gradesheet
advertisement

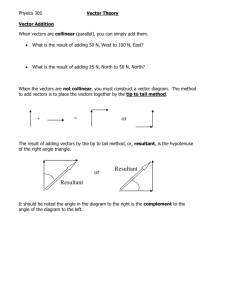
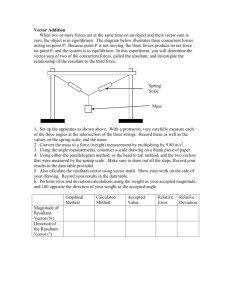
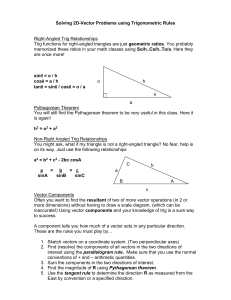
Vector Addition and Subtraction Report Your report must include the following: (notice this report is different than usual). You only need to type the cover page. Everything else is handwritten. Start each part in a separate page and include the headers for each section. 0. Cover page (typed) / 5 points 1. Step 1: Mass Conversion / 10 points a. Show one calculation of how to convert the masses from grams to weight in Newtons. b. List the answers for the other two masses. 2. Step 2: Graphical Representation / 15 points a. Show the Graphical construction to scale of the sum A + B + C. b. Include the scale use to graph. Label vectors and angles c. List the value of the resultant in Newtons and the angle it makes with the positive X-axis. Box results. 3. Step 3: Component Method / 15 points a. Use the component method to calculate R = A + B + C. Show all the calculation steps. b. Calculate the angle it makes with the positive X-axis. c. List the value of R in Newtons and the angle it makes with the positive X axis. Box the answers. 4. Step 4 : Percent Difference / 10 points a. Calculate the percent difference between the values in Part II and part III for the resultant vector and the angle. Box your answers. 5. Step 5: Equilibrium Force: / 10 points a. Calculate the magnitude (in Newtons) and direction of vector E; such that, A+B+C+E=0 6. Step 7: Graphical Method for vector D / 15 points a. Calculate D graphically. Show the scale you used. Label the vectors and angles as before. b. List and box the magnitude and direction of D. 7. Step 8: Component Method for vector D / 15 points a. Use the component method to calculate D. Show all your calculation steps. b. Find the direction (the angle D makes with the positive X-axis) of vector D. c. List and box the results. 8. Step 9: Percent Difference / 5 points a. Calculate the percent difference for the values of the resultant and the angle between the values in steps 7 and 8. 9. Total: / 100 points Things to consider for this experiment Step 1: 1. To convert the mass from grams to a weight in Newtons, you must first convert the mass to kilograms and then multiply by g= 9.81 m/sec2. Weight = mass * gravity Step 2: 1. 2. 3. 4. You are converting your vector values from Newtons to cm values to graph them. The scale you are using is 3.50 cm = 1 Newton. Draw your vectors neatly and measure your angles carefully. You will read the value of R in cm and convert it back to Newtons. Step 4: 1. You are comparing the values of R in step 2 and step 3. Remember the magnitudes must be in Newtons and the directions in degrees. 2. You are calculating a percent difference. Refer to the previous handout for questions. Step 5: 1. Use the average value of R and θ to calculate E (the equilibrant). Step 7: 1. Use the same vector and angle values as in part I to calculate D. Step 9: 1. You are calculating the percent difference between the values in part 7 and part 8.