MA Jewish Studies - University College London
PROGRAMME SPECIFICATION
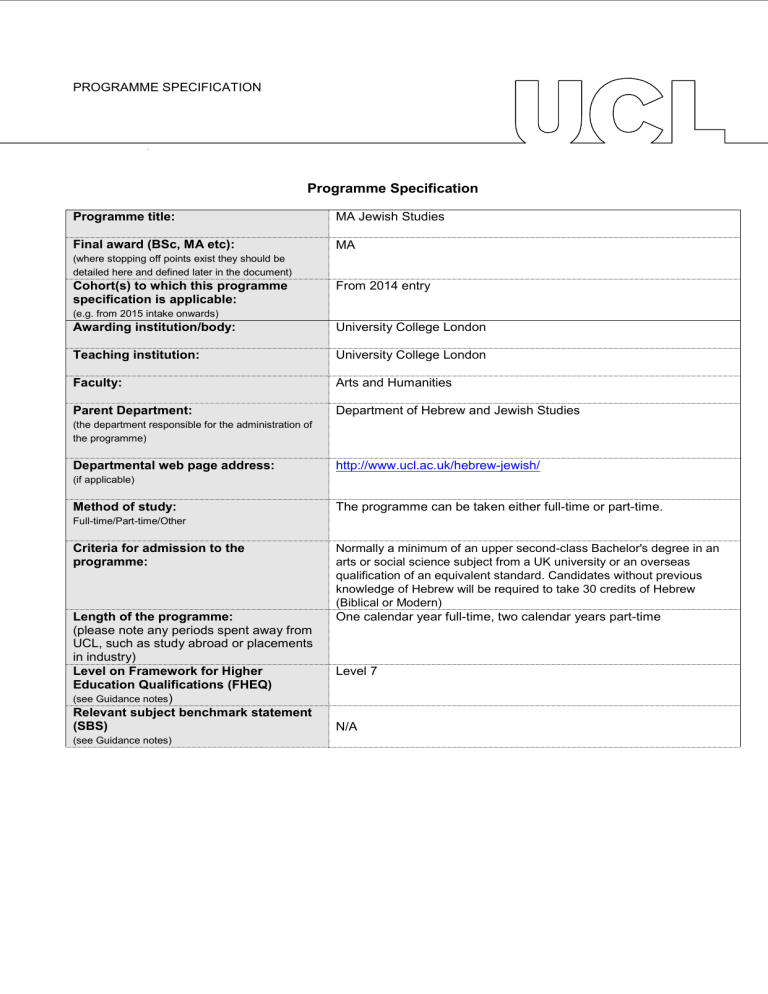
Programme title:
Final award (BSc, MA etc):
(where stopping off points exist they should be detailed here and defined later in the document)
Cohort(s) to which this programme specification is applicable:
(e.g. from 2015 intake onwards)
Awarding institution/body:
Teaching institution:
Faculty:
Parent Department:
(the department responsible for the administration of the programme)
Departmental web page address:
(if applicable)
Programme Specification
MA Jewish Studies
MA
From 2014 entry
University College London
University College London
Arts and Humanities
Department of Hebrew and Jewish Studies http://www.ucl.ac.uk/hebrew-jewish/
Method of study:
Full-time/Part-time/Other
Criteria for admission to the programme:
The programme can be taken either full-time or part-time.
Normally a minimum of an upper second-class Bachelor's degree in an arts or social science subject from a UK university or an overseas qualification of an equivalent standard. Candidates without previous knowledge of Hebrew will be required to take 30 credits of Hebrew
(Biblical or Modern)
One calendar year full-time, two calendar years part-time Length of the programme:
(please note any periods spent away from
UCL, such as study abroad or placements in industry)
Level on Framework for Higher
Education Qualifications (FHEQ)
(see Guidance notes )
Relevant subject benchmark statement
(SBS)
(see Guidance notes)
Level 7
N/A
Brief outline of the structure of the programme and its assessment methods:
(see guidance notes)
Students undertake modules to the value of 180 credits. The programme consists of a core course (30 credits), three taught modules of specialisation (90 credits) and a research dissertation (60 credits).
Students must take:
Board of Examiners:
Professional body accreditation
(if applicable):
N/A
EDUCATIONAL AIMS OF THE PROGRAMME:
One core course which is assessed by 6 assignments
Three optional courses
Submit a 12,000 word dissertation (based in part on primary sources)
If taken part-time students must take the core course and one optional module in year one, followed by two optional modules and the dissertation in year two.
Name of Board of Examiners:
MA Hebrew and Jewish Studies
Date of next scheduled accreditation visit:
The programme aims to allow students to construct their own field of study by selecting their courses from the wide range of disciplinary approaches, regional and chronological specialisations within the vast and diverse field of
Jewish Studies. The programme will (a) introduce students to a variety of skills essential for the investigation of these fields of Hebrew and Jewish Studies; (b) give them practical training in those skills; and (c) introduce students to aspects of Hebrew and Jewish Studies at an intellectually demanding level.
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES:
The programme provides opportunities for students to develop and demonstrate knowledge and understanding,
qualities, skills and other attributes in the following areas:
A knowledge and understanding of:
1. How to assess historical, political and cultural evidence critically, synthesize data from different types of primary
A: Knowledge and understanding
Teaching/learning methods and strategies
Acquisition of 1, 2 and 3 through three-hour weekly seminars (except language classes which may be taught more intensively), special seminars and evening sources, solve problems of conflicting interpretations, locate source materials and interpretative studies (such as scholarly reviews), use research resources (particularly research library catalogues, archival inventories, on-line catalogues, digital databases and other traditional and digital resources relevant lectures, and occasional films. The core course will also entail practical instruction in how to evaluate both primary and secondary sources, focussing on critical evaluation of significant secondary works in the field.
Students will be expected to visit the major archives and libraries in the London area, depending on their specific areas of research and interest. Students will be required to attend all classes, study extensively on their own and to Jewish Studies).
2. Subject specific skills, for instance,
Hebrew (ancient and modern), Near
Eastern and Jewish Languages (Yiddish).
3. Aspects of Jewish literature, philosophical speculations, visual records and arts and history connected to Jewish
Studies.
for all the required courses mentioned above and on all the optional courses, prepare non-assessed coursework regularly. Students will also be required to attend the
HJS departmental seminar, which comprises of sessions devoted to research methods and presentations by students about their projects. Students are also encouraged to take the relevant research training courses offered by the faculty.
Intellectual (thinking) skills - able to:
The programme aims to help students:
(a) be precise, to be cautious in their assessment of evidence, and to understand through practice what historical, political and cultural documents can and cannot tell us.
(b) question interpretations, however authoritative, and reassess evidence for themselves.
Students will be assessed by a variety of methods:
‘unseen’ examinations, long essays, course work and a dissertation. The last mentioned is a required method of assessment.
B: Skills and other attributes
Teaching/learning methods and strategies
Acquisition of (a) and (b) and (c) is fostered in relevant courses offered in the Programme, in that all courses will introduce information that will need to be assessed critically and will demonstrate that how conflicting interpretations arise from the same information.
(c) apply linguistic and literary concepts and gain deeper insight in the interplay of text and context
Practical skills - able to:
This programme aims to help students with the following practical skills:
(a) communicate effectively in writing
(b) improve their knowledge of a relevant language, history, politics, literature and culture of Jewish studies.
(c) use data bases, digital resources and word-processing programmes
(d) present (non-assessed) seminar papers
(e) listen and discuss ideas introduced during seminars
(f) practice research techniques in a variety of specialised research libraries and institutes
(g) maintain a constant rhythm of learning and research
(h) choose their own long-essay and dissertation topics
(i) adapt long-essays and dissertation topics to the information that they discover while working on their longessays and dissertations.
Assessment:
Through ‘unseen’ examinations, course work, longessays, dissertation. The latter is a required method of assessment.
C: Skills and other attributes
Teaching/learning methods and strategies
(a) through the writing of long-essays and dissertations
(b) through language class input and required readings and scholarship pertaining to their particular area of interest
(c) through ‘hands-on’ instruction
(d) through regular seminar presentations
(e) through seminar discussion
(f) through visits to libraries and institutes
(g) through the setting of clear deadlines for the submission of written work
(h) through individual discussion with students
Skills (a)-(g) inclusive will be taught mainly on the required courses for students on the programme. The courses will be taught by scholars who have specialist expertise in these fields. The classes will include practical instruction, visits to libraries and archives, consultation of printed or digital catalogues in research libraries.
Assessment:
(a)-(c), (f)(i) by ‘unseen’ examination, course work, long-essays and dissertation. The latter is a required method of assessment; (e) not assessed in courses currently listed on the programme though courses added in future may include oral assessment.
D: Skills and other attributes
Teaching/learning methods and strategies: Transferable skills - able to:
The programme will encourage students to:
(a) write good essays and dissertations
(b) improve their Hebrew (or relevant research language)
(c) use computer resources and information technology
(d) present material orally
(e) listen and contribute in class
(f) understand ideas that are very different to conventional ones
(g) study a variety of written and digital materials, in libraries and research institutes of a kind that they will not have
(a) long-essays, course work, dissertation
(b) through class input, translation, grammar and vocabulary exercises, and use of dedicated self-study areas which contain computers with Hebrew (enabled) programmes.
(c) submitting word-processed written work; using data bases, consulting on-line library catalogues, using website material
(d) seminar presentations
(e) seminars, library visits, ‘hands-on’ instruction
(f) reading about and discussing aspects of Hebrew and
Jewish studies
(g) essays, dissertation, seminar presentations, ‘handson’ instruction, library and archive visits
(h) seminar presentations and papers
(i) reading, class discussion
(j) essays, dissertation, seminar discussion
(k) essays, dissertation, seminar discussion used as undergraduates
(h) present (non-assessed) material orally
(i) reflect on their own ideas by becoming acquainted with ideas and practices foreign to them
(j) make original contributions to Jewish
Studies scholarship by following through their ideas
(k) assess evidence for themselves and scruntinize previous interpretations
Assessment:
(a)-(c), (f)(k) ‘Unseen’ examination, text analysis, language exams, long-essays and dissertation; (e) not assessed in courses currently listed on the programme though courses added in future may include oral assessment.
The following reference points were used in designing the programme:
the Framework for Higher Education Qualifications:
( http://www.qaa.ac.uk/en/Publications/Documents/qualifications-frameworks.pdf
);
the relevant Subject Benchmark Statements:
( http://www.qaa.ac.uk/assuring-standards-and-quality/the-quality-code/subject-benchmark-statements );
the programme specifications for UCL degree programmes in relevant subjects (where applicable);
UCL teaching and learning policies;
staff research.
Please note: This specification provides a concise summary of the main features of the programme and the learning outcomes that a typical student might reasonably be expected to achieve and demonstrate if he/she takes full advantage of the learning opportunities that are provided. More detailed information on the learning outcomes, content and teaching, learning and assessment methods of each course unit/module can be found in the departmental course handbook. The accuracy of the information contained in this document is reviewed annually
by UCL and may be checked by the Quality Assurance Agency.
Programme Organiser(s)
Name(s):
Date of Production:
Date of Review:
Date approved by Chair of
Departmental Teaching
Committee:
Date approved by Faculty
Teaching Committee:
Dr. Tsila Ratner
March 2014
October 2015
October 2015
October 2015