math_trig
advertisement

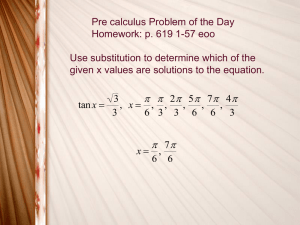
MATHEMATICS EXTENSION 2 4 UNIT MATHEMATICS GEOMETRY and TRIGONOMETRY Essential Background Topic The topics of geometry and trigonometry are essential in the study of most of mathematics and is a fundamental topic in mathematics, physics, chemistry, engineering etc. 1. CIRCLE 2. TRIANGLE 3. TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS 4. TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES and EQUATIONS Double Angle Formulae 5. SINE and COSINE FUNCTIONS TOP ONLINE: 4 UNIT MATHS 1 1 CIRCLE Equation of a circle: centre xC , yC and radius a Circumference Area x xC 2 y yC a 2 2 C 2 a A a2 In many scientific and engineering calculations radians are used in preference to degrees in the measurement of angles. An angle of one radian is subtended by an arc having the same length as the radius. 1 revolution 360o 2 rad TOP ONLINE: 4 UNIT MATHS 2 The length of an arc s of a circle which subtends an angle is s a The ratio of the area of the sector to the area of the full circle is the same as the ratio of the angle to the angle in a full circle. The full circle has area a 2 . Therefore area of sector area of circle 2 a2 area of sector 2 TOP ONLINE: 4 UNIT MATHS 3 2 TRIANGLE The Theorem of Pythagoras c 2 a 2 b2 Trigonometrical ratios in a right-angled triangle Sine ratio sin( ) a c Cosine ratio cos( ) b c Tangent ratio tan( ) a b Cosecant ratio cosec( ) Scant ratio sec( ) Cotangent ratio TOP cot( ) 1 c sin( ) a 1 c cos( ) b 1 b tan( ) a ONLINE: 4 UNIT MATHS 4 or sin cos tan TOP 0 0 1 0 30o / 6 rad 45o / 4 rad 60o / 3 rad 90o / 2 rad 1 1/ 2 1/ 2 3/2 0 1/ 2 1/ 2 3/2 1 1/ 3 3 ONLINE: 4 UNIT MATHS 5 Law of Sines a b c sin( A) sin( B) sin(C ) sin( A) sin( B) sin(C ) a b c Law of Cosines a 2 b2 c 2 c a b 2ab cos(C ) cos(C ) 2a b 2 2 2 b2 c 2 a 2 a b c 2b c cos( A) cos( A) 2b c 2 2 2 a 2 c 2 b2 b a c 2ac cos( B ) cos( B ) 2a c 2 2 2 Law of Tangents ab tan a b 2 ab ab tan 2 Area A 1 2 base height A 12 b h TOP ONLINE: 4 UNIT MATHS 6 3 TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Knowledge of the trigonometric functions is vital in very many fields of engineering, mathematics and physics. Sine function TOP y sin ONLINE: 4 UNIT MATHS 7 Cosine function y cos EVEN FUNCTION cos( ) cos( ) spacing between blue dots is 30o TOP ONLINE: 4 UNIT MATHS 8 Tangent function y tan ODD FUNCTION tan( ) tan( ) TOP ONLINE: 4 UNIT MATHS 9 4 TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES and EQUATIONS sin 2 ( ) cos2 ( ) 1 sec2 ( ) 1 tan 2 ( ) cosec 2 ( ) 1 cot 2 ( ) sin( x ) 1 cos2 ( x ) tan 2 ( x) 1 cos( x ) 1 sin 2 ( x ) sin 2 ( x) sin 2 ( x) cos2 ( x) 1 1 2 2 cos ( x) cos ( x) cos2 ( x) sin( ) sin( ) cos( ) cos( )sin( ) sin( ) sin( ) cos( ) cos( )sin( ) cos( ) cos( ) cos( ) sin( )sin( ) cos( ) cos( ) cos( ) sin( )sin( ) TOP tan( ) tan( ) tan( ) 1 tan( ) tan( ) tan( ) tan( ) tan( ) 1 tan( ) tan( ) ONLINE: 4 UNIT MATHS 10 sin( ) sin( ) 2sin cos 2 2 cos( ) cos( ) 2sin sin 2 2 TOP ONLINE: 4 UNIT MATHS 11 Double angle formulae sin(2 x) 2sin( x)cos( x) cos(2 x ) cos2 ( x ) sin 2 ( x ) 2cos 2 ( x ) 1 cos 2 ( x) sin(2 x ) 2sin( x ) cos( x ) cos(2 x ) cos2 ( x ) sin 2 ( x ) 2 tan( x ) tan(2 x ) 1 tan 2 ( x ) tan(2 x ) 1 2 1 cos(2 x) cos2 ( x ) sin 2 ( x ) 1 cos(2 x ) cos2 ( x ) sin 2 ( x ) cos 2 ( x ) 1 1 tan 2 ( x) 2 2 cos ( x ) sec ( x ) 1 tan 2 ( x ) cos(2 x ) 1 tan 2 ( x ) 2sin( x ) cos2 ( x ) 2 tan x sin(2 x ) 2sin( x ) cos( x ) cos( x ) sec2 ( x ) 2 tan x sin(2 x ) 1 tan 2 ( x ) The substitution t tan( x / 2) is often a useful one for integration of trigonometric functions because we can express 2t sin( x ) 1 t2 TOP 1 t2 cos( x ) 1 t2 dx 2 dt 1 t2 ONLINE: 4 UNIT MATHS 12 5 SINE and COSINE FUNCTIONS sin( ) sin( )cos( ) cos( )sin( ) TOP 90o / 2 rad sin( / 2) cos( ) sine curve shifted to left through /2 rad 90o / 2 rad sin( / 2) cos( ) sine curve shifted to right through /2 rad 180o rad sin( ) sin( ) sine curve shifted to left through rad 180o rad sin( ) sin( ) sine curve shifted to right through rad ONLINE: 4 UNIT MATHS 13 cos( ) cos( )cos( ) sin( )sin( ) 90o / 2 rad cos( / 2) sin( ) cosine curve shifted to left through /2 rad 90o / 2 rad cos( / 2) sin( ) cosine curve shifted to right through /2 rad 180o rad cos( ) cos( ) cosine curve shifted to left through rad 180o rad cos( ) cos( ) TOP ONLINE: 4 UNIT MATHS cosine curve shifted to right through rad 14 TOP ONLINE: 4 UNIT MATHS 15