File - Calhoun Science
advertisement

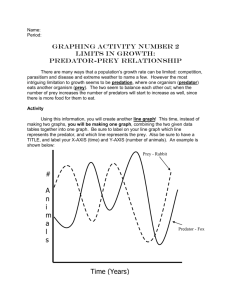
HSPE Science Notes Evolution: it is the change of a species over time Natural selection: The change in a species over time from things like the environment, food sources, predators, and anything else that can help or hurt a species chances of success. Artificial selection: When human decide who breeds. For example dog breeding or plants we eat. Sexual selection: When a member of species chooses traits (typically the female choosing) thing bright colors on birds or songs from birds. Phylogeny: the evolutionary history of a species. What is related to, what did it evolve from. DNA and Genetics: DNA: stored in the nucleus and is the code for all your genes. All your DNA is in all your cells RNA: codes for proteins similar to DNA but smaller and used once. Protein: large molecules that are essential for life Dominate: A trait that is always expressed if present in the genes (T) Recessive: A trait that is only expressed if it is the only version present (t) Homozygous: Two of the same versions of a trait (TT or tt) Heterozygous: Two different versions of a trait (Tt) The Scientific Method: A way of finding out information that is self-correcting, repeatable, and testable. Experiments: needs to be a question you can actually test. Controlled Variable: The group you keep conditions normal and compare your experimental group to. Experimental variable: The group we apply a variable we want to test. Observation: using the five senses Hypothesis: an educated guess or prediction Conclusion: What facts or statement that is supported by the experiment Graphs: Read the title and the axis (the sides) first. Line graph: dealing with time or distance. Known as continuous data. Bar graph: groups Pie chart (circle graph): part of a whole or percent Charts: number data Cells: look up the function of the parts of this cell Parts of a cell: Plant vs animal cell: plants have cell wall and chloroplast Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic: Pro are simple have no nucleus (bacteria), euk are complex and have a nucleus and other organelles (all other cells but bacteria) Somatic vs gametes: somatic cells are normal body cells, gametes are sex cells (sperm and egg cells) Photosynthesis: making sugar from capturing light (plants); you need carbon dioxide, water and you make sugar and oxygen Cellular respiration: how a cell makes energy from sugar; done in the mitochondria of cells Cancer: uncontrolled cell growth, malignant tumors are bad (deadly) and can spread through your body, benign tumors are not as deadly Energy: is never destroyed it just transformed into different forms Kinetic energy: movement Potential energy: when something is high and can drop, a spring that is compressed, or a rubber banded stretched out. Thermal energy: heat energy, can be cause by friction Atoms: make up all mater Parts of an atom: Proton: found in the nucleus make an atom the element that it is. Cannot be changed. Has a positive charge Neutron: found in the nucleus. Has a neutral charge. Changes the mass of atoms and can come in different amounts. Electron: found outside of nucleus in orbitals. Negative charge. Weighs nothing. Does all the bonding with other elements Matter: Matter has mass and is never created or destroy (law of conservation of mass) Radiation: can be from atoms breaking down (uranium or atomic bombs) or can be the electromagnetic spectrum (solar radiation) States of matter: move to different states as energy is added or removed. Solid: has a set volume, has a shape Liquid: has a set volume, shaped by its container. Gas: no set volume (based on container), no set shape (container) The solar system and space: Stars: a collection of gases that are so big they join atoms together that releases heat and light. This is where all atoms other than hydrogen are made Big bang: A theory (backed by lots of evidence) that all matter was at one point billions of years ago and it blew up sending all the matter across the universe. We have observed that everything in the universe is moving away from a common point. Telescopes: best where there is as little atmosphere to get in the way so space and the tops of high mountains are best. Can use light or any other part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Ecology: Water: All life is based around it. Made of 2 hydrogen atoms and an oxygen atom. Follows a cycle. Precipitation: water falling from the sky (rain or snow) Carbon: all life we know is carbon based. Also follows a cycle called the carbon cycle. Primary secession: is the beginning of a ecological community starting with bare rock Secondary secession: is the beginning of a ecological community starting with bare soil Producer: Plants that make their own food from the sun Consumers: Primary consumers are herbivores that eat plants. Secondary consumers eat herbivores and are call carnivores. Scavengers and decomposers: eat dead thing or break down dead things. Predator Prey relationships: The number of available prey items effect how large the population of predators can be. If a large amount of prey is present the predator population will grow. If the predator population gets to large it will lower the prey population and the predator population will fall after the prey population falls. Biodiversity: The amount of different types of life. Highest in tropical rainforest. Lowest in cold polar regions. Food web and food chains: show the movement of energy throughout an ecosystem. Always less top predators than prey or plants. Nevada: Trees: We have pines throughout mountain ranges including the bristle cone pine which is the oldest tree in the world. We also have Joshua trees living down south by Vegas. Basin and range: Nevada has 52 different mountain ranges that run north south across the whole state. This gives us many different types of areas life can be found thus increasing our biodiversity. Random words on the test: Initial: existing or occurring at the beginning. Frequently: regularly or habitually; often. Fraudulent: characterized by, involving, or proceeding from fraud, as actions, enterprise, methods, or gains Consumptive: the act of consuming, as by use, decay, or destruction Essential: absolutely necessary; extremely important