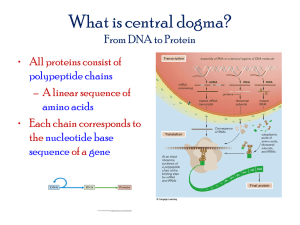
VE #14
advertisement
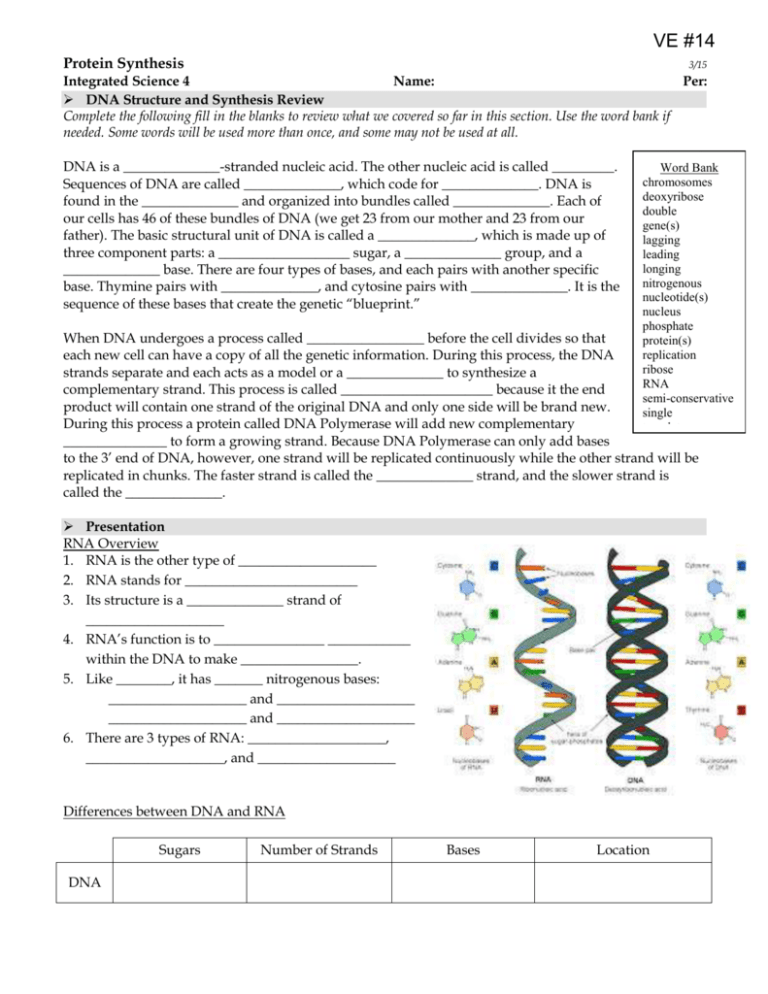
VE #14 Protein Synthesis 3/15 Integrated Science 4 Name: Per: DNA Structure and Synthesis Review Complete the following fill in the blanks to review what we covered so far in this section. Use the word bank if needed. Some words will be used more than once, and some may not be used at all. DNA is a ______________-stranded nucleic acid. The other nucleic acid is called _________. Sequences of DNA are called ______________, which code for ______________. DNA is found in the ______________ and organized into bundles called ______________. Each of our cells has 46 of these bundles of DNA (we get 23 from our mother and 23 from our father). The basic structural unit of DNA is called a ______________, which is made up of three component parts: a ___________________ sugar, a ______________ group, and a ______________ base. There are four types of bases, and each pairs with another specific base. Thymine pairs with ______________, and cytosine pairs with ______________. It is the sequence of these bases that create the genetic “blueprint.” Word Bank chromosomes deoxyribose double gene(s) lagging leading longing nitrogenous nucleotide(s) nucleus phosphate When DNA undergoes a process called _________________ before the cell divides so that protein(s) replication each new cell can have a copy of all the genetic information. During this process, the DNA ribose strands separate and each acts as a model or a ______________ to synthesize a RNA complementary strand. This process is called ______________________ because it the end semi-conservative product will contain one strand of the original DNA and only one side will be brand new. single During this process a protein called DNA Polymerase will add new complementary template _______________ to form a growing strand. Because DNA Polymerase can only add bases transcription translation to the 3’ end of DNA, however, one strand will be replicated continuously while the other strand will be replicated in chunks. The faster strand is called the ______________ strand, and the slower strand is called the ______________. Presentation RNA Overview 1. RNA is the other type of ____________________ 2. RNA stands for _________________________ 3. Its structure is a ______________ strand of ____________________ 4. RNA’s function is to ________________ ____________ within the DNA to make _________________. 5. Like ________, it has _______ nitrogenous bases: ____________________ and ____________________ ____________________ and ____________________ 6. There are 3 types of RNA: ____________________, ____________________, and ____________________ Differences between DNA and RNA Sugars DNA Number of Strands Bases Location RNA Protein Synthesis Overview _______ ________ ________ _______________ ________________ ________________ Transcription 1. In the first step of protein synthesis, a _____________________________ 2. A half of the DNA helix is used as a _______________ to create ___________________________ (mRNA) 3. Transcription occurs in the _________________ of the cell. Determine the sequence of the developing mRNA strand: Template DNA Strand Sequence G T C T A C T T G Messenger RNA Sequence Translation 1. _______________ leaves the nucleus and travels to the ___________________ 2. _______________________ (tRNA) meets mRNA at the ribosome carrying the appropropriate __________________________ (the building blocks of proteins) 3. Amino acids attach together (through peptide bonds) to form a ________________________ chain. 4. A 3-base sequence of ___________ called a _________________ codes for a specific amino acid 5. A 3-base sequence of ____________ called an ______________________ bonds with a specific corresponding codon, delivering its amino acid. Proteins 1. ___________________ bond together to make proteins. 2. Proteins ____________ due to the number, kind, sequence, and arrangement of amino acids. 3. Amino acids are attached to one another by __________________________ to form polypeptide chains. 4. The _________________ of the protein determines its function. 2 5. Polypeptide chains spontaneously ____________________ themselves into 3-dimensional structures to form _______________________ proteins. 6. There are _________ levels of arrangement from primary, the straight _____________ of amino acids, to quaternary, _______________ polypeptide chains bonded together. Human Genes & Proteins Reading Guide Read pages 364-370 in chapter 17 of your Integrated Science textbook and answer the following questions. Part 1. RNA and Transcription 1. Compare and contrast RNA and DNA (1 similarity and 3 differences). 2. Name and describe the three main types of RNA. 3. What is the purpose of transcription? How does it differ from DNA replication? 4. Why is it necessary for DNA to transfer its genetic information to RNA? 3 5. Summarize transcription. Describe the roles of DNA, messenger RNA and RNA polymerase in your response. 6. Use the following sequence of a template strand of DNA to transcribe a segment of messenger RNA. The letters represent nucleotides. DNA Template Strand Sequence: A G G Complementary mRNA Strand Sequence: 4 T T C G T A T T C A A Part 2. Translation 7. Summarize the genetic code. Include the connection between codons and amino acids. 8. Describe the relationship between amino acids, polypeptides, peptide bonds and proteins. 9. In detail, describe the process of translation. In your response, describe the roles of messenger RNA, transfer RNA, ribosomal RNA, ribosomes and amino acids. 10. What is a “stop” codon? Describe its role in protein synthesis. 11. Describe the importance of proteins. Give several examples of protein functions in living cells. Part 3. Summary and Application DNA RNA Protein 12. Put the following steps of protein synthesis in order; (1) happens first to (7) happens last. ____ tRNA carries amino acids to the ribosome, matching its anticodon with an mRNA codon ____ a stop codon on mRNA is encountered. The ribosome releases the polypeptide. ____ messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. 5 ____ messenger RNA leaves nucleus and travels to cytoplasm. ____ amino acids are added to a growing chain as mRNA codons are read by the ribosome. ____ an initiation codon on messenger RNA binds to a ribosome. ____ the polypeptide bends and folds into a 3-dimensional shape, forming a functional protein. 13. Step Initial Macromolecule (What do you start with?) Final Macromolecule (What is created?) Location in Cell (Where does this occur?) 1. Transcription 2. Translation Use the codon chart provided to help answer questions #14-#17. 14. If a three nucleotide sequence on a DNA molecule is CTA, what is the messenger RNA codon sequence? What is the amino acid this portion of the DNA molecule codes for? 15. RNA polymerase binds to a portion of the DNA molecule and reads the sequence of bases below. Transcribe and translate the DNA sequence to determine the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain. Remember that you always translate the messenger RNA codon sequence! Template DNA Strand Sequence: T A C T T G G G A T G C C C C A C T Messenger RNA Strand Sequence: Transfer RNA anticodon Sequence: Amino Acid Sequence: 16. RNA polymerase binds to a portion of the DNA molecule and reads the sequence of bases below. Transcribe and translate the DNA sequence to determine the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain. Remember that you always translate the messenger RNA codon sequence! Template DNA Strand Sequence: T A C G C C T C T G G T C T T A Messenger RNA Strand Sequence: Transfer RNA anticodon Sequence: Amino Acid Sequence: 17. UAG is a stop codon. What might happen if the uracil in this codon was changed to cytosine? 6 T C 18. List the four different sets of DNA nucleotide sequences that code for the amino acid Valine. Explain why this redundancy in the genetic code is significant to life. 19. Once a polypeptide chain is formed, it must be arranged into a 3-dimensional conformation before it is considered a functional protein. List and describe the 4 levels of protein structure. 7