EOC Cum Review
advertisement

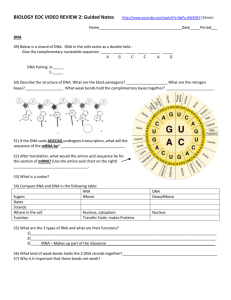
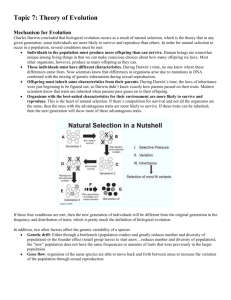
Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide Oxygen BIOLOGY REVIEW Unit 1 – The Matter of Life Use the models below (plant, cow, cell) to identify and explain the concepts to the left. Chlorophyll Glucose Starch Biomolecules Carbohydrates Protein Lipid (Fatty Acid) Nucleic Acid Enzyme Rearrange, recycle, reassemble. Cellular respiration ATP/energy Cell wall Nucleus Chromosome Photosynthesis -- Inputs and outputs of this chemical reaction in plants (LS1A) Describe the chemical reaction in photosynthesis. Where does the mass of the plant come from? Why do plants make glucose? Why do animals need plants? Cellular Respiration --Inputs and outputs of this chemical reaction in all living things (LS1B) Describe the chemical reaction in cellular metabolism. How do living things get energy (ATP) from glucose? How is this chemical reaction similar to burning fossil fuels (oil, gasoline)? Chloroplast Mitochondrion Cells -- Structure and function of organelles within all cells (LS1C) Describe function of structures within cells. Ribosome Vacuole Cytoplasm Cell membranes -- Structure and function of membrane within all cells (LS1D) Describe the transport of O2, CO2, H2O, glucose, and biomolecules into/out of a cell. Cellular membrane Lipid bi-layer Metabolism -- Breakdown of biomolecules for energy and synthesis of new molecules (LS1F) Explain how cows eat corn and turn it in to milk. Active transport Passive transport Osmosis Facilitated diffusion Mitosis Describe the function of enzymes in metabolism. Mitosis – In cells, chromosomes are copied and equally divided for growth and repair (LS1H) Describe the process of mitosis and the product of mitosis. Unit 2 – Traits and Fates DNA, Genes and Protein Synthesis – DNA specifies the sequence of protein synthesis (LS1E) Describe the components and structure of the DNA molecule. Identify which nucleotides (base pairs) are complimentary to each other. Trait Chromosome Gene DNA Describe the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, genes, amino acids, proteins and traits. Recessive Predict the complementary strand of mRNA given the nucleotide sequence in a single strand of DNA. Homozygous Describe the steps in the process by which gene sequences are copied to produce proteins in the cell. Mutations—Changes in DNA can change the proteins synthesized in a cell (LS3B) Describe causes and effects of mutations on an organism. Dominant Heterozygous Messenger RNA (mRNA) Transfer RNA (tRNA) Nucleotides (bases) Meiosis, Fertilization, and Offspring Variation -- Sexual reproduction results in variation (LS1I) Describe how the process of meiosis results in unique egg/sperm cells. Adenine Thymine Explain how fertilization allows for siblings from the same set of parents to look different. Create a Punnett square to predict possible combinations of two traits in offspring. Describe the possible offspring in a cross involving incomplete or codominance. Guanine Cytosine Uracil Complimentary Phenotype Genotype Allelle Mutation Unit 4 – What on Earth? Cycles of Matter and Energy (LS2A) Describe the cycle of carbon through an ecosystem. List examples of how cycling matter can affect the health of an ecosystem (composting, insecticide spraying, fertilizer run-off, bioaccumulation). Describe the cycle of nitrogen through an ecosystem. Describe the transfers and transformations of matter and energy in an ecosystem. (Sunlight transforms into chemical energy in a plant, carbon dioxide is transferred from animals to plants then transformed into glucose). Meiosis Fertilization. Unit 4 – What on Earth? Ecosystem Food Web Bioaccumulation Population density Population Density (LS2BCD) Describe conditions necessary for populations to increase or decrease rapidly. List factors that affect population density (disease, predators, space). Carbon Cycle Calculate the population density of organisms within a given area. Nitrogen Cycle Use a graph to predict changes in population. (carrying capacity J-curve, predator-prey) Biodiversity Sustainability Niche Habitat Invasive species Biodiversity and Sustainability (LS2EF) Given 2 ecosystems; describe differences in biodiversity. List factors that affect the sustainability of each ecosystem. Describe how sustainable development could help an ecosystem. (recycling, using renewable vs. non-renewable resources). Native species Succession Non-renewable Natural Selection (LS3AB) Explain biological evolution in terms of genetic variability, selective pressure, survivability, and reproduction. Renewable Describe how environmental pressure drives natural selection. Unintended Consequences Predict how a mutation will allow a species to survive and reproduce in a given environment. Adaptation Natural Selection Gene pool Speciation Evolution Divergent Common Ancestor Embryology Analogous structure Species Diversification (LS3C) Explain how species alive today have diverged from a common ancestor. Describe how genes from very different organisms can be similar because they share a common ancestor. Evolution (LS3D) Use evidence from fossil record, anatomical/DNA similarities to explain evolutionary development of a species. Describe how genes from very different organisms can be similar because they share a common ancestor. Relatedness of Organisms (LS3E) Describe the how closely related two organisms are using traits, DNA and ability to produce fertile offspring. Use embryology, homology, analogous structures and DNA to describe the evolution of a species. (Darwin’s finches). Determine the evolutionary relationship between two organisms using a diagram or evolutionary tree.