Natural Disasters
advertisement

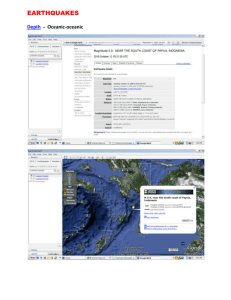
Sam Goold E-portfolio assignment Natural Disasters Tracking Earthquakes using Google Earth Oceanic Continental – When an oceanic plate pushes into and subducts under a continental plate, the overriding continental plate is lifted up and a mountain range is created. Magnitude 5.0 Location - near the coast of Ecuador Date: Tuesday, January 10, 2012 18:07:11 UTC Tuesday, January 10, 2012 01:07:11 PM at epicenter Depth: 27.90 km (17.34 mi) Magnitude 4.4 Location - near the west coast of Honshu, Japan Date: Tuesday, January 10, 2012 13:15:53 UTC Tuesday, January 10, 2012 10:15:53 PM at epicenter Depth: 35.00 km (21.75 mi) Continental Continental- When two continents meet head-on, neither is subducted because the continental rocks are relatively light and, like two colliding icebergs, resist downward motion. Instead, the crust tends to buckle and be pushed upward or sideways. Magnitude 5.0 Location - northern Xinjiang, China Date: Sunday, January 8, 2012 06:20:08 UTC Sunday, January 8, 2012 02:20:08 PM at epicenter Depth: 23.00 km (14.29 mi) Oceanic-Oceanic – two oceanic plates converge one is usually subducted under the other and in the process a deep oceanic trench is formed. Magnitude - 5.2 Location - Vanuatu region Date:Tuesday, January 10, 2012 01:45:39 UTC Tuesday, January 10, 2012 12:45:39 PM at epicenter Depth: 15.50 km (9.63 mi) Divergent - At divergent boundaries new crust is created as two or more plates pull away from each other. Magnitude – 7.2 Location – off the west coast of northern Sumatra Date: Tuesday, January 10, 2012 18:36:59 UTC Wednesday, January 11, 2012 12:36:59 AM at epicenter Depth: 20.50 km (12.74 mi) Transform – They offset active spreading ridges, producing zig-zag plate margins, and are generally defined by shallow earthquakes. Magnitude – 4.1 Location – Gulf of California Date: Friday, January 6, 2012 17:11:11 UTC Friday, January 6, 2012 10:11:11 AM at epicenter Depth: 12.10 km (7.52 mi) Tracking Volcanoes Using Google Earth Composite Volcano- Some of the Earth's grandest mountains are composite volcanoes. They are typically steep-sided, symmetrical cones of large dimension built of alternating layers of lava flows, volcanic ash, cinders, blocks, and bombs and may rise as much as 8,000 feet above their bases. Mt. St. Helens Tectonic Plate- Continental Cinder Volcano- Cinder cones are the simplest type of volcano. They are built from particles and blobs of congealed lava ejected from a single vent. Paricutin, Michoacan, Mexico Tectonic Plate- Oceanic-Continental Shield Volcano- built almost entirely of fluid lava flows, flow after flow pours out in all directions from a central summit vent, or group of vents, building a broad, gently sloping cone of flat, domical shape, with a profile much like that of a warrior's shield. They are built up slowly by the accretion of thousands of highly fluid lava flows called basalt lava that spread widely over great distances, and then cool as thin, gently dipping sheets. Kilauea, Hawaii Tectonic Plate – Hot Spot Caldera- Bulbous masses of lava too viscous to flow any great distance; consequently, on extrusion, the lava piles over and around its vent. A dome grows largely by expansion from within. As it grows its outer surface cools and hardens, then shatters, spilling loose fragments down its sides. Lassen Peak, California Tectonic Plate – Transform (San Andreas) 1. Describe the correlation between earthquakes and volcanoes in terms of the Theory of Plates Tectonics. In the article, Unanswered Questions they discuss that both volcanoes and earthquakes need internal heat to function and it is the escape of this heat from volcanoes that fuels plate tectonics. These plates are in constant motion. When they connect, volcanoes and earthquakes form. 2. Analyze the spatial relationship and distribution that exists with these forces of nature. Everything is located on a fault line or where two plate tectonics are colliding. Where there is pressure being pushed against one another, either an earthquake is bound to occur or, a volcano will soon start to emerge. In the Ring of Fire, the earth most active hot spot for earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, there is two plates being pushed together and has started forming a ring of volcanic outlets. Hawaii for instance did not exist years ago, but now it continues to grow each and every year because it is being pushed upward. The earth is constantly changing and we all need to be prepared and aware of what can and will occur. 3. Describe what you learned about earthquakes and volcanoes that you didn’t already know. I learned a lot of plate tectonics; the how and why volcanoes and earthquakes work. I learned of the different types of earthquakes and volcanoes and how they are differ from each other. I learned of the different lava flows. I learned the different magnitudes of the earthquakes and what changes it from a disaster to a catastrophe. 4. How has this shaped your worldview about natural disasters now that you have a strong scientific understanding of the concept? This has made me be a lot more aware of natural disasters and everything that could come with them. I used to think that as long as I was living in Utah with the mountains, I would be fine. But then I found out about the floods, landslides and avalanches that have happened here. It just really opens my eyes to the world and everything that has happened that I hadn’t thought twice about until after this class. It gives me a better understanding of my surroundings and everything that could potentially go wrong. It helped me know how to react in those situations if I was ever in them, and it has also given me the knowledge to lend a hand to those in need that have recently been affected by a disaster. Works Cited Google Earth http://www.platetectonics.com/book