File
advertisement

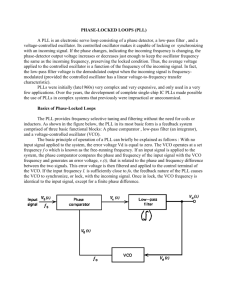
Experiment 2 AM demodulation Equipments 736 201 CF-Transmitter 20 KHZ 736 221 CF-Receiver 20 KHZ 726 09 Panel Frame-T130, Two Level 726 86 DC-Power Supply ± 15 V/3 A 726 961 Function Generator 200 kHz 501 46 Pair cables 100 cm, red/blue 501 461 Pair cables 100 cm, black 501 511 Set of 10 Bridging plugs, black 524 013S Sensor-CASSY 2 - Starter Procedure: Assemble the components as shown in the following figure: Figure 2.1: Synchronous AM demodulation 1. Set the phase controller on the CF transmitter to far left limit. Feed the DSB signal from the output of the modulator M2 directly into the demodulator D2 (do not use channel filter CH2!). 2. Using a connecting lead feed the carrier signal (𝑓𝑐 = 20 kHz) of the CF transmitter into the auxiliary carrier input of the demodulator D2. What have you achieved by this? 3. Display the modulating signal 𝒔𝑴 (t) on CASSY lab 2 as well as the demodulated signal SD (t) at the output of the LP filter of the CF receiver. Sketch the curve of the modulating signal and the demodulated signal in Diagram 3.3-1. Tap the auxiliary carrier for the demodulator D2 in front of the phase shifter of the CF transmitter. 4. Start the measurement by pressing F9. Carrier recovery Carrier recovery is performed in the CF receiver using a PLL circuit. The PLL circuit is a control loop whose function is to match the frequency and phase of an oscillator to the reference oscillation. Fig. 2.2 illustrates the structure of a PLL circuit. Let's assume that the input signal S1(t) is supplied with the frequency f1 to the phase detector. You can be fairly certain that the VCO is not going to be so friendly as to oscillate precisely at the same frequency. So its frequency f2 will initially differ from f1. At the output of the phase detector an AC voltage is generated whose frequency is equal to the difference f2 – f1. This AC voltage is now supplied to the input of the VCO via the loop filter. The VCO will respond to an AC voltage at its input with a corresponding change in frequency. In turn the VCO's changing frequency is detected by the phase detector. With a little luck the PLL locks into the frequency of the input signal. The PLL corrects the VCO until the input frequency and the VCO frequency coincide. A voltage Uф arises behind the PD based on the phase shift. This is supplied to the VCO free of interfering AC components (UF) through the loop filter. The following relationship prevails between the control voltage UF and the frequency fVCO of the VCO: FVCO = kF · UF The control characteristic of the VCO (CF receiver) Remove the bridging plug between the loop filter and VCO input at the PLL. Feed a variable DC voltage U1 from the function generator into the VCO input. Use this variable DC voltage to control the frequency of the VCO. Sketch the results in Diagram 4.2. Attention: 0 V< UF < 5 V. Synchronous demodulation with the aid of a PLL-controlled VCO Remove the cable connected to the auxiliary carrier input of the demodulator D2. For this insert the bridging plug between the CARRIER RECOVERY and auxiliary carrier input of D2. Use now for demodulation the recovered auxiliary carrier from the PLL CARRIER RECOVERY. Assemble the experiment set-up as shown below. Figure 2.2: Synchronous demodulation with the PLL. DSB-SC demodulation Assemble the experiment set-up as shown below. Figure 2.3: DSB-SC demodulation 1. Set the toggle switch to CARRIER OFF. Repeat the experiment in accordance to the previous paragraph “DSB”. 3. Start the measurement by pressing F9. 4. Discuss the results. Summarize the requirements made on the auxiliary carrier in synchronous demodulation. SSB demodulation Set up the experiment as specified below. 1. Start with the settings of the Sensor-CASSY 2 – Starter given in point 4.1. With the aid of a connecting lead feed the carrier signal (fC = 20 kHz) of the CF transmitter directly into the RF input of the demodulator D2. What have you achieved by this? Set the function generator to: sinusoidal, AM = 2 V and fM = 2 kHz. SSB-RC 2. Display the modulating signal sM(t) on Sensor-CASSY 2 - Starter as well as the demodulated signal sD(t) at the output of the LP filter of the CF receiver. 3. Start the measurement by pressing F9. 4. Adjust the phase between the original carrier of the transmitter and the auxiliary carrier of the receiver. What do you observe? SSB-SC Remove the connecting lead between the CF transmitter and the demodulator. Now, for the demodulation use the recovered auxiliary carrier from the PLL circuit to recover the carrier. For this connect the bridging plug between CARRIER RECOVERY and the auxiliary carrier input of D2. Discuss your findings. 1. Set the toggle switch to CARRIER OFF. This time repeat the experiment for SSBSC. 2. Start the measurement by pressing F9.