Ch 7.6 Student Notes CD
advertisement

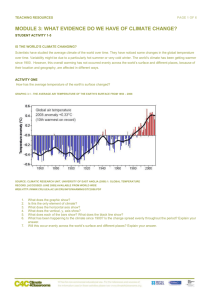
Environmental Science Name: ______________________________ Atmosphere and Climate Goal: The student will identify one possible explanation for the increase in average global temperatures and describe what a warmer Earth might be like. Vocabulary: 1. global warming – 2. Kyoto Protocol – Notes: Chapter 7.6: Greenhouse Earth and Global Warming Global Warming The average temperature of Earth’s surface has increase during the 20th century; also known as global warming The temperature has been rising at a similar rate as the increase in greenhouse gases, scientists believe the greenhouse gases have caused the increase in temperature; thousands of experiments and computer models support this hypothesis Increase in temperatures is predicted to continue throughout the 21st century; does not mean temps are rising at a constant rate or that they are rising in all parts of the world. We do, however, experience natural climatic variability, which means that temperatures change naturally over the centuries; so this change cannot be ruled out. Modeling Global Warming Computer models are used to predict future changes in climate; equations are written by scientist that represent the atmosphere and oceans, then CO2 levels, prevailing winds and other variables are entered into it; the resulting models are used to predict factors like temperature and sea levels will be affected Weather forecasters use similar programs; as you know, programs and models are not always accurate (ex: get rained on when it was predicted to be dry) Computer models are becoming more reliable as more data is available and additional variables are added The Consequences of a Warmer Earth • Earth’s climate has dramatically changed in the past; ice ages came and went • These changes occur over hundreds or thousands of years • Scientists don’t know how quickly the Earth will warm or how severe the effects will be • In North America, tree swallows, Baltimore orioles and robins are nesting about 11 days earlier than they did 50 years ago; In Britain, at least 200 species of plants are flowering up to 55 days earlier in the year than 40 years ago • There is no evidence that global warming is the cause but the nesting of birds and flowering of plants are influenced by temperature • Scientists cannot predict how quickly Earth will warm or how severe the effects will be; different computer models give different predictions • However, the possible effects of global warming can create a number of potentially serious environmental problems (ex: changes in weather patterns, rising sea levels) Melting Ice and Rising Sea Level • As polar regions warm, icebergs may break and melt in the sea resulting in a rise in the sea level • The result of the rise in the sea level will cause coastal areas to become covered with water; coastal wetlands and other low-lying areas will become flooded, people will lose their homes and sources of income, beaches will be eroded, salinity levels of bays and estuaries will increase and affect marine fisheries, and coastal freshwater aquifers could become too salty to be used as sources of fresh water. Global Weather Patterns • If it heats up significantly, oceans will absorb more heat energy resulting in an increase of hurricanes and typhoons • Scientists are concerned about changes in ocean current patterns if there are changes in the world’s weather; some areas may get more rain (flooding) than normal and other areas may get even less (severe droughts) Human Health Problems Warmer average global temperatures pose potential threats to human health Greater numbers of heat related deaths could occur; very young and very old city dwellers are at the greatest risk during heat waves People with allergies to pollen would suffer more as a result of the increase in growing time for flowering plants Warmer and longer summers could allow mosquitoes to establish themselves in areas which are too cold for them now (ex: bring diseases like malaria, dengue fever and encephalitis) Agriculture • Agriculture will be greatly affected if there are severe weather changes • Some of the most fertile, productive areas may get hotter and drier resulting in a shift northward for farming rather than the areas where farming is prevalent today • We would see decreased crops yields and higher demand for irrigation, further depleting aquifers Effects on Plants and Animals Climate change could alter both the range of plant species and the composition of plant communities; trees colonizing cooler areas, forest could shrink in the warmer part of their range, lose of diversity Could cause a shift in the geographical range of some animals (ex: migrating birds may not have to go as far south for winter, warm surface water in the ocean might cause a reduction in zooplankton, and warming in tropical waters ma kill the algae that nourish corals, killing the coral reefs) Recent Findings Intergovernmental Plan on Climate Change (IPCC) is a network of about 2,500 of the world’s leading climatologists from 70 countries; they provide future estimates about the state of the global climate system Findings have included: the average global surface temperatures have increases by 0.6 degrees C during the 20th century, snow cover and ice extent have decreased and average global sea level has risen They also have reported that atmospheric greenhouse gases have continued to increase as a result of human activities and predict that human influences will continue to change the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere throughout the 21st century Reducing the Risk In 1997, representative from 160 countries met and set timetables for reducing emissions of greenhouse gases; this treaty is called the Kyoto Protocol (ratified by 55% of the attending nations) Kyoto Protocol requires developed countries to decrease emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases by an average of 5% below their 1990 levels by 2012; US decided not to ratify the Kyoto Protocol. Slowing the Temperature Change • • • • How can we slow down global warming? Use less fossil fuels will lessen the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere Preserve Earth’s existing forests and plant more trees; this will help remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere Limit greenhouse gas emissions Lesson Reflection: Assessment: 1. Explain why carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is increasing. 2. Name some of the possible consequences of a warmer Earth. Active Reading: Global Warming Lesson Extension (Technology/Application/Connection to Real World): Finish watching: Six Degrees the Change the World (parts 3 degrees to 6 degrees)







![About Climate Change [WORD 513KB]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006779911_1-826a4f3b0cc557ea0fc08071735f54ad-300x300.png)