Nick-Essential+Biology+05.2+The+Greenhouse+Effect
advertisement
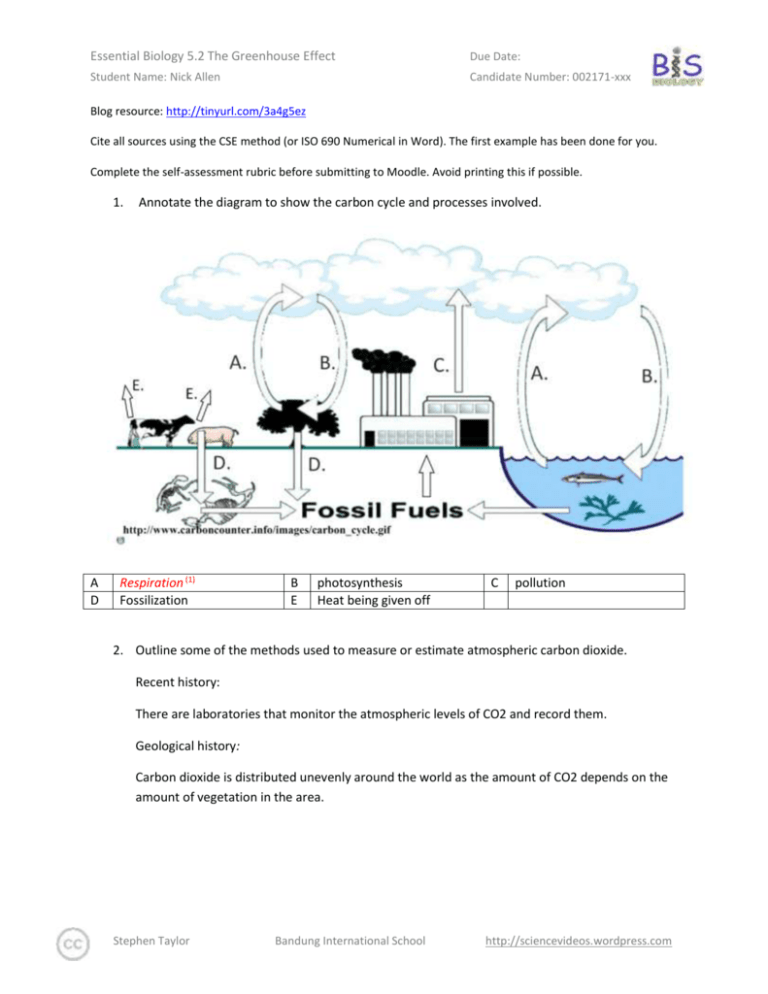
Essential Biology 5.2 The Greenhouse Effect Due Date: Student Name: Nick Allen Candidate Number: 002171-xxx Blog resource: http://tinyurl.com/3a4g5ez Cite all sources using the CSE method (or ISO 690 Numerical in Word). The first example has been done for you. Complete the self-assessment rubric before submitting to Moodle. Avoid printing this if possible. 1. A D Annotate the diagram to show the carbon cycle and processes involved. Respiration (1) Fossilization B E photosynthesis Heat being given off C pollution 2. Outline some of the methods used to measure or estimate atmospheric carbon dioxide. Recent history: There are laboratories that monitor the atmospheric levels of CO2 and record them. Geological history: Carbon dioxide is distributed unevenly around the world as the amount of CO2 depends on the amount of vegetation in the area. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.2 The Greenhouse Effect Due Date: Student Name: Nick Allen Candidate Number: 002171-xxx 3. The topic of increasing carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere has been the source of intense debate with regard to climate change in recent years. This graph shows the famous ‘Keeling Curve’ from Mauna Loa laboratory in Hawaii. Find out more here: http://earthguide.ucsd.edu/globalchange/keeling_curve/01.html a. Describe the overall trend shown in the graph. The amount of carbon dioxide is going up and down very frequently, but it is steadily increasing such that the lowest amount of CO2 in 2006 is equal to the highest amount of CO2 in 2003, therefore it took about three years for the CO2 levels in the atmosphere to double. The peaks of co2 levels are at the start of the year whereas the toughs are near the end of the year. b. Explain the annual fluctuations in CO2 levels. Peaks: The peaks of CO2 levels occurred usually earlier in the year because there is more sunshine. Troughs: The troughs of CO2 levels in the atmosphere were recorded later on in the year because there are less plants. c. Suggest one human impact and one natural cause that could have led to the overall trend shown in the graph: Anthropogenic: Carbon dioxide is released during the fermentation process of beer, whisky and other alcoholic beverages. Industries, pollution, Deforestation also results in greater CO2 levels because there are less plants to convert CO2 to O2. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.2 The Greenhouse Effect Due Date: Student Name: Nick Allen Candidate Number: 002171-xxx Natural: three sources of carbon dioxide are volcanic out gassing, the combustion of organic matter and the burning of fossil fuels. 4. Identify three greenhouse gases other than carbon dioxide. Methane gas, water vapor and nitrous oxide. 5. Explain the greenhouse effect with the aid of a diagram. Include short-wave and long-wave radiation. atmosphere earth Light comes through the atmosphere but does not all get back out, heat is also kept in. the light that comes in is short wave (UV light) and the light is reflected off the earth’s surface where it becomes long-wave. 6. Explain how increased atmospheric levels of greenhouse gases lead to an enhanced greenhouse effect. The atmospheric levels keep the heat in depending on how great it is. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.2 The Greenhouse Effect Due Date: Student Name: Nick Allen Candidate Number: 002171-xxx 7. Outline some of the possible consequences of a global temperature rise on arctic ecosystems. Ice coverage: the amount of ice would go down as it melts and the sea levels will rise. Climate changes: The tips of the world will become warmer, and there will be less cold places. Niches: Plant distributions: Areas that were frozen tundra before now become wetlands, giving opportunities for some plant species but hurting others. Animal populations: some animal species will disappear as their climate changes and they are not adapted to it, however, with the world getting warmer, animals in a temperate climate will be able to expand farther north where they could not before. 8. Outline the precautionary principle. If the effects of human-induced change would be large, perhaps catastrophic, those responsible for the change must prove that it will not do harm before proceeding. 9. Describe how the precautionary principle can be applied to anthropogenic climate destabilisation. 10. Give two other examples of the precautionary principle in effect in Biology or Medicine. The precautionary principle could be applied to medicine, for example when a new type of medical drug comes out. The precautionary principle can be applied to the greenhouse effect for example, when there is to be an attempt at stopping or slowing down the greenhouse effect, one must be certain that their action does not have the opposite effect. Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.2 The Greenhouse Effect Due Date: Student Name: Nick Allen Candidate Number: 002171-xxx 11. Evaluate the precautionary principle as a justification for taking strong action in response to the threats posed by the enhanced greenhouse effect. What are some of the steps that we could take? This video might help: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mF_anaVcCXg True False Global climate destabilization is… Take significant action Take no action If we take significant action in response to global climate change then and the threat turned out to be true, then everyone is happy because they are alive. =) If we take no action against global climate change and it turns out to be true, then we will have major problems and many people could die. Humanity…not very happy =( If we take significant action against global climate change and it turns out to be false, then people won’t be very happy because of the expenses. =( If we take no action against global climate change and it turns out to be false, then everyone will be very happy because they are no major problems and no major expenses. =) Conclusion: Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 5.2 The Greenhouse Effect Due Date: Student Name: Nick Allen Candidate Number: 002171-xxx Works Cited 1. Taylor, Stephen. 5.2 Greenhouse Effect (presentation). Science Video Resources. [Online] Septmber 2009. http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com/bis-ib-diploma-programme-biology/05-ecology-andevolution/the-greenhouse-effect/. 2. Allott, Andrew. IB Study Guide: Biology for the IB Diploma. s.l. : Oxford University Press, 2007. 978-019-915143-1. Self Assessment: Essential Biology Criterion Presentation & Organisation Academic Honesty Objective 1 understanding Objective 2 understanding Objective3 understanding Logic, notation, mathematical working Further research Assessment Complete (2) Partially complete (1) NA Complete and neat. All command terms highlighted, tables and diagrams well presented. Self Sources cited using the CSE (ISO 690 numerical) method, with Works Cited section complete and correct. All answers for the following command terms Most answers for the following command terms correct: correct: Define Draw Label List Measure State Most answers for the following command terms All answers for the following command terms correct: correct: Annotate Apply Calculate Describe Distinguish Estimate Identify Outline Most answers for the following command terms All answers for the following command terms correct: correct: Analyse Comment Compare Construct Deduce Derive Design Determine Discuss Evaluate Explain Predict Show Solve Sketch Suggest Answers are presented in a logical and concise manner. SI units used most times, with correct NA unit symbols and definitions of terms. All mathematical working shown. Evidence is apparent of research and reading beyond the textbook and presentations to find correct answers to challenging questions. If any NA questions are unanswered, this criterion scores zero. NA Total (max 10): Stephen Taylor Bandung International School http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com MrT