File - Bowie Aquatic Science
advertisement

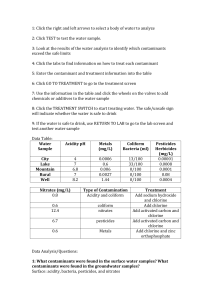
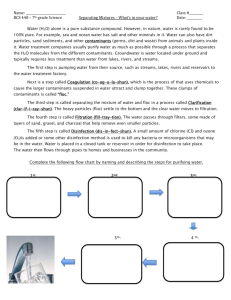
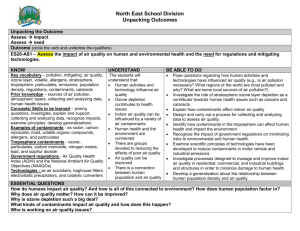
Water Quality Indicators Test Review 2013 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. What is the most important water quality indicator and why is it so important? Describe the process of photosynthesis in terms of energy, oxygen and who performs it. Describe cellular respiration in terms of energy, oxygen and who performs it. Write out the balanced equation for photosynthesis? How is the amount of oxygen (O2) dissolved in water is related to the temperature of the water. How does DO affect species diversity? How is DO related to pressure? Describe the process of eutrophication, be sure to discuss changes in oxygen levels. What are some common sources of nitrate? Why are nitrates (NO3-) important for plants? Atmospheric nitrogen can be converted to nitrates (NO3-) by what phenomenon? What does pH measure? What is the pH of: an acid, a base, pure water, rain water? What is alkalinity? What are some problems with abnormal pH? What does TDS stand for? What does a TDS meter measure? What are some problems associated with out of range TDS values? What is turbidity? What are some problems that can occur when there is high turbidity? Can moderately turbid water have an abundance of life? Changes in temperature can cause organisms to be more susceptible to: What does pathogenic mean? E. coli is a fecal coliform bacteria. Since it does not usually cause disease, why do we test for fecal coliform bacteria? What is the difference between a pervious and an impervious surface? Give examples of each. What is the difference between point and non-point source pollution? Give examples of each. Describe the following foraging techniques: Piercers, Scrapers, Parasites, Collectors, Shredders Which snail belongs to group IV organisms and why? What adaptation do group IV bloodworms have to allow them to survive in low oxygen conditions? Which organism is considered the “canary of clean water” and why? What portion of a stream or river would have a rocky bottom and fast moving water? What causes blue baby syndrome? Which contaminants are considered inorganic chemical contaminants? Which contaminants are considered organic chemical contaminants? Which contaminants are considered primary standards? Which contaminants are considered secondary standards? What is a main difference between primary and secondary standards? What are the factors that affect the toxicity of a chemical? What does MCL stand for? Make a true statement: The higher / lower the MCL, the more / less hazardous the chemical. What does NOEL stand for? How does the NOEL relate to the MCL? What is the oldest and largest lake and where is it located? Water Quality Indicators Test Review 2013 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. What is the most important water quality indicator and why is it so important? Describe the process of photosynthesis in terms of energy, oxygen and who performs it. Describe cellular respiration in terms of energy, oxygen and who performs it. Write out the balanced equation for photosynthesis? How is the amount of oxygen (O2) dissolved in water is related to the temperature of the water. How does DO affect species diversity? How is DO related to pressure? Describe the process of eutrophication, be sure to discuss changes in oxygen levels. What are some common sources of nitrate? Why are nitrates (NO3-) important for plants? Atmospheric nitrogen can be converted to nitrates (NO3-) by what phenomenon? What does pH measure? What is the pH of: an acid, a base, pure water, rain water? What is alkalinity? What are some problems with abnormal pH? What does TDS stand for? What does a TDS meter measure? What are some problems associated with out of range TDS values? What is turbidity? What are some problems that can occur when there is high turbidity? Can moderately turbid water have an abundance of life? Changes in temperature can cause organisms to be more susceptible to: What does pathogenic mean? E. coli is a fecal coliform bacteria. Since it does not usually cause disease, why do we test for fecal coliform bacteria? What is the difference between a pervious and an impervious surface? Give examples of each. What is the difference between point and non-point source pollution? Give examples of each. Describe the following foraging techniques: Piercers, Scrapers, Parasites, Collectors, Shredders Which snail belongs to group IV organisms and why? What adaptation do group IV bloodworms have to allow them to survive in low oxygen conditions? Which organism is considered the “canary of clean water” and why? What portion of a stream or river would have a rocky bottom and fast moving water? What causes blue baby syndrome? Which contaminants are considered inorganic chemical contaminants? Which contaminants are considered organic chemical contaminants? Which contaminants are considered primary standards? Which contaminants are considered secondary standards? What is a main difference between primary and secondary standards? What are the factors that affect the toxicity of a chemical? What does MCL stand for? Make a true statement: The higher / lower the MCL, the more / less hazardous the chemical. What does NOEL stand for? How does the NOEL relate to the MCL? What is the oldest and largest lake and where is it located?