Landform Regions of Canada
advertisement

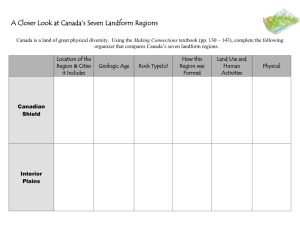
Date: _______________________ Landform Regions of Canada Use Experience Canada pages 39-51 to fill in the blanks below. For each Landform Region, look for the headings in the text. The Canadian Shield (page 39-40) This region covers almost ________ of Canada. The Canadian shield formed in stages starting about ___________________ years ago. Massive _______________ eruptions raised mountains from the sea to form the core of a new continent. Rich veins of metallic minerals, such as ___________, ___________, and nickel, squeezed into these igneous rocks. Then, billions of years of erosion levelled the mountains, putting he minerals within reach of miners. Today, this region is covered by thousands of __________ and __________. ________________, hydroelectric power, and ___________ are all important resources in this landform region. The Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Lowlands (pages 41-42) This is a low-lying area located around the _______________________ and along the __________________________ River. It is a region of ___________________ rock – material deposited in ancient seas as the Canadian Shield eroded. The Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Lowlands (continued) Much of this rock is about ____________________ years old. During the ice ages, ___________________ moved south into the region, pushing earth and rock along with them. For this reason, much of the region is covered with deep layers of _______. Huge ______________ scraped out basins, which filled with water as the glaciers _____________. These basins became the __________________. ____________ of Canada’s people live here, particularly clustered in the Greater ____________ Area and Metropolitan ______________. The Appalachians (page 43) The rugged old ________________ found in the region began to form about ________ million years ago. Plate movements forced the __________________ rock on the ocean floor to fold upwards, and in some places metallic minerals squeezed into cracks in the rock. Then, ____________ forces ground these mountain ranges down to a fraction of their original height. Rising oceans drowned some lowland areas, creating a jagged ______________ with many natural _____________. Today, the Appalachian region has about _____________ of Canada’s total population. The Interior Plains (page 45) This is the Interior Plains region – a large _____________ area, without ________________ or trees to limit the horizon. Much of the Interior Plains is ________________ -year-old sedimentary rock. As inland seas filled with ____________, fossilized sea life was chemically changed into _______ and ________________. ____________ and other field crops are grown on large _________, while even larger beef cattle _____________ are found in dry areas of southern _______________. The Western Cordillera (pages 48-49) The Western Cordillera (‘cordillera’ is a Spanish word for ______________) is a fairly _________ Geologic region. During the dinosaur age, _________ movements folded the Earth’s crust up to form the oldest part, the ___________ Mountains. Then, about _______ million years ago, volcanic eruptions further _______ built the Coast Range along the ____________ Ocean. ____________ cover all three areas, while orchards in sheltered interior valleys yield ________, cherries, and __________. About ___________ of Canada’s people live in the region, with most concentrated in Greater ___________ and _____________. The Innuitians (page 50) The Appalachian, the Rockies, and the _______________ Mountains are all folded ________________ rock pushed up from the ocean floor by plate movement. The Innuitians, in Canada’s far North, are ____________ than the Appalachians and _________ than the _____________. _________ and gas deposits have been discovered here, good evidence that the Innuitian region was once covered by warm tropical seas. But it’s not lke that anymore, now these mountains are covered by large ______________. The Arctic (page 51) The Arctic region is largely made up of islands formed by _______________ rock. Most of the region was first scraped bare by moving ______, then drowned by rising sea levels as the ice ________. Both the Innuitian and Arctic regions are part of the new territory of _____________.