Name__________________________________ Practice: Direct
advertisement

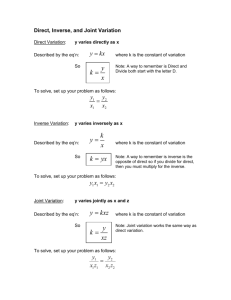
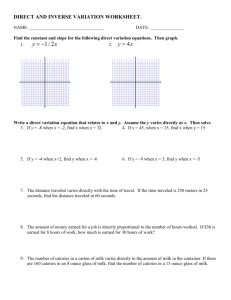
Name__________________________________ Practice: Direct, Inverse and Joint Variation SOL: A2.T10 1. Write and graph a direct variation equation that contains the point (4,10) . Equation: _____________ 2. X and y vary directly. Write an equation that relates x and y , when x = -18 and y = 4. Find y when x = 12. 3. X and y vary directly. Write an equation that relates x and y , when x = -12 and y = 84. Find x when y = -4. Tell whether the data in the table show direct variation. If so, write an equation relating x and y. 4. 5. 6. The time it takes a diver to ascend safely to the surface varies directly with the depth. It takes a minimum of 0.75 minutes for a safe ascent from a depth of 45 feet. Write an equation that relates time and depth, then predict the minimum time for a safe ascent from a depth of 100 feet. Tell whether x an y show a direct variation, inverse variation or neither. 7. y 2 x 3 11. 8. y x 3 9. 12. 2x 1 y 10. y 4 2( x 2) 13. The variables x and y vary inversely. Use the given values to write an equation relating x and y. Find y when x = 0.5. 14. x 4, y 6 15. x 48, y 1 12 16. x 2.4, y 3.6 The variable z varies jointly with x and y. Use the given values to write an equation relating x, y and z. Find z when x = 4 and y=7. 17. x 3. y 5, z 30 18. x 6, y 1 , z 24 2 19. x 3 , y 18, z 9 2 20. Boyle’s Law states that for a constant temperature, the pressure of p of a gas varies inversely with its volume. A sample of oxygen gas has a volume of 50.25 cubic milliliters at a pressure of 20.6 atmospheres. a. Find the constant of variation. b. Write an equation that relates p and V. c. Find the volume of the oxygen gas if the pressure changes to 15.2 atmospheres. Write an equation for the given relationship. (question s 21 – 23) 21. x varies directly with y and inversely with z 22. y varies jointly with x and the square of z. 23. w varies inversely with y and jointly with x and z. Write a function for the given statement. Use k as the constant of variation. (questions 24-29) 24. h varies directly as W, and inversely as the square of r. 25. L varies jointly as A and H, and inversely as T. 26. The mass M of a concrete block varies jointly as the length l, width w and thickness t of the block. 27. The collision impact I of an automobile varies jointly as the mass m and the square of the speed v. 28. The intensity of a sound S varies directly as the amplitude A of a sound source, and inversely as the square of the distance d from the source. 29. For a horizontal beam supported at both ends, the maximum safe load L, varies directly as the width w and the square of the thickness t, and inversely as the distance d between supports.