Appendix Table 1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of
advertisement
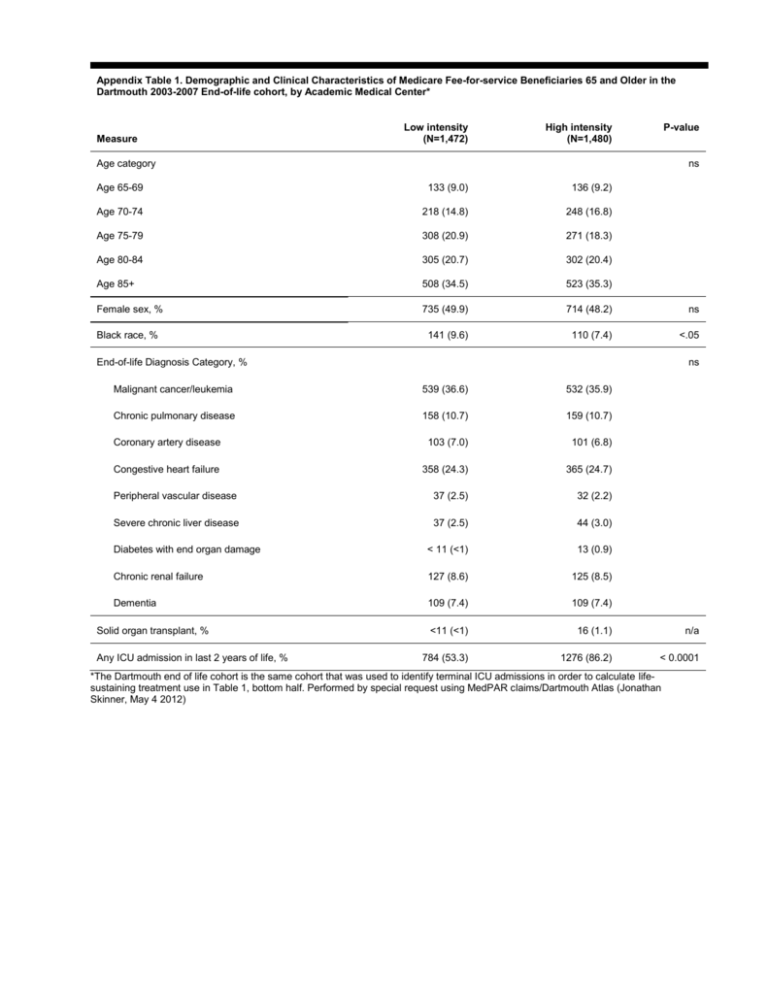
Appendix Table 1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Medicare Fee-for-service Beneficiaries 65 and Older in the Dartmouth 2003-2007 End-of-life cohort, by Academic Medical Center* Measure Low intensity (N=1,472) High intensity (N=1,480) P-value Age category ns Age 65-69 133 (9.0) 136 (9.2) Age 70-74 218 (14.8) 248 (16.8) Age 75-79 308 (20.9) 271 (18.3) Age 80-84 305 (20.7) 302 (20.4) Age 85+ 508 (34.5) 523 (35.3) Female sex, % 735 (49.9) 714 (48.2) ns Black race, % 141 (9.6) 110 (7.4) <.05 End-of-life Diagnosis Category, % ns Malignant cancer/leukemia 539 (36.6) 532 (35.9) Chronic pulmonary disease 158 (10.7) 159 (10.7) Coronary artery disease 103 (7.0) 101 (6.8) Congestive heart failure 358 (24.3) 365 (24.7) Peripheral vascular disease 37 (2.5) 32 (2.2) Severe chronic liver disease 37 (2.5) 44 (3.0) Diabetes with end organ damage < 11 (<1) 13 (0.9) Chronic renal failure 127 (8.6) 125 (8.5) Dementia 109 (7.4) 109 (7.4) <11 (<1) 16 (1.1) n/a 784 (53.3) 1276 (86.2) < 0.0001 Solid organ transplant, % Any ICU admission in last 2 years of life, % *The Dartmouth end of life cohort is the same cohort that was used to identify terminal ICU admissions in order to calculate lifesustaining treatment use in Table 1, bottom half. Performed by special request using MedPAR claims/Dartmouth Atlas (Jonathan Skinner, May 4 2012) Appendix Table 2. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Medicare Fee-for-service Beneficiaries 65 and Older in the Dartmouth 2003-2007 End-of-life Cohort with >1 ICU Admission in the Last 2 Years of Life, by Academic Medical Center* Measure Low intensity (N=784) High intensity (N=1,276) Age category P-value <0.05 Age 65-69 81 (10.3) 118 (9.3) Age 70-74 129 (16.5) 203 (15.9) Age 75-79 183 (23.3) 230 (18.0) Age 80-84 153 (19.5) 265 (20.8) Age 85+ 238 (30.4) 460 (36.1) Female sex, % 379 (48.3) 609 (47.7) ns 77 (9.8) 99 (7.8) <0.05 Black race, % End-of-life Diagnosis Category, % <0.05 Malignant cancer/leukemia 240 (30.6) 405 (31.6) Chronic pulmonary disease 93 (11.9) 144 (11.3) Coronary artery disease 53 (6.8) 91 (7.1) Congestive heart failure 224 (28.6) 355 (27.8) Peripheral vascular disease 23 (2.9) 28 (2.2) Severe chronic liver disease 20 (2.6) 38 (3.0) Diabetes with end organ damage < 11 (<1) 12 (0.9) Chronic renal failure 91 (11.6) 118 (9.3) 37 (4.7) 85 (6.7) <11 (<1) 16 (1.1) Dementia Solid organ transplant, % *The Dartmouth end of life cohort is the same cohort that was used to identify terminal ICU admissions in order to calculate lifesustaining treatment use in Table 1, bottom half. Performed by special request using MedPAR claims/Dartmouth Atlas (Jonathan Skinner, May 4 2012) n/a