Classifying_Living_Things_Final_Study_Guide_Part_B
advertisement

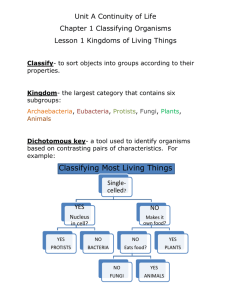
Classifying Living Things Final Study Guide Part B 1. Animals can be divided into two main groups: 2. Invertebrates are animals without ___________ , and make up more than _______ % of animal species, most of which are ________. 3. Vertebraes are animals with some form of ____________. 4. ______ is the official language for naming organisms. The Swedish scientist ______ ____________ used ________ when he created the first classification system in the 18th century, because it was a common language that enabled ____________ to communicate with one another across national borders; it doesn’t change and is the same worldwide. 5. The number of animal species presently identified totals about _____________, of which ____________ are insects, and about ___________ are vertebrates. Scientists believe there may be as many as 9.6 million other species of animals that have not yet been identified. 6. __________ believed all organisms could be classified into one of two kingdoms, _______ and __________. In the Linnean system, organisms that produce their own _______ and do not move are classified as __________, while organisms that move and obtain their food by eating other organisms were classified as _________. 7. Linneaus had classified fungi as plants that do not move, but scientists discovered that fungi do not make their own _______. They take in nutrients from ________ animals and plants, and are different from plants in this regard. Scientists also discovered tiny single-celled organisms like ________. Some of these tiny organisms are able to move around, like animals, but many of them also make their own _______, like plants. 8. Scientists began to modify their classification systems. Taxonomists are relying more and more heavily on ______ and genetic evidence. By comparing DNA sequences of various species and noting the number of ____________ in these sequences, scientists are able to determine which organisms are most closely related. 9. Based on extensive DNA research, one view holds that organisms should in fact be divided into 3 large groups which scientists have begun to call “________”: 1. _________, 2. _________ singlecelled organisms like “archea”, and 3. __________ which includes animals, plants, fungi, and other organisms. Vocab Quiz on Thursday, Jan 8 Define these terms: Algae: a group of living things that can make their own food; algae does not have true roots, stems, or leaves, but they do have chlorophyl Amoeba: a one-celled organism that moves by continually changing its shape called psuedopods Classify: to put things into groups according to their characteristics Diaphragm: an important muscle located between the chest and the abdomen in mammals; it’s used in respiration (breathing) Euglena: a tiny, single-celled organism often classified as algae because it has chlorophyll and seeks sunlight Eukaryote: a cell that has a membrane-bound nucleus Fungus: a parasitic (doesn’t move) plant lacking chlorophyll, leaves, true stems, and roots; reproduces by spores Gills: organ in fish and amphibians for breathing oxygen dissolved in water; made of thin pliable layers of tissue lining the neck Homo sapiens: the Latin or scientific name for the human genus and species Kingdom: the largest category of taxonomic classification based on common characteristics Moneran: an organism without a membrane-bound nucleus, prokaryote; most are single-celled. Prokaryote: a cell with no nucleus, the DNA floats freely inside the cytoplasm Protist: single-celled or simple multi-celled organism with a nucleus and organelles Protozoan: animal-like protist, most live in water, get food by eating other small organisms, singlecelled Taxonomist: a biologist who specializes in classification Vertebrata: animals with a backbone made of bony segments Invertebrate: animals without backbones, most are insects, characterized by the presence or absence of symmetry, a gut, a segmented body, organs, and organ systems