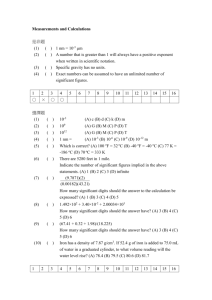
place value study guide
advertisement
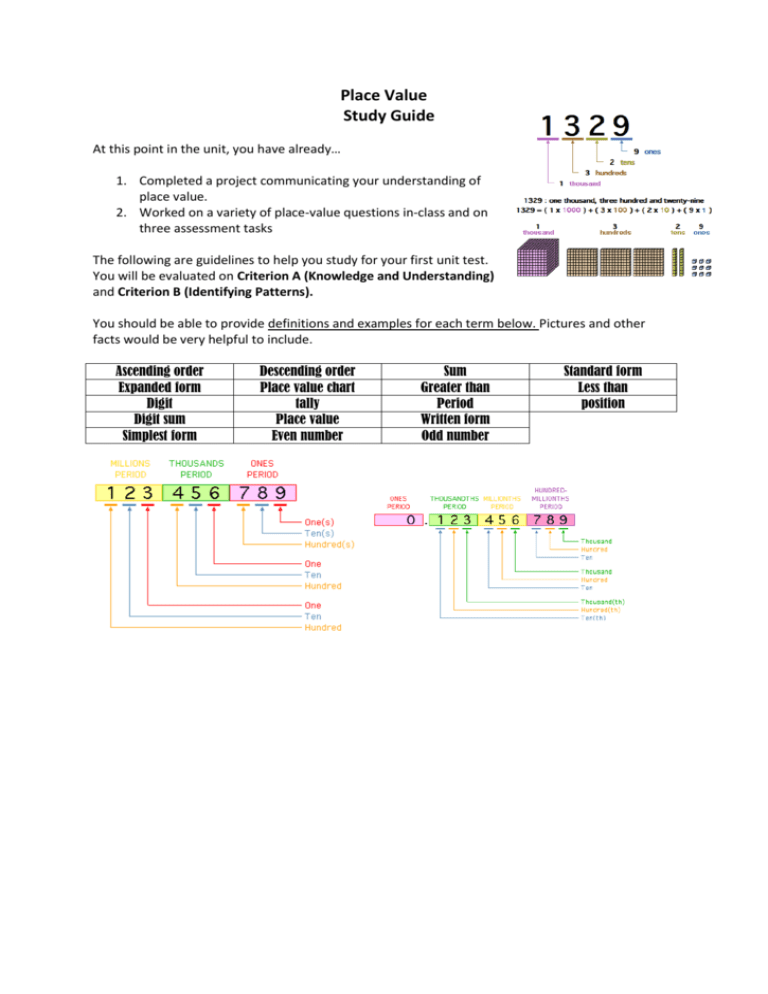
Place Value Study Guide At this point in the unit, you have already… 1. Completed a project communicating your understanding of place value. 2. Worked on a variety of place-value questions in-class and on three assessment tasks The following are guidelines to help you study for your first unit test. You will be evaluated on Criterion A (Knowledge and Understanding) and Criterion B (Identifying Patterns). You should be able to provide definitions and examples for each term below. Pictures and other facts would be very helpful to include. Ascending order Expanded form Digit Digit sum Simplest form Descending order Place value chart tally Place value Even number Sum Greater than Period Written form Odd number Standard form Less than position Study suggestions: 1. Review your assessments (pre-assessment, quiz 1 and quiz 2) 2. Review IXL modules that have been assigned (A1,A2,B2,B3) 3. Use the following websites to practice with place-value… http://education.jlab.org/placevalue/gamepage.html http://www.funbrain.com/tens/index.html http://www.aaamath.com/plc.htm 4. Attempt and complete the questions below. 5. Work on the following from your textbook… Page 21-22 All (including Activity 3) Page 18-19 Even numbers As practice, fill in the chart below… Term Example standard form 5, 255, 3459 2 x 100 + 5 x 10 + 5 x 1 = 251 Expanded form 3 x 1000 + 4 x 100 + 0 x 10 + 9 x 1= 3,409 Explanation The standard form is the normal symbol we write for a number The expanded form shows the value of each digit of a number in standard form. Sample Criterion A Questions 1-2 1. Express the following in simplest form a) 8 x 100,000 + 9 x 1000 + 3 x 100 + 2 x 1 2. Write in expanded form a) 56702 3. Put the following numbers in ascending order: a) 554 992, 594 522, 545 922, 595 242 3-4 1. The number 372474 contains two 7s and two 4s a) How many times larger is the first 7 compared with the second 7? b) How many times smaller is the second 7 compared with the first 7? c) Which of the 4s represents a larger number? By how much is it larger than the other one? 2. What number is 26 more than two hundred and nine thousand? 3. True or False: A billion is 1000 million 4. True or False: A billion is 1 000 000 000 5. Between which two numbers is the following sum? 736+ 132. Can you estimate to the closest tens? 6. A student reads 3 000 146 as “three thousand one hundred forty-six.” Explain the student’s error? Clue: Remember to use appropriate vocabulary. 5-6 1. How many two-digit integers are increased by exactly nine when the digits are reversed? 1. I am a number between 7 000 000 and 8 000 000. All my digits are odd. All the digits in my thousands period are the same. All the digits in my units period are the same. The sum of my digits is 31. What number am I? Give as many answers as you can. What strategies did you use to find the mystery number? 7-8 Sample Criterion B Questions 1-2 Consider all of the five-digit numbers which we can form using only the digits 2, 4, 6 and 8. If these numbers are arranged in ascending order, what is the 16th number? Describe how you arrived at your answer. 3-4 How many numbers from 1000 to 2000 have all of its digits even numbers? 5-6 How may three-digit numbers between 100 and 200 are there for which one of the digits equals the sum of the other two? 7-8 How many whole numbers (not negative numbers) less than 4000 can be written down without using the digits 7, 8 or 9? Notes: Rubric for Criterion A: Knowledge and Understanding of Mathematics Level of Achievement 0 1-2 3-4 5-6 7-8 Descriptor The student does not reach a standard described by any of the descriptors given below. selects appropriate concept and skills in simple problems attempts to solve simple problems in familiar situations selects appropriate concept and skills in simple problems sometimes solves more complex problems in familiar situations selects appropriate concept and skill in challenging problems usually solves challenging problems in a variety of familiar situations selects appropriate concept and skill in challenging problems, including unfamiliar situations consistently solves challenging problems, including unfamiliar situations Criterion B Investigating Patterns Level of Achievement 0 1-2 3-4 5-6 7-8 Descriptor The student does not reach a standard described by any of the descriptors given below. uses, with help, simple problem-solving techniques Recognizes simple patterns uses problem-solving techniques to recognize patterns suggests relationships and rules selects and applies problem- solving techniques to recognize patterns finds and describes a relationship or rule makes predictions consistent with findings. selects and uses problem-solving techniques to recognize patterns finds and describes many correct relationships or rules Gives many correct conclusions consistent with square numbers