Biology - The Roblesite
advertisement

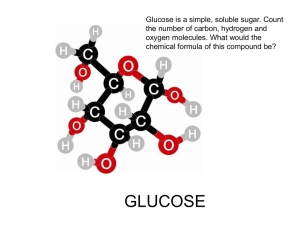
Biology Señor Robles 70 Things I know about Macromolecules ANSWERS! I am soooooooo smart Carbohydrates 1. What is the general term used for macromolecules containing only the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen? Carbohydrates 2. What molecular formula do (ALMOST) all monosaccharides share? C6H12O6 3. What do you call molecules (such as the monosaccharides glucose and fructose) which share the same formula but are arranged differently? Isomers 4. What chemical indicator is used to show the presence of monosaccharides? Benedict’solution 5. When two monosaccharides are chemically bonded together, what is the general term for the resultant (and twice as large) molecule? Hint: read the next two questions. Dissacharide 6. A water molecule is removed in the formation of a bond linking together monosaccharides. What are the two names for this process? Dehydration synthesis (and condensation reaction, but don’t worry about that one) 7. A disaccharide can be broken into its component parts by the addition of water. What’s this process called? Hydrolysis 8. Glucose + Glucose → ? Maltose 9. Glucose + Fructose → ? Sucrose 10. What do you call any chain of glucose molecules linked together? A polysaccharide 11. What type of atom connects any two glucose molecules in any polysaccharide (or any two monosaccharides in a disaccharide)? Oxygen 12. Glucose + Glucose + Glucose + Glucose + Glucose etc. in long chains side by side → ? Cellulose 13. What type of bond holds these chains together on their sides? Hydrogen 14. Where is the above polysaccharide found, and what is it used for? Plant cell walls / structural support 15. What do we call it in the human diet, and how is it beneficial? (dietary) fiber / exercise your intestines 1 16. What is the storage form of sugar found in the roots and tubers of plants? Describe its shape. Starch / branched chain 17. What is the principle storage form of sugar found in vertebrates? (Your liver makes and stores this when there is too much glucose in your blood.) How do you describe its shape? Glycogen / branched chain 18. What modified polysaccharide can be found in animals, in the form of the tough exoskeleton of insects and crustaceans? Chitin 19. Where else can this structural material be found? Fungal cell walls 20. How is this polysaccharide “modified?” The addition of amino groups to each glucose 21. What are the monomers that link together to form any carbohydrate polymer? Glucose 22. What is the difference between the terms polymer and polysaccharide? A polymer is any large molecule composed of repeated similar units A polysaccharide is a specific polymer, namely a series of glucose rings 23. What chemical indicator tells of the presence of polysaccharides like starch? Lugol’s iodine 24. What simple sugar seems to be the sweetener of McDonald’s shakes? Fructose (in the form of High Fructose Corn Syrup) 25. Describe how it is made: Corn is milled into starch, starch is converted into glucose using enzymes, up to 90% of the glucose is converted into fructose using other enzymes. 26. What is the main health concern with HFCS? It has been shown that HFCS causes obesity 27. How is this reflected in the human population? 28. How is it that fructose is more fattening than sucrose? 29. Draw the structural formula for glucose. Lipids 30. What lipids (or fats) are structurally different from other lipids because they are composed of four linked carbon rings? Steroids (although some are actually “sterones”, --steroids that act like hormones.) 31. What are three examples of these special lipids? Estrogen, testosterone, & cholesterol 32. What lipids are composed of two fatty acid chains linked to a glycerol and a phosphate group? phospholipids 2 33. Lipids don’t like water. What term describes this? hydrophobic 34. What term describes the region of some fat molecules that is water tolerant? hydrophilic 35. Most fats/lipids are involve with energy storage, but some (like phospholipids and wax) have other purposes. What are they involved with? Cell membrane structure 36. If you were stranded on a desert island with very little food, would you rather have a pound of starch or a pound of lard? Why? Lard, because it has more calories for its mass 37. Fatty acids (and amino acids) always have this trademark group of four atoms: COOH (carboxyl) 38. What does an unsaturated fat molecule have that a saturated fat molecule does not? A double bond 39. When your body burns fat, and therefore oxidizes fatty acids, what poisonous compound is released into your blood? Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) 40. What term applies to the fat molecule made of a single glycerol molecule attached to three fatty acid chains? triglyceride 41. What is the difference between HDLs and LDLs? 42. What are trans fats, and what’s wrong with them? 43. Why do fattening foods taste so good? Proteins 44. What element does protein always contain in addition to the three elements found in carbohydrates and lipids? nitrogen 45. What other two elements are found in select proteins (think cysteine and hemoglobin)? iron 46. What monomers link up to form proteins? amino acids 47. What special proteins have names that end (usually) with the suffix --ase? enzymes 48. Circle and identify the component parts of an amino acid (make sure to explain the significance of the R): The variable “R” group gives each amino acid its individual identity Amino group Carboxyl group (makes it acidic) Single hydrogen atom 3 49. What term applies to enzymes because they enable reactions to occur more quickly? catalysts 50. A protein is composed of a string of amino acids linked together. What do you call this string? A polypeptide chain 51. What kind of bond holds these amino acids together? How is it formed? A peptide bond, linking the carbon of a carboxyl group in one amino acid to the nitrogen of the amino group in the next amino acid. It is formed by dehydration synthesis. 52. What do you call the four levels of organization of protein molecules? Primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary 53. What are two examples of the secondary structure of protein? Alpha helix, pleated sheet, and random coil 54. Fibrous protein includes collagen, elastin, silk, and keratin. Which one of these is abundant in skin, claws, hair, feathers, and hooves? keratin 55. What protein is involved in the transport of oxygen in your bloodstream? hemoglobin 56. What liquid indicator changes color when heated in the presence of protein? Biuret’s solution (Biuret reagent) 57. What are two membrane proteins found suspended in cell membranes? What do these two proteins do? 58. What class of proteins transmits messages throughout your body? hormones 59. Describe the role of insulin, and the cause of type 2 Diabetes: Nucleic Acids 60. What are the monomers of nucleic acids? nucleotides 61. What are the two principal types of nucleic acids, and where do each reside? DNA (in the nucleus) and RNA (in the nucleus or cytoplasm, depending on what type of RNA) 62. What are the three components of a nucleotide? (label the diagram) Phosphate group Nitrogen base Deoxyribose sugar 4 63. Which particular sugar is part of the DNA molecule? Deoxyribose 64. This sugar is described as a pentose sugar. What does that mean, and why is it specified? Five sided. It is a different shape than the hexagonal sugars like glucose. 65. What are the four names of the nitrogen bases which comprise the “rungs of the ladder” of the DNA molecule? adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C) 66. How do the nitrogen bases pair up? A with T, and C with G 67. Besides carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, what other two elements are always found in nucleic acids? Nitrogen (in the nitrogen bases) and phosphorus (in the phosphate group) The formula of the phosphate group is PO4 68. Label this little section of DNA: “rungs” C G sugar Phosphate group “siderails” sugar Phosphate group A T T A Nitrogen bases / base pairs 69. Once this nucleic acid gets long enough, what characteristic and famous shape does it have? The double helix 70. How many base pairs does your (as a species) particular genome have? 5