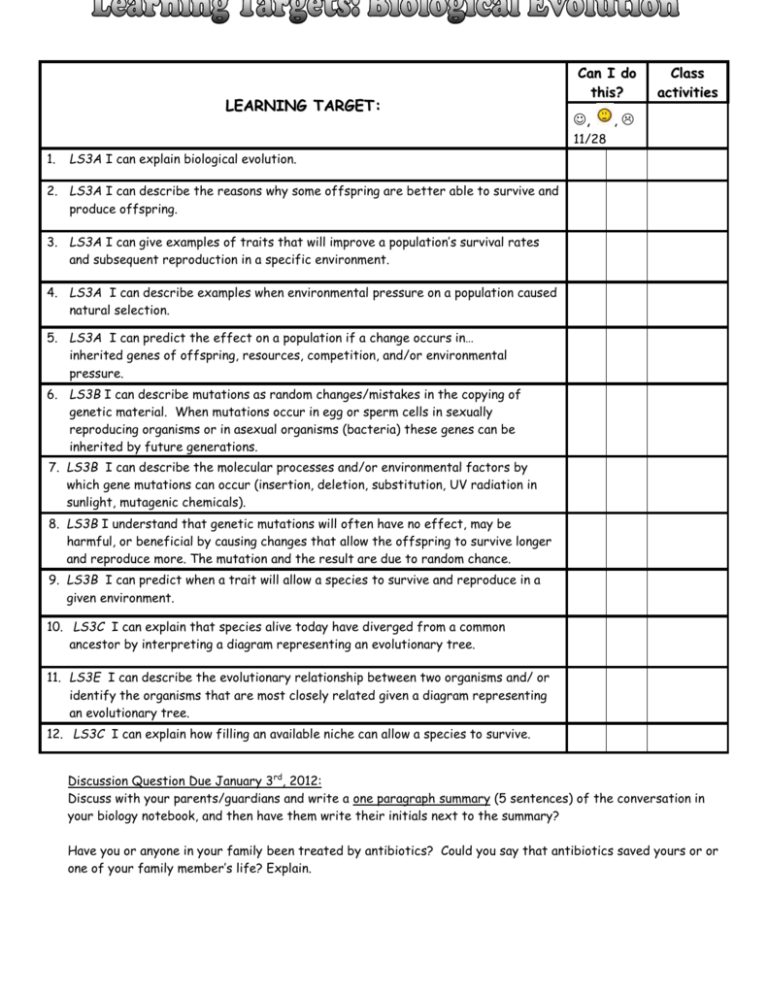
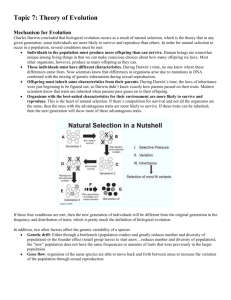
LEARNING TARGET: Can I do this? , Class activities , 11/28 1. LS3A I can explain biological evolution. 2. LS3A I can describe the reasons why some offspring are better able to survive and produce offspring. 3. LS3A I can give examples of traits that will improve a population’s survival rates and subsequent reproduction in a specific environment. 4. LS3A I can describe examples when environmental pressure on a population caused natural selection. 5. LS3A I can predict the effect on a population if a change occurs in… inherited genes of offspring, resources, competition, and/or environmental pressure. 6. LS3B I can describe mutations as random changes/mistakes in the copying of genetic material. When mutations occur in egg or sperm cells in sexually reproducing organisms or in asexual organisms (bacteria) these genes can be inherited by future generations. 7. LS3B I can describe the molecular processes and/or environmental factors by which gene mutations can occur (insertion, deletion, substitution, UV radiation in sunlight, mutagenic chemicals). 8. LS3B I understand that genetic mutations will often have no effect, may be harmful, or beneficial by causing changes that allow the offspring to survive longer and reproduce more. The mutation and the result are due to random chance. 9. LS3B I can predict when a trait will allow a species to survive and reproduce in a given environment. 10. LS3C I can explain that species alive today have diverged from a common ancestor by interpreting a diagram representing an evolutionary tree. 11. LS3E I can describe the evolutionary relationship between two organisms and/ or identify the organisms that are most closely related given a diagram representing an evolutionary tree. 12. LS3C I can explain how filling an available niche can allow a species to survive. Discussion Question Due January 3rd, 2012: Discuss with your parents/guardians and write a one paragraph summary (5 sentences) of the conversation in your biology notebook, and then have them write their initials next to the summary? Have you or anyone in your family been treated by antibiotics? Could you say that antibiotics saved yours or or one of your family member’s life? Explain. 1. adaptation 2. antibiotic 3. bacteria 4. biological evolution 5. common ancestor 6. diverge 7. environment 8. evidence BIOLOGICAL EVOLUTION VOCABULARY: genetically present within a population and passed on to future generations within a species a medicine that destroys microorganisms most evolved organisms on earth, microscopic, single celled the consequence of the interaction of population growth, inherited variability of offspring, a finite supply of resources, and/or natural selection by the environment of offspring better able to survive and reproduce. all living organisms on Earth are descended from this 9. evolutionary tree 10. extinction 11. gene developed in a different direction natural surroundings including living and non-living components observations, measurements, or data collected through established and recognized scientific processes. a diagram with different branches representing relatedness amongst species (current and extinct). the death of all members of a species a segment of DNA (information) that codes for a specific trait. 12. gene mutation 13. genetic a change in the genetic material (DNA) of an organism which occurs by random chance. the regrouping of genes in offspring recombination 14. genetic variation 15. heredity 16. inference difference in the gene makeup of offspring due to mutation and the recombination of genes. the passing of traits to offspring. a logical conclusion based upon evidence 17. molecule 18. natural selection a stable unit of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. The process by which heritable traits that are favored by environmental conditions become more common in successive generations and heritable traits that are less favored by environmental conditions become less common. Over time, this process may result in the emergence of new species. how and where an organism makes a living (it’s position in the ecosystem) an animal’s young a group of organisms of the same species living in the same habitat production of offspring continue to live a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring a genetically determined characteristic 19. niche 20. offspring 21. population 22. reproduce 23. survive 24. species 25. trait 26. variation a measure of the tendency of individuals in a population to differ from one another