Practice Test
Name: ______________________________________
Ecology Practice Test
Ecology
1.
An increase in the atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide (CO which of the following?
A.
ozone depletion
2
) is the biggest contributor to
C. global warming
D. El Nino B.
wind storms
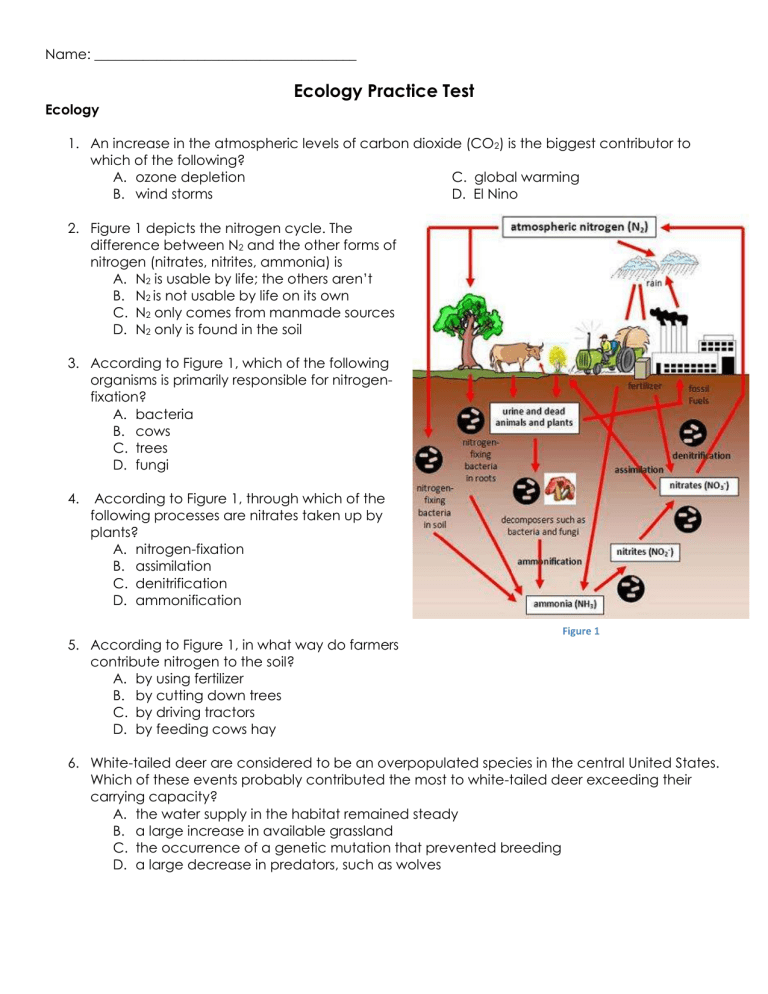
2.
Figure 1 depicts the nitrogen cycle. The difference between N
2
and the other forms of nitrogen (nitrates, nitrites, ammonia) is
A.
N
B.
N
2
2
C.
N
2
is usable by life; the others aren’t is not usable by life on its own
D.
N
2
only comes from manmade sources
only is found in the soil
3.
According to Figure 1, which of the following organisms is primarily responsible for nitrogenfixation?
A.
bacteria
B.
cows
C.
trees
D.
fungi
4.
According to Figure 1, through which of the following processes are nitrates taken up by plants?
A.
nitrogen-fixation
B.
assimilation
C.
denitrification
D.
ammonification
5.
According to Figure 1, in what way do farmers contribute nitrogen to the soil?
A.
by using fertilizer
B.
by cutting down trees
C.
by driving tractors
D.
by feeding cows hay
Figure 1
6.
White-tailed deer are considered to be an overpopulated species in the central United States.
Which of these events probably contributed the most to white-tailed deer exceeding their carrying capacity?
A.
the water supply in the habitat remained steady
B.
a large increase in available grassland
C.
the occurrence of a genetic mutation that prevented breeding
D.
a large decrease in predators, such as wolves
7.
The gypsy moth is a species native to Europe that has been brought to the United States. It prefers to feed on oak trees in the U.S., and its caterpillars can consume all of the leaves off of trees. This leads to tree death after a few years of repeated defoliation.
Why is the gypsy moth able to do so much damage to trees in the United States?
A.
The gypsy moth is a uniquely dangerous species of insect around the world.
B.
It is a parasite and therefore does not need its host to survive.
C.
It is a non-native species and therefore has fewer predators.
D.
The ecosystems found in the United States are less stable than those in Europe.
8.
In any ecosystem, the basic resources that organisms need for survival are always in limited supply.
Which of the following are examples of limited resources in an ecosystem?
A.
Sunlight
B.
Water
C. Food
D. All of these
9.
The biological interaction in which one organism hunts, kills, and eats another organism for energy is known as _______.
A.
Commensalism
B.
Parasitism
C. Mutualism
D. Predation
10.
Which of the following shows the organizational level of a biome from the broadest category to the most specific category?
A.
biome → population → community → ecosystem → organism
B.
biome → ecosystem → population → community → organism
C.
biome → community → ecosystem → population → organism
D.
biome → ecosystem → community → population → organism
11.
Plants require nitrogen and phosphorous but cannot efficiently absorb these nutrients from the soil. Instead, they obtain the nutrients through fungi that live in their roots. In return, the fungi have access to carbohydrates manufactured by the plants. Without the fungi, plants would not be healthy and abundant, and the food supply of all of the organisms in the ecosystem would be in danger.
This is an example of how _______ relationships maintain balance within an ecosystem.
A.
Abiotic C. Symbiotic
B.
Divergent D. Competitive
12.
Examine the following food chain and choose the organism that would best fill in the blank portion.
A.
B.
oak tree algae
Wheat Mouse [?] Hawk
C. cow
D. snake
13.
The water cycle shows the continuous movement of Earth's water.
During which of the following water cycle processes does water move from living, organic matter (such as plants) to the atmosphere?
A.
Precipitation C. Transpiration
D. Vapor Transport B.
Condensation
14.
The biosphere can best be defined as
A.
any region on Earth where life can exist.
B.
a region with distinct climate characteristics.
C.
all of the plants on Earth.
D.
all of the abiotic components of the Earth.
15.
Figure 4 below shows population data for two species.
Figure 2
What can be said about the relationship between species 1 and species 2?
A.
When the population of species 1 increases, the population of species 2 decreases.
B.
The populations of species 1 and species 2 stay the same over the time period shown.
C.
The population of species 1 is not influenced by the population of species 2.
D.
When the population of species 1 increases, the population of species 2 increases.
16.
Over the past generations, there has been a great deal of deforestation to accommodate the increase in the human population. Which statement describes one of the main impacts of deforestation?
A.
decrease in sea levels
B.
decrease in carbon monoxide emissions
C.
decrease in animal populations
D.
decrease in global warming
17.
When a(n) __________ organism enters an established ecosystem, it competes with some of the native organisms for food. As a result, the entire ecosystem can be thrown out of balance.
A.
Symbiotic
B.
Pioneer
C. Invading
D. Large
18.
Chemicals can affect an ecosystem. Which of the following is a result of pesticide application?
A.
It always leaves a residue on plant leaves, reducing photosynthesis.
B.
Pesticide kills all kinds of insects, including predatory insects, which in turn can increase the population of insects for which the pesticide was intended.
C.
Pesticide application does not affect ecosystems. This is why it is widely used on farms and ranches.
D.
Pesticide application improves soil fertility, increasing the diversity of plants in the ecosystem.
19.
Human beings are part of Earth's ecosystems. Thus, human activities can, deliberately or unintentionally, alter the equilibrium in ecosystems.
Humans often change ecosystems as a result of population growth, consumption, and technology. Which of the following exemplifies a way in which humans modify ecosystems?
A.
factory and automotive emissions causing acid rain
B.
cutting down trees to build new buildings and roads
C.
redirecting and storing freshwater behind dams
D.
all of these
20.
A savanna ecosystem is shown in Figure 5 below.
Figure 3
_______ is an example of a(n) ________ factor of this ecosystem.
A.
Air; biotic
B.
Temperature range; biotic
C. Grass; abiotic
C. Sunlight; abiotic
21.
A farmer plants two species of grass with similar nutrient needs on the same small plot of land.
What kind of interaction will most likely occur between the two species?
A.
Commensalism
B.
Parasitism
C. Competition
D. Mutualism
22.
Which level in a food web contains the highest amount of total available energy?
A.
secondary consumer
B.
decomposer
C. producer
D. primary consumer
Figure 4
23.
Based on the food chain shown in Figure 6 above, energy in this ecosystem flows from
A.
the mouse to the snake.
B.
the hawk to the snake.
24.
Which population in Figure 6 above would most likely increase if the mouse was removed from the food chain?
C. the mouse to the plant.
D. the snake to the mouse.
A.
Mouse
B.
Hawk
C. Plant
D. Snake
25.
Why is it important for carbon to be recycled in an ecosystem?
A.
Recycling carbon allows organisms to create less carbon.
B.
Recycling carbon allows organisms to create more carbon.
C.
If carbon isn't recycled, there will be too much of it on Earth.
D.
The carbon cycle is a closed system, and recycling carbon is the only way to replenish it for an ecosystem.
26.
Which of the following interactions is an example of symbiosis?
A.
a mother bear feeds and protects her cubs
B.
a tropical bird performs a courtship dance for a mate
C.
an insect acts as a pollinator for a plant species
D.
a population of hummingbirds migrates during the summer
27.
Most modern forms of transportation are powered by fossil fuels. Carbon dioxide, methane, carbon monoxide, and other gases are released into the atmosphere during the production and combustion of these fuels. How might these gases cause climatic changes?
A.
These gases cause more water vapor to condense, making climates wetter than they were in the past.
B.
These gases reduce the amount of thermal energy escaping into space, effectively warming the atmosphere.
C.
These gases block solar radiation, making the atmosphere cooler than it would otherwise be.
D.
These gases have no effect on atmospheric temperatures, so they are unable to cause any type of climatic changes.
28.
Select the list below that would best exemplify a community.
A.
a warm, humid climate with plenty of rainfall
B.
a nest of mockingbirds, some bullfrogs, a pond, and a sandy shore
C.
bees and wasps around a group of purple cornflowers
D.
a school of sunfish
29.
A population of pheasants grew until it reached the maximum carrying capacity of an ecosystem. Then, the pheasants' food supply increased. As a result, the carrying capacity of the pheasants' habitat changed.
Which graph could represent the history of the pheasant population?
A.
C.
B.
D.
30.
In the carbon cycle, carbon is taken in by plants
A.
as water vapor in the process of photosynthesis.
B.
as ammonia in the process of assimilation.
C.
as carbon dioxide in the process of photosynthesis.
D.
as carbon dioxide in the process of decomposition.
31.
Which of the following best describes an ecosystem?
A.
a region with a distinct climate
B.
all the living organisms of the same species throughout the world
C.
all the living organisms in an area
D.
all the living organisms in an area and their physical surroundings
32.
Populations of typical prey animals, such as deer, might exceed the carrying capacity of an ecosystem if top predators, such as mountain lions, are removed. Without the mountain lions, increased numbers of deer may reduce the food supply available to other herbivores, such as field mice and crickets. As a result, populations of deer, mice, and crickets might decline, causing a population decrease in species that feed on these organisms as well.
This example implies that properly functioning predator/prey relationships
A.
harm all of the organisms in an ecosystem.
B.
can throw an ecosystem out of balance.
C.
result in food shortage for the entire ecosystem.
D.
maintain balance within an ecosystem.
33.
Increases in the sizes of human populations have caused a demand for more houses. When new subdivisions are built, trees are often cut down to make space for the new houses. Which of the following is an immediate impact of this deforestation?
A.
A reduction in tree populations will increase global temperatures.
B.
Wood from the felled trees must be used immediately.
C.
The deforestation will increase atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
D.
Animals that live in those areas must find new homes.
34.
Almost no species ever reaches its biotic potential—the population size that the species could produce if all individuals survived and produced offspring.
Anything that prevents the species from reaching its biotic potential is called a
A.
symbiote. C. capacity limiter
B.
producer. D. limiting factor
35.
An algal bloom is a sudden and dramatic increase in the population of certain microorganisms such as algae or cyanobacteria in a body of water. When there are high levels of nutrients in the water, microorganisms will reproduce rapidly until they have used all the available resources. At that point, the algae dies off in tremendous quantities, vastly reducing the amount of oxygen in the water as it dies and begins to decompose.
Figure 10 to the immediate right is a photograph of an algal bloom using visible light. The image to the far right shows the concentrations of chlorophyll present in the water, which is an indication of the amount of algae present.
What impact, if any, would an algal bloom be likely to have on its local ecosystem?
A.
It would kill many other organisms in the ecosystem by removing oxygen and nutrients from the water.
B.
It would have no significant effect on the ecosystem since the algae dies off by itself after a time.
C.
It would help the ecosystem by providing extra algae for primary consumers to eat.
D.
It would have no effect on the ecosystem because ecosystems are self-balancing.
Figure 5
36.
Figure 9 represents a forest ecosystem is shown below. Which level of the energy pyramid represents the forest's secondary consumers?
Figure 6
A.
Coyotes
B.
Mice, Gophers, and Birds
C. Snakes and Hawks
D. Grasses, Tree leaves, flowers, vines
37.
Which level of the energy pyramid in Figure 9 represents the forest's tertiary consumers?
A.
B.
Coyotes
Mice, Gophers, and Birds
38.
Examine the energy pyramid in Figure 9 above.
C. Snakes and Hawks
D. Grasses, Tree leaves, flowers, vines
Is it possible for the top level to be wider than the level before it?
A.
Yes, if climatic conditions are right, there can be more predators than prey.
B.
No, it is not possible for a large population of coyotes to exist because of their mating habits.
C.
No, it is not possible for an ecosystem to support more predators than prey.
D.
Yes, if the population of coyotes swells, the top level will be larger than the level before it.
39.
The trophic levels of the energy pyramid in Figure 9 above show that
A.
energy is not transferred between organisms in an ecosystem.
B.
there is a great amount of energy lost as it travels up the energy pyramid.
C.
the same amount of energy is available at every level of the energy pyramid.
D.
there is a great amount of energy gained as it travels up the energy pyramid.
40.
Figure 9 above could possible amount of energy, in kilocalories, available in the organisms at each trophic level in an ecosystem.
According to the law of conservation of energy, energy can neither be created nor destroyed.
If this is true, why is there less energy in the top of the energy pyramid than there is in the bottom of the energy pyramid?
A.
Organisms in the top of the energy pyramid use up energy the fastest.
B.
The law of conservation of energy does not apply to ecosystems.
C.
Energy is lost between each trophic level as heat.
D.
The extra energy in the bottom is slower to reach the top.
41.
The diagram in Figure 11 to the right shows an energy pyramid.
Which of the following best explains why the amount of pollution at each level increases while moving up the energy pyramid?
A.
Biomagnification
B.
The 10% Rule
C.
Endangered species
D.
Decrease in biodiversity
Figure 7
Figure 8
42.
If a disease killed all of the frogs in Figure 12 above, which population would be most directly affected in a negative way?
A.
Insects C. Owls
B.
Mice D. Hawks
43.
Which of the following has had the greatest effect on ozone depletion?
A.
carbon monoxide (CO)
B.
chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
C.
water vapor (H
2
O)
D.
carbon dioxide (CO
2
)
44.
Humans depend upon a variety of Earth's natural resources. Certain resources should be conserved because humans are able to consume them much faster than they can be replaced by natural processes.
Which of the following is a resource that should be conserved?
A.
Wind C. Water
B.
Fossil fuels D. Solar
45.
Which statement explains the impact that ozone depletion has had on the Earth?
A.
It has decreased the production of ultraviolet light.
B.
It has decreased surface levels of ultraviolet light.
C.
It has increased surface levels of ultraviolet light.
D.
It has increased the production of ultraviolet light.








