notes - St. Paul School
advertisement

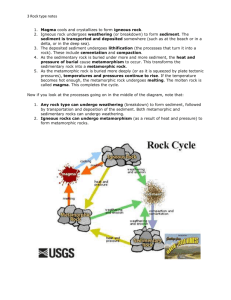
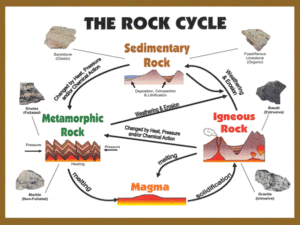
ROCK CYCLE What processes change rock? 1. Weathering, erosion, and deposition. a. Weathering – breaks down rocks into sediments ( rain, freezing, snow) b. Erosion – moving of that sediment (wind, water, ice, gravity) c. Deposition – when sediment comes to a rest 2. Temperature and Pressure What are the Classes of Rock? 1. Sedimentary: sediment from older rocks is pressed (compaction) and/or cemented together. a. Clastic: form when sediments are buried, compacted, and cemented b. Chemical: form when water evaporates c. Organic: composed from the fragmented remains of ocean animals, plants (fossils) 2. Igneous: a. forms from magma and lava, b. As the rock cools, crystals form: i. cools quickly = small crystals and sometimes tiny holes throughout it ii. cools slowly= large crystals c. Extrusive Igneous Rocks: form at or above the earth’s surface d. Intrusive Igneous Rocks form BELOW the earth’s surface 3. Metamorphic : temperature (heating) and pressure (squeezing) and/or chemical reactions. a. Foliated: Mineral grains (crystals) line up in parallel distorted bands b. Non foliated: no bands or lines What is the rock cycle? The series of processes in which rock changes from one rock type to another. Igneous: at earth’s surface can weather and erode to form sedimentary rock, or may turn into metamorphic rock when already below earth’s surface and undergoes heating and squeezing Sedimentary: temperature and pressure can turn it into metamorphic, or may melt and become igneous Metamorphic: can melt to form magma, when cools will become igneous, and it can be broken down by weathering and erosion to form sedimentary rock How do tectonic plate motions affect the rock cycles? 1. By moving rock up and down – uplift (rising of region of the crust to higher elevation and subsidence (sinking of regions of crust to lower elevations – forms basins where sediment can deposit) 2. By pulling apart earth’s surface – rift zone (an area where a set of deep cracks form) Essay questions: 1. Is metamorphic rock the only type of rock that serves as a source of material for making magma? 2. How does the conversion of sediments into rock DIFFER from the conversion of sedimentary rock into metamorphic rock? Key words to use: pressure, cementing, temperature