Module 1 - Leon County Schools
advertisement

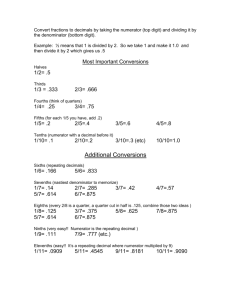
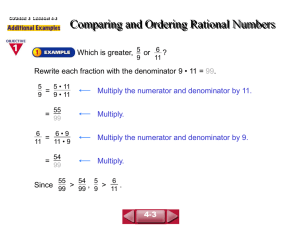
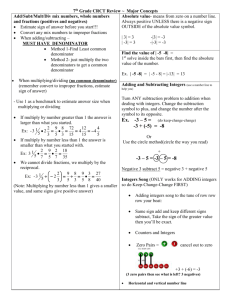
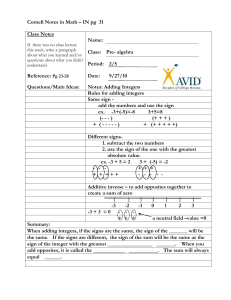
Module 1: Adding & Subtracting Integers Adding integers with the SAME signs: add & keep the signs the same (*Remember: If you’re adding & the signs are the SAME, keep the SAME signs & ADD.) + + + = + positive + positive = positive negative - + - = negative + negative = Adding integers with DIFFERENT signs: subtract & take the sign of the number farthest from 0 (*Remember: If you’re adding & the signs are DIFFERENT take the DIFFERENCE (subtract).) Subtracting integers: add the opposite (Keep the first number the same, change the subtraction sign to addition, and change the second number to its opposite; if it’s positive, make it negative & if it’s negative, make it positive.) Module 2: Multiplying & Dividing Integers If the signs are the SAME, your answer is POSITIVE If the signs are DIFFERENT, your answer is NEGATIVE Module 3: Rational Numbers (Rational Numbers are numbers that can be written as a fraction.) Fractions to Decimals: divide numerator (top) BY denominator (bottom) (Calculator: numerator (top), division sign, denominator (bottom), equals) (Long Division: DIVIDE Denominator INTO Numerator; denominator on OUTSIDE of the house, numerator on INSIDE of the house) Adding or Subtracting Rational Numbers: o Fractions must have a common denominator (Find the least common multiple and make equivalent fractions) o You must line up the decimals o *Don’t forget the rules of integers for adding & subtracting fractions and decimals Writing Mixed Numbers as Decimals o “MAK” (multiply, add, keep) the mixed number & divide numerator by denominator o Separate whole number from fraction & change fraction to a decimal. Rejoin it with the whole number. Multiplying Rational Numbers: o Fractions- cross cancel (if you want), multiply straight across & simplify o Decimals- do not line up the decimals. Multiply as normal. Count how many numbers are after the decimal(s) in the problem & put the decimal (in the answer) that many places (going from right to left) o *Don’t forget the rules of integers for multiplying Dividing Rational Numbers: o Fractions- SAME, CHANGE, FLIP. Next, cross cancel (if you want), multiply straight across. o Decimals- the divisor (number that’s doing the dividing; the number outside the house) cannot be a decimal. So, move the decimal out of the divisor. You must also move the decimal in the dividend (number that’s being divided; the number inside the house) the same number of places you moved it in the divisor. Divide as normal. o *Don’t forget the rules of integers for dividing Module 6: Expressions and Equations Algebraic Expressions: o Combining like terms: variables with variables (letters) & constants with constants (numbers) o Distributive Property: When you have a number on the outside of parenthesis, multiply that by each term in the parenthesis. o Factoring Expressions: Pull out (divide by) the GCF of the terms and write it on the outside of parenthesis. o REMEMBER- If you see the word “than”, switch the order of the terms. Equations: o Whatever you do to one side of the equals sign, you must do to the other. o The goal is to get the variable alone (solve for the variable). Undo every operation that is being done to the variable by doing the inverse (opposite) operation. Module 7: Inequalities Solve inequalities exactly like you solve an equation (see the steps above). The difference is you use an inequality sign (>, <, ≥, ≤, =) When you multiply or divide by a negative number, REVERSE the direction of the inequality sign. Graphing solutions of inequalities: o OPEN CIRCLE – greater than or less than (> or <) o CLOSED CIRCLE – greater than or EQUAL to OR less than or EQUAL to (≥ or ≤) o SHADE in the direction that the arrow points (from the inequality sign). *The VARIABLE must be on the LEFT.