Unpacking Outcomes - North East School Division
advertisement

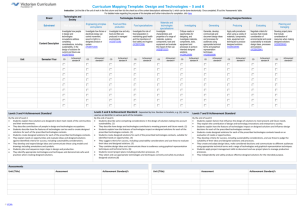
North East School Division Unpacking Outcomes Unpacking the Outcome Investigate resource use Investigate waste management Investigate methods and technologies Outcome (circle the verb and underline the qualifiers) ES20-HP1 – Investigate resource use and waste generation associated with human populations as well as methods and technologies used for mitigation or management. KNOW UNDERSTAND BE ABLE TO DO Key vocabulary – global human population, food security, waste audit, waste reduction, mitigation, fertilizer, irrigation, sustainability, soil salinization, groundwater, stewardship, contaminants, waste diversion, inorganic chemicals, petrochemicals, natural resources, aquaculture, pathogens The students will understand that: Environmental factors and medical advancements help support the human population Everything is connected in a system Human actions impact overall sustainability of an environment (fertilizer, food production, development of medicine, irrigation) Technologies and processes have been developed to support sustainability Our human population is growing at a rate that is at risk of being unsustainable A variety of factors impact human population Population, consumption, technology and stewardship have an effect on the environment Our values and needs affect the decision we make Prior knowledge – data collection and analysis, sustainability of resources Concepts/ Skills to be learned – how to conduct a waste audit, research skills, waste technologies, mitigation technologies, how to construct an action plan Models for assessing impact: I = P x A x T or I = (P x A x T)/S (I=impact, =population, A=affluence, T = technology, S=stewardship) Examine current and historical rates of global human population growth. Describe the impact of food security and access to medicine on human population growth. Investigate technologies which support sustainability in industries such as agriculture, forestry, aquaculture, and mining. Identify mitigation technologies and processes that have been developed to minimize the impacts of mining operations on water quality and quantity. Describe benefits and challenges associated with the use and production of fertilizer for food crops necessary to sustain a growing human population Assess how irrigation projects affect food production, water quality, soil salinization, and groundwater. Assess the impacts (e.g., overfishing and declining marine mammal populations) of resource use and a growing human population on marine ecosystems. Design and carry out a waste audit, and propose a plan of action for waste reduction and/or diversion based on the findings. Investigate advances in technologies and processes (e.g., sewage treatment plants, incineration, composting, engineered landfills, and curbside recycling) used for storing, handling, and disposing of human and/or livestock waste. Discuss how population, consumption, technology, and stewardship impact the environment, with reference to models Research the sources and effects of contaminants such as pathogens, organic matter, heavy metals, sediment, heat, and petrochemicals, and inorganic chemicals such as pesticides in an ecosystem, as well as contaminant management and mitigation strategies. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What factors support and harm the human population? Can Earth sustain our current population growth? How are things connected in a system? How does changing one thing change everything? How do humans affect our own populations? How do we impact our environments? What technologies and processes have been developed to support sustainability? Why do we make the decisions (sustainable and non-sustainable) we do?