ecology study guide
advertisement
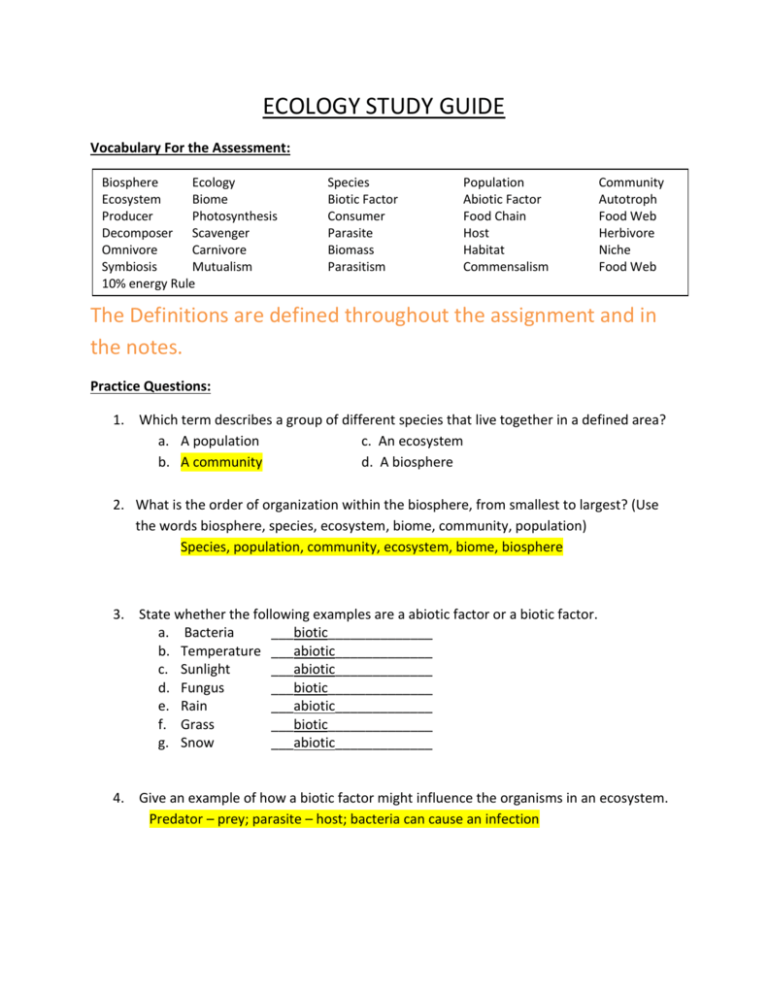
ECOLOGY STUDY GUIDE Vocabulary For the Assessment: Biosphere Ecology Ecosystem Biome Producer Photosynthesis Decomposer Scavenger Omnivore Carnivore Symbiosis Mutualism 10% energy Rule Species Biotic Factor Consumer Parasite Biomass Parasitism Population Abiotic Factor Food Chain Host Habitat Commensalism Community Autotroph Food Web Herbivore Niche Food Web The Definitions are defined throughout the assignment and in the notes. Practice Questions: 1. Which term describes a group of different species that live together in a defined area? a. A population c. An ecosystem b. A community d. A biosphere 2. What is the order of organization within the biosphere, from smallest to largest? (Use the words biosphere, species, ecosystem, biome, community, population) Species, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere 3. State whether the following examples are a abiotic factor or a biotic factor. a. Bacteria ___biotic______________ b. Temperature ___abiotic_____________ c. Sunlight ___abiotic_____________ d. Fungus ___biotic______________ e. Rain ___abiotic_____________ f. Grass ___biotic______________ g. Snow ___abiotic_____________ 4. Give an example of how a biotic factor might influence the organisms in an ecosystem. Predator – prey; parasite – host; bacteria can cause an infection 5. Primary producers are organisms that a. Rely on other organisms for their energy and food supply b. Consume plant and animal remains and other dead matter c. Use energy they take in from the environment to convert inorganic molecules into complex organic molecules. d. Obtain energy by eating only plants. 6. Which of the following describes how ALL of consumers get their energy? a. Directly from the sun b. From eating primary producers c. From inorganic chemicals like hydrogen sulfide d. From eating organisms that are living or were once living 7. The series of steps in which a large fish eats small fish that has eaten algae is a a. Food web c. pyramid of numbers b. Food chain d. Pyramid of biomass 8. The total amount of living tissue at each trophic level in an ecosystem can be shown in a(n) a. Energy pyramid c. biomass pyramid b. Pyramid of numbers 9. Which group of organisms is always found at the base of a food chain or food web? Primary producers 10. A group of individuals that belong to a single species that live together in a defined area is termed a(n) a. Population b. Ecosystem c. Community d. Biome 11. Which is the source of energy for Earth’s living things? a. Wind energy only b. Sunlight only c. Wind energy and sunlight 12. Which of the following is a primary producer? a. Producer, like a plant b. A carnivore, like a lion c. An omnivore, like a human d. A decomposer, like a fungus 13. What are the physical, or nonliving components of an ecosystem called? a. Abiotic factors b. Temperate conditions c. Biotic factors d. Antibiotic factors 14. A relationship in which one organism is helped and another organism is neither helped nor hurt is called a. Parasitism b. Mutualism c. Competition d. Commensalism 15. What is the difference between an organism’s habitat and its niche? Niche is an organism’s role in the ecosystem. Habitat is an organism’s physical location 16. How is predation and parasitism similar? How are they different? It both situations an organism is being harmed. Predation is killing of an organism for food. Parasitism is living in or on the host. 17. In a tropical rain forest, the dense covering formed by the leafy tops of tall trees is called the a. Canopy b. Taiga c. Niche d. Understory 18. Permafrost characterizes the biome called a. Taiga b. Boreal forest c. Savanna d. Tundra 19. Why are plants generally few and far between in a desert? Temperature and water