Relative Dating Lecture Notes

Relative Dating & Deforming the Earth’s Crust
Uniformitarianism
1.
Geologic processes that occurred in the past can be explained
___________________________________________________________________________________________ a.
Erosion and weathering that happens today must have been the same millions of years ago b.
Very slow, gradual, predictable process
Catastrophism
1.
_____________________________________________________________________________ a.
Mountains, canyons and oceans formed during rare events b.
These rare events are called catastrophes
2.
Up until the mid-1800’s, this was the accepted principle
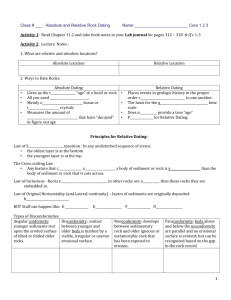
Relative Dating
1.
Relative Dating – a method used to determine whether an object or event ______________________________
_______________________________________________________________
Absolute Dating
1.
Absolute Dating – any method used to determine the _______________________________________________
Certain molecules called Isotopes decay over time
Isotope – An atom that has the same number of protons, _________________________
________________________________________________________________________
We can use this decay to measure how old something is (rocks, fossils, etc…)
Half-life – the amount of time it takes for half of a radioactive substance to decay
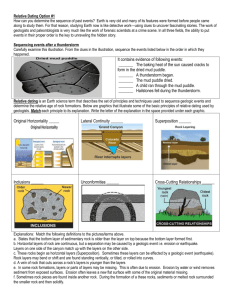
Disturbances
Unfortunately not all rock layers are laid out perfectly. Some things that can make things more difficult are…
1.
Unconformity – _______________________________________________________________________ a.
Missing rock layer(s) due to either Erosion or Non-deposition
2.
Deformations – Altering of rock layers after they are laid down, _________________________________
Deformations
Tectonic plates move, causing stress to build up in the lithosphere a.
Stress = force (three types)
1.
Compression =
2.
Tension =
3.
Shearing =
Stress from tectonic plates cause rock layers in the lithosphere to change
Folding
Definition: _____________________________________________________________ a) Older rock starts on bottom
Anticline =
Syncline =
Folds can be large or small
Some measured in kilometers or centimeters
Faults
Definition: surface along which rocks break and slide past each other
Can be seen on the earth’s surface
Usually have a ___________________________________________________
Faults, Unconformities and Deformations raise a very important problem…
Rock layers aren’t always perfect
So what do we do when rock layers aren’t perfect?
How do we find Relative Age?
One way scientists calculate relative age is by using a set of rules
1.
Superposition – if undisturbed, rock layers will always be older as you go down (youngest on top)
2.
Original Horizontality – Layers of rock are always formed in relatively even horizontal layers
3.
Cross-Cutting Rule – _________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
4.
Deformation Rule – _________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
Another way geologists can figure out disturbed layers of rock is with the Geologic Column
Geologic Column – a complete set of the rock layers with all known fossils and layers in their proper order
Geologic Columns are used to find _____________________________
When a layer of rock is missing from Erosion or Non-Deposition ________________
____________________________________________________________________