Test: Matter Study Guide
advertisement
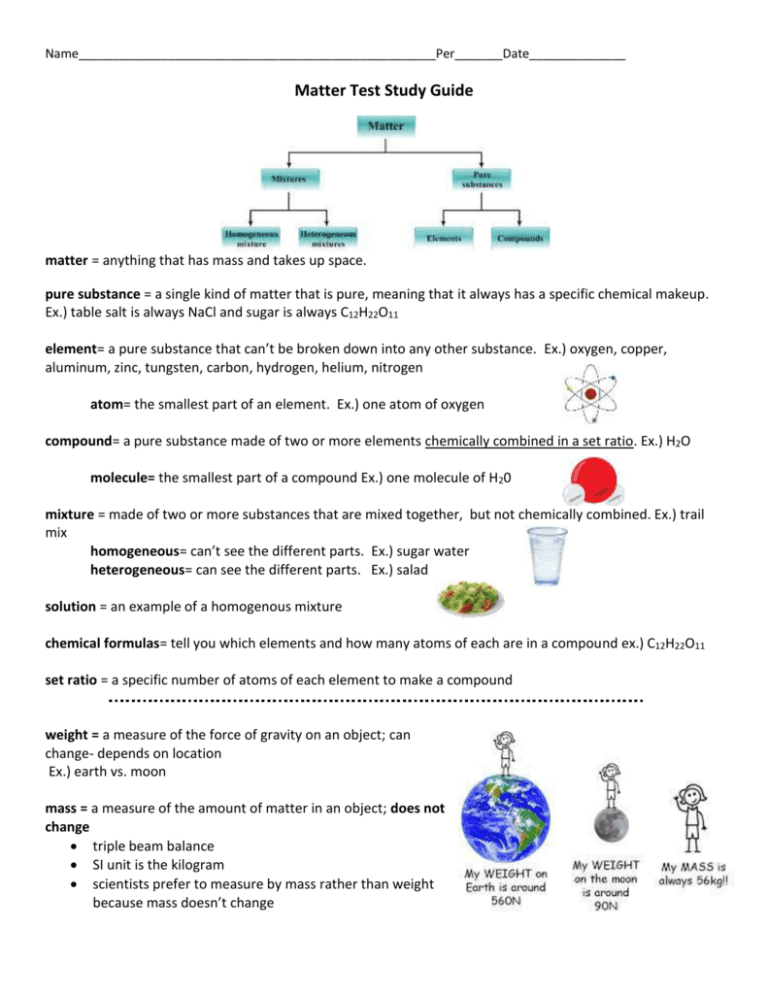
Name____________________________________________________Per_______Date______________ Matter Test Study Guide matter = anything that has mass and takes up space. pure substance = a single kind of matter that is pure, meaning that it always has a specific chemical makeup. Ex.) table salt is always NaCl and sugar is always C12H22O11 element= a pure substance that can’t be broken down into any other substance. Ex.) oxygen, copper, aluminum, zinc, tungsten, carbon, hydrogen, helium, nitrogen atom= the smallest part of an element. Ex.) one atom of oxygen compound= a pure substance made of two or more elements chemically combined in a set ratio. Ex.) H2O molecule= the smallest part of a compound Ex.) one molecule of H20 mixture = made of two or more substances that are mixed together, but not chemically combined. Ex.) trail mix homogeneous= can’t see the different parts. Ex.) sugar water heterogeneous= can see the different parts. Ex.) salad solution = an example of a homogenous mixture chemical formulas= tell you which elements and how many atoms of each are in a compound ex.) C12H22O11 set ratio = a specific number of atoms of each element to make a compound weight = a measure of the force of gravity on an object; can change- depends on location Ex.) earth vs. moon mass = a measure of the amount of matter in an object; does not change triple beam balance SI unit is the kilogram scientists prefer to measure by mass rather than weight because mass doesn’t change Name____________________________________________________Per_______Date______________ volume = the amount of space that matter occupies graduated cylinder for liquids ruler using the formula LxWxH for regularly shaped solids water displacement for irregularly shaped solids Units include: liquids- L, mL and solids- cm3 Volume of a liquid = graduated cylinder Volume of an irregular solid = water displacement Volume of a regular solid = l x w x h density = relates the mass of a material in a given volume D= M/V (density = mass divided by volume) Units include: g/cm3 density of water = 1 g/cm3 if something has a density greater than 1 g/cm3, it will sink in water. if something has a density less than 1 g/cm3, it will float in water. physical properties = a characteristic of a pure substance that can be observed without changing it into another substance. states of matter= solid, liquid, gas physical change = a change that affects the physical properties of matter such as appearance, state of matter, etc. examples of a physical change: boiling water crushing a can melting iron breaking a glass state of matter change freezing water cutting your hair chopping carrots water evaporating off of the ocean chemical properties = a characteristic of a pure substance that describes its ability to change into a different substance. chemical change = a change that results in the formation of a new substance with properties that are different from those of the original substance. examples of a chemical change: frying an egg leaves changing color in the fall fireworks oxidation tarnishing electrolysis combustion cooking a turkey rust on a bike Name____________________________________________________Per_______Date______________ endothermic reaction = a reaction in which energy is absorbed; it makes the environment cooler ex.) ice melting- ice absorbs heat energy from the environment exothermic reaction = a reaction in which energy is released; it makes the environment warmer ex.) fireworks exploding in the sky and giving off light law of conservation of mass = matter is neither created nor destroyed; whatever elements you start with in the reactants, you must also end up with in the products during a chemical reaction. Ex.) Na + Cl NaCl energy= the ability to do work types of energy kinetic = the energy of matter in motion potential = the stored energy of an object because of its position chemical = the internal energy stored in chemical bonds between atoms electromagnetic = a form of energy that travels through space waves