Environmental Science
advertisement
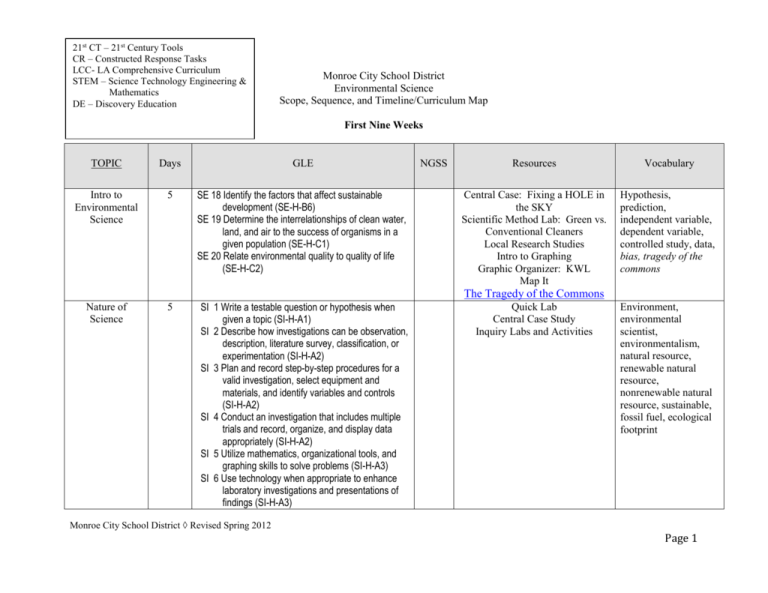
21st CT – 21st Century Tools CR – Constructed Response Tasks LCC- LA Comprehensive Curriculum STEM – Science Technology Engineering & Mathematics DE – Discovery Education Monroe City School District Environmental Science Scope, Sequence, and Timeline/Curriculum Map First Nine Weeks TOPIC Days GLE Intro to Environmental Science 5 SE 18 Identify the factors that affect sustainable development (SE-H-B6) SE 19 Determine the interrelationships of clean water, land, and air to the success of organisms in a given population (SE-H-C1) SE 20 Relate environmental quality to quality of life (SE-H-C2) NGSS Resources Vocabulary Central Case: Fixing a HOLE in the SKY Scientific Method Lab: Green vs. Conventional Cleaners Local Research Studies Intro to Graphing Graphic Organizer: KWL Map It Hypothesis, prediction, independent variable, dependent variable, controlled study, data, bias, tragedy of the commons The Tragedy of the Commons Nature of Science 5 SI 1 Write a testable question or hypothesis when given a topic (SI-H-A1) SI 2 Describe how investigations can be observation, description, literature survey, classification, or experimentation (SI-H-A2) SI 3 Plan and record step-by-step procedures for a valid investigation, select equipment and materials, and identify variables and controls (SI-H-A2) SI 4 Conduct an investigation that includes multiple trials and record, organize, and display data appropriately (SI-H-A2) SI 5 Utilize mathematics, organizational tools, and graphing skills to solve problems (SI-H-A3) SI 6 Use technology when appropriate to enhance laboratory investigations and presentations of findings (SI-H-A3) Quick Lab Central Case Study Inquiry Labs and Activities Environment, environmental scientist, environmentalism, natural resource, renewable natural resource, nonrenewable natural resource, sustainable, fossil fuel, ecological footprint Monroe City School District Revised Spring 2012 Page 1 TOPIC Days Nature of Science (cont’d) Economics and Env. Policy 5 GLE SI 7 Choose appropriate models to explain scientific objects, mathematical relationships, plans, schemes, examples, role-playing, computer simulations) (SI-H-A4) SI 8 Give an example of how new scientific data can cause an existing scientific explanation to be supported, revised, or rejected (SI-H-A5) SI 9 Write and defend a conclusion based on logical analysis of experimental data (SI-H-A6) (SI-HA2) SI 10 Given a description of an experiment, identify appropriate safety measures (SI-H-A7) SI 11 Evaluate selected theories based on supporting scientific evidence (SI-H-B1) SI 12 Cite evidence that scientific investigations are conducted for many different reasons (SI-H-B2) SE 18 Identify the factors that affect sustainable development (SE-H-B6) SE 19 Determine the interrelationships of clean water, land, and air to the success of organisms in a given population (SE-H-C1) SE 21 Analyze the effect of common social, economic, technological, and political considerations on environmental policy (SE-H-C3) SE 25 Discuss how education and collaboration can affect the prevention and control of a selected pollutant (SE-H-D2) (SE-H-D3) SE 26 Determine local actions that can affect the global environment (SE-H-D4) SE 27 Describe how accountability toward the environment affects sustainability (SE-H-D5) NGSS Resources Vocabulary Peer review, theory, ethics Central Case Study Bellringer Video (ABC News) Quick Lab In Your Neighborhood Activities 21st Century Skills Inquiry Labs and Activities DE: Economics: A Framework for Teaching the Basic Concepts: Microeconomic Concepts Economics, supply, demand, cost-benefit analysis, ecological economics, environmental economics, nonmarket value, market failure, ecolabeling, policy, environmental impact statement, subsidy, green tax, lobbying, goods, services, centrally planned economy, free market economy, mixed economy Monroe City School District Revised Spring 2012 Page 2 TOPIC Days GLE Matter and Earth’s Systems 4 SE 7 Illustrate the flow of carbon, water, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus through an ecosystem (SE-H-A6) (LS-H-D1) SE 26 Determine local actions that can affect the global environment (SE-H-D4) Earth’s Spheres & Biogeochemical Cycles 3 ESS 2 Trace the flow of heat energy through the processes in the water cycle (ESS-H-A1) ESS 12 Relate lithospheric plate movements to the occurrences of earthquakes, volcanoes, midocean ridge systems, and off-shore trenches found on Earth (ESS-H-A7) ESS 13 Explain how stable elements and atoms are recycled during natural geologic processes (ESS-H-B1) ESS 15 Identify the sun-driven processes that move substances at or near Earth’s surface (ESS-HB2) SE 7 Illustrate the flow of carbon, water, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus through an ecosystem (SE-H-A6) (LS-H-D1) SE 26 Determine local actions that can affect the global environment (SE-H-D4) Same ESS GLEs as above NGSS Resources Vocabulary Central Case Earth’s Spheres Foldable/Graphic Organizer Bell Ringer Video (ABC News) Map It Online Plate Boundaries Foldable/Graphic Organizer Quick Lab Matter, atom, element, nucleus, molecule, compound, hydrocarbon, solution, macromolecule, protein, nucleic acid, carbohydrate, lipid, pH, feedback loop, erosion, sphere, lithosphere, biosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, Elements and Atoms Earth Formation Bellringer Video: Volcano to Earthquake Introduction to Field Studies Field Observations Compositional and Mechanical Layers of the Earth Structure of the Earth Plate Tectonics-- Difference between crust and lithosphere Pangaea Plate Tectonics -- Evidence of plate movement tectonic plate, landform, deposition, aquifer, groundwater, law of conservation of matter, biogeochemical cycle, eutrophication, nitrogen fixation, Pangaea, asthenosphere, ozone, sink, nitrification Monroe City School District Revised Spring 2012 Page 3 TOPIC Days GLE Earth’s Spheres & Biogeochemical Cycles (cont’d) NGSS Resources Vocabulary Plates Moving Due to Convection in Mantle Ozone Layer and Eukaryotes Show Up Population Ecology 5 SE 1 Describe the abiotic and biotic factors that distinguish Earth’s major ecological systems (SE-H-A1) SE 4 Determine the effects of limiting factors on a population and describe the concept of carrying capacity (SE-H-A3) Central Case Modeling Lab: Using Mark & Recapture Bellringer Video Go Outside Scientific Method Lab Inquiry Labs and Activities Ecological Footprints Evolution & Community Ecology 7 SE 3 Use the 10% rule and data analysis to measure the flow of energy as represented by biomass in a system (SE-H-A2) SE 5 Examine and discuss the major stages of succession, describing the generalized sequential order of the types of plant species (SE-H-A4) SE 8 Explain how species in an ecosystem interact and link in a complex web (SE-H-A7) (SE-HA10) SE 9 Cite and explain examples of organisms’ adaptations to environmental pressures over time (SE-H-A8) SE 10 Analyze the effect of an invasive species on the biodiversity within ecosystems (SE-H-A9) SE 19 Determine the interrelationships of clean water, land, and air to the success of organisms in a given population (SE-H-C1) Central Case Modeling Lab Simulating Adaptations Bell Ringer Video Outdoors Lab Real Data Neighborhood Activity: Invasive Species Near You Quick Lab Science Behind the Stories population, community, ecosystem, survivorship curve, immigration, emigration, exponential growth, limiting factor, carrying capacity, Evolution, extinction, niche, chemosynthesis, trophic level, food chain, food web, succession, invasive species, pioneer species Introduction to Evolution and Natural Selection DE: The Ecosphere: Where All Life Exists Biology: The Science of Life: The Flow of Matter and Energy in the Living World: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Monroe City School District Revised Spring 2012 Page 4 TOPIC Evolution & Community Ecology (cont’d) Project-based Activity Days GLE NGSS ESS 1 Describe what happens to the solar energy received by Earth every day (ESS-H-A1) 5 Resources Vocabulary Biologix: Succession and Climax Communities Combination of Science as Inquiry and Environmental Science GLEs Review & Assessment Monroe City School District Revised Spring 2012 Page 5 21st CT – 21st Century Tools CR – Constructed Response Tasks LCC- LA Comprehensive Curriculum STEM – Science Technology Engineering & Mathematics DE – Discovery Education Monroe City School District Environmental Science Scope, Sequence, and Timeline/Curriculum Map Second Nine Weeks TOPIC Days GLE Biomes & Aquatic Ecosystems 7 SE 2 Describe the characteristics of major biomes on Earth (SE-H-A1) NGSS Resources Vocabulary Central Case Outdoors Lab: Collecting Climate Data Bellringer Video Point Counterpoint Inquiry Labs and Activities Ecological Footprints DE: PLANET EARTH: Caves Biome, climate, weather, climatograph, canopy, emergent layer, understory, epiphyte, deciduous, estivation, permafrost, salinity, photic zone, aphotic zone, benthic zone, littoral zone, limnetic zone, Central Case Study Outdoors Lab: Exploring Plant Diversity Modeling Lab Map It In Your Neighborhood Bellringer Video Real Data Inquiry Labs and Activities Biodiversity, extirpation, Endangered Species Act PLANET EARTH: Deep Ocean PLANET EARTH: Deserts PLANET EARTH: Fresh Water PLANET EARTH: Great Plains PLANET EARTH: Ice Worlds PLANET EARTH: Jungles PLANET EARTH: Mountains PLANET EARTH: Pole to Pole PLANET EARTH: Seasonal Forests PLANET EARTH: Shallow Seas Biodiversity & Conservation 5 SE 10 Analyze the effect of an invasive species on the biodiversity within ecosystems (SE-H-A9) SE 11 Explain why biodiversity is essential to the survival of organisms (SE-H-A9) SE 12 Cite evidence that scientific investigations are conducted for many different reasons (SI-H-B2) SE 14 Analyze data to determine the effect of preservation practices compared to conservation practices for a sample species (SE-H-B2) Monroe City School District Revised Spring 2012 Page 6 TOPIC Days Biodiversity & Conservation (cont’d) Human Population Environmental Health 6 3 GLE NGSS SE 18 Identify the factors that affect sustainable development (SE-H-B6) LS 18 Classify organisms from different kingdoms at several taxonomic levels, using a dichotomous key (LS-H-C4) LS 19 Compare characteristics of the major kingdoms (LS-H-C5) SE 15 Identify the factors that cause the inequitable distribution of Earth’s resources (e.g., politics, economics, climate) (SE-H-B3) SE 17 Analyze data to determine when reuse, recycling, and recovery are applicable (SE-H-B5) SE 20 Relate environmental quality to quality of life (SE-H-C2) SE 21 Analyze the effect of common social, economic, technological, and political considerations on environmental policy (SE-H-C3) SE 26 Determine local actions that can affect the global environment (SE-H-D4) SE 12 Cite evidence that scientific investigations are conducted for many different reasons (SI-H-B2) SE 19 Determine the interrelationships of clean water, land, and air to the success of organisms in a given population (SE-H-C1) SE 20 Relate environmental quality to quality of life (SE-H-C2) SE 25 Discuss how education and collaboration can affect the prevention and control of a selected pollutant (SE-H-D2) (SE-H-D3) Resources Vocabulary DE: PLANET EARTH: The Future: Saving Species Central Case Bellringer Video Real Data In Your Neighborhood Graph It A Closer Look Ecological Footprints Industrial Revolution, demography, demographic transition CIA - The World Factbook Central Case Quick Lab In Your Neighborhood Scientific Method Lab: Testing for Lead Map It Ecological Footprints DE: PLANET EARTH: The Future: Into the Wilderness Pathogen, epidemiology, toxicology, pollution, carcinogen, teratogen, neurotoxin, asbestos, radon, bioaccumulation, biomagnification Tsunami Thanksgiving Break Monroe City School District Revised Spring 2012 Page 7 TOPIC Days GLE NGSS Resources Environmental Health Urbanization 5 5 SE 17 Analyze data to determine when reuse, recycling, and recovery are applicable (SE-H-B5) SE 26 Determine local actions that can affect the global environment (SE-H-D4) LS 27 Analyze positive and negative effects of human actions on ecosystems (LS-H-D4) (SE-H-A7) Project-based Activity 5 Combination of Science as Inquiry and Environmental Science GLEs Review & Semester Assessment Christmas Break Vocabulary Same as above Central Case In Your Neighborhood Activity Bellringer Video Real Data Go Outside Inquiry Labs and Activities DE: Ecopolis: Building the Future Land cover, urbanization, infrastructure, GIS, greenway, UGB Monroe City School District Revised Spring 2012 Page 8 21st CT – 21st Century Tools CR – Constructed Response Tasks LCC- LA Comprehensive Curriculum STEM – Science Technology Engineering & Mathematics DE – Discovery Education Monroe City School District SCIENCE Scope, Sequence, and Timeline/Curriculum Map Third Nine Weeks TOPIC Days GLE Resource Management 2 Forest Management 3 SE 11 Explain why biodiversity is essential to the survival of organisms (SE-H-A9) SE 19 Determine the interrelationships of clean water, land, and air to the success of organisms in a given population (SE-H-C1) SE 23 Describe the relationship between public support and the enforcement of environmental policies (SE-H-C5) SE 13 Evaluate whether a resource is renewable by analyzing its relative regeneration time (SE-H-B1) SE 19 Determine the interrelationships of clean water, land, and air to the success of organisms in a given population (SE-H-C1) SE 23 Describe the relationship between public support and the enforcement of environmental policies (SE-H-C5) SE 6 Analyze the consequences of changes in selected divisions of the biosphere (e.g., ozone depletion, global warming, acid rain) (SE-H-A5) (SE-H-A7) ESS 22 Analyze data related to a variety of natural processes to determine the time frame of the changes involved (e.g., formation of sedimentary rock layers, deposition of ash layers, fossilization of plant or animal species) (ESS-H-C5) Soil 4 NGSS Resources Vocabulary Central Case Outdoor Activity Modeling Lab: Making recycled Paper Real Data Resource management, MSY, deforestation, In Your Neighborhood Bellringer Video Inquiry Labs and Activities Multiple use, monoculture, prescribed burn, salvage logging, sustainable forestry certifications Southern Forests for the Future DE: Enviro-Tacklebox: Module 04: Forces in the Environment: Rebirth in Fire Central Case Scientific Method Lab Modeling Lab In Your Neighborhood Map It Bell Ringer Video Soil, parent material, bedrock, weathering, soil horizon, soil profile, clay, silt, sand, loam Natural Resources Conservation Service Monroe City School District Revised Spring 2012 Page 9 TOPIC Days GLE Agriculture of Food Production 4 SE 6 Analyze the consequences of changes in selected divisions of the biosphere (e.g., ozone depletion, global warming, acid rain) (SE-H-A5) (SE-H-A7) SE 18 Identify the factors that affect sustainable development (SE-H-B6) ESS 22 Analyze data related to a variety of natural processes to determine the time frame of the changes involved (e.g., formation of sedimentary rock layers, deposition of ash layers, fossilization of plant or animal species) (ESS-H-C5) LS 27 Analyze positive and negative effects of human actions on ecosystems (LS-H-D4) (SE-H-A7) SE 17 Analyze data to determine when reuse, recycling, and recovery are applicable (SE-HB5) ESS 13 Explain how stable elements and atoms are recycled during natural geologic processes (ESS-H-B1) Mineral Resources & Mining 5 Water & Its Uses 2 Water Pollution 3 SE 13 Evaluate whether a resource is renewable by analyzing its relative regeneration time (SE-HB1) SE 19 Determine the interrelationships of clean water, land, and air to the success of organisms in a given population (SE-H-C1) SE 19 Determine the interrelationships of clean water, land, and air to the success of organisms in a given population (SE-H-C1) NGSS Resources Inquiry Labs and Activities Bell Ringer Video Inquiry Labs and Activities U.S. Dept. of Agriculture United Nations World Food Programme Central Case Scientific Method Lab Outdoors Lab Go Outside Map It Bellringer Video Inquiry Labs and Activities Central Case Graph It Map It Bellringer Video Real Data In Your Neighborhood Activity Scientific Method Lab Quick Lab Inquiry Labs and Activities Vocabulary Arable land, genetic engineering, biotechnology, aquaculture, Mineral, rock, Rock cycle, ore, subsurface mining, placer mining, smelting River system, permeable, salinization, xeriscaping point-source pollution, wastewater, algal bloom, septic system Flocculation: Making Clean Water Monroe City School District Revised Spring 2012 Page 10 TOPIC Days Earth’s Atmosphere 2 Atmospheric & Air Pollution 3 GLE SE 21 Analyze the effect of common social, economic, technological, and political considerations on environmental policy (SE-H-C3) SE 22 Analyze the risk-benefit ratio for selected environmental situations (SE-H-C4) SE 25 Discuss how education and collaboration can affect the prevention and control of a selected pollutant (SE-H-D2) (SE-H-D3) ESS 8 Explain why weather only occurs in the tropospheric layer of Earth's atmosphere (ESSH-A5) ESS 9 Compare the structure, composition, and function of the layers of Earth’s atmosphere (ESS-H-A6) ESS 10 Analyze the mechanisms that drive weather and climate patterns and relate them to the three methods of heat transfer (ESS-H-A6) ESS 21 Use fossil records to explain changes in the concentration of atmospheric oxygen over time (ESS-H- C4) SE 21 Analyze the effect of common social, economic, technological, and political considerations on environmental policy (SE-H-C3) SE 22 Analyze the risk-benefit ratio for selected environmental situations (SE-H-C4) SE 25 Discuss how education and collaboration can affect the prevention and control of a selected pollutant (SE-H-D2) (SE-H-D3) ESS 8 Explain why weather only occurs in the tropospheric layer of Earth's atmosphere (ESSH-A5) NGSS Resources Vocabulary Central Case Quick Lab Graphic Organizer Go Outside In Your Neighborhood Bellringer Video Graph It Real Data Unit Project Atmosphere, relative humidity, troposphere, stratosphere, ozone layer, mesosphere, thermosphere, radiation, convection current, air mass, front Unit Project Clean Air Act, emission, fossil fuel, temperature inversion, acid deposition, catalytic converter, ozone hole, chlorofluorocarbon, Montreal Protocol, scrubber The Ozone Layer Air Pollutants | Air and Radiation | US EPA Monroe City School District Revised Spring 2012 Page 11 TOPIC Days Atmospheric & Air Pollution (cont’d) Global Climate Change Energy Overview Project-based Activity 9 2 5 GLE NGSS ESS 9 Compare the structure, composition, and function of the layers of Earth’s atmosphere (ESS-H-A6) ESS 10 Analyze the mechanisms that drive weather and climate patterns and relate them to the three methods of heat transfer (ESS-H-A6) ESS 21 Use fossil records to explain changes in the concentration of atmospheric oxygen over time (ESS-H- C4) SE 28 Discuss the reduction of combustible engines needed to significantly decrease CO2 in the troposphere (SE-H-D6) ESS 1 Describe what happens to the solar energy received by Earth every day (ESS-H-A1) ESS 2 Trace the flow of heat energy through the processes in the water cycle (ESS-H-A1) ESS 15 Identify the sun-driven processes that move substances at or near Earth’s surface (ESS-H-B2) SE 13 Evaluate whether a resource is renewable by analyzing its relative regeneration time (SE-HB1) SE 25 Discuss how education and collaboration can affect the prevention and control of a selected pollutant (SE-H-D2) (SE-H-D3) Resources Vocabulary Central Case Modeling Lab Quick Lab Real Data Science Behind the Stories Inquiry Labs and Activities Ecological Footprints Greenhouse effect, thermohaline circulation, El Niño, topography, global climate change, global warming, proxy indicator, fossil fuel, carbon footprint, Kyoto Protocol, prevailing winds, trade winds Energy efficiency, combustion, electricity, renewable & nonrenewable energy How Earth's Tilt Causes Seasons Central Case In Your Neighborhood Quick Lab Energy, Climate Change and Our Environment-The White House Combination of Science as Inquiry and Environmental Science GLEs Review & Assessment Monroe City School District Revised Spring 2012 Page 12 21st CT – 21st Century Tools CR – Constructed Response Tasks LCC- LA Comprehensive Curriculum STEM – Science Technology Engineering & Mathematics DE – Discovery Education Monroe City School District Environmental Science Scope, Sequence, and Timeline/Curriculum Map Fourth Nine Weeks TOPIC Days Fossil Fuels and Nuclear Power 5 GLE SE 13 Evaluate whether a resource is renewable by analyzing its relative regeneration time (SE-H-B1) NGSS Resources Vocabulary Bellringer Video Graph It Map It Inquiry Labs and Activities Strip mining, subsurface mining, petroleum, petrochemical, oil sands, oil shale, methane hydrate, acid drainage, energy conservation, fracking, net energy Biomass energy, biofuel, biopower, geothermal energy, hydropower, solar heating, photovoltaic cell, tidal energy, wind turbine, electrolysis, fuel cell, Waste, sanitary landfill, leachate, incineration, source reduction, biodegradable, composting, recycling, ewaste, Superfund, surface impoundments, radioactive waste, deepwell injection, EPA Response to BP Spill in the Gulf of Mexico Renewable Energy Alternatives 9 Waste Management 8 SE 17 Analyze data to determine when reuse, recycling, and recovery are applicable (SE-H-B5) SE 28 Discuss the reduction of combustible engines needed to significantly decrease CO2 in the troposphere (SE-H-D6) ESS 1 Describe what happens to the solar energy received by Earth every day (ESS-H-A1) SE 11 Explain why biodiversity is essential to the survival of organisms (SE-H-A9) SE 17 Analyze data to determine when reuse, recycling, and recovery are applicable (SE-H-B5) SE 24 Identify the advantages and disadvantages of using disposable items versus reusable items (SE-H-D1) SI 1 Write a testable question or hypothesis when given a topic (SI-H-A1) SI 2 Describe how investigations can be observation, description, literature survey, classification, or experimentation (SI-H-A2) Central Case In Your Neighborhood Bellringer Video Real Data Go Outside Map It Central Case In Your Neighborhood Scientific Method Lab Graph It Quick Lab Real Data Ecological Footprints http://www.epa.gov/superfund DE: Ecopolis: A World of Trash Monroe City School District Revised Spring 2012 Page 13 TOPIC Days Project-based Activity 10 GLE NGSS SI 3 Plan and record step-by-step procedures for a valid investigation, select equipment and materials, and identify variables and controls (SIH-A2) SI 4 Conduct an investigation that includes multiple trials and record, organize, and display data appropriately (SI-H-A2) SI 5 Utilize mathematics, organizational tools, and graphing skills to solve problems (SI-H-A3) SI 6 Use technology when appropriate to enhance laboratory investigations and presentations of findings (SI-H-A3) SI 7 Choose appropriate models to explain scientific knowledge or experimental results (e.g., objects, mathematical relationships, plans, schemes, examples, role-playing, computer simulations) (SI-H-A4) SI 8 Give an example of how new scientific data can cause an existing scientific explanation to be supported, revised, or rejected (SI-H-A5) SI 9 Write and defend a conclusion based on logical analysis of experimental data (SI-H-A6) (SI-HA2) SI 10 Given a description of an experiment, identify appropriate safety measures (SI-H-A7) SI 11 Evaluate selected theories based on supporting scientific evidence (SI-H-B1) SI 12 Cite evidence that scientific investigations are conducted for many different reasons (SI-H-B2) Semester Review Semester Assessment Resources Vocabulary Unit Project DE: PLANET EARTH: The Future: Living Together Monroe City School District Revised Spring 2012 Page 14







