Ecology Vocabualry Review without answers
advertisement

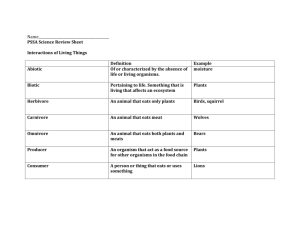
Name: ________________________ Date:_______________ Group:_____________ Organized Ecology Vocabulary Directions: Use your textbook and notes to mach each word to its correct definition. The words above each box are the ones used for that box. Each word is used only once! Levels of Organization Organism Population Community 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Ecosystem Biome Biosphere ______________________ The highest level of environmental organization. It extends from pole to pole and from the top of the atmosphere to below the ocean floor. ______________________ All the members of one species in a particular place ______________________ A living thing ______________________ All of the different populations that live together in an area ______________________ The community of organisms that live in an area, along with their nonliving surroundings ______________________ A group of land ecosystems with similar climates and organisms Use the following terms in the chart below. Arrange them from the smallest (lowest) to the largest (highest) level of organization. Populations Biosphere (Ecosphere) Organisms Biomes Ecosystems Communities Levels of Organization Biomes Organisms Types of ecosystems found all over the world Estuary Freshwater 1. 2. 3. 4. ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ Marine Wetlands Ponds, lakes and rivers. Ocean and saltwater environments. Land that is covered by water at least part of the year (Example: a swamp). A habitat in which the freshwater of a river meets the saltwater of the ocean. Living Things and the Environment Ecology Abiotic Factor Biotic Factor Limiting Factor Habitat 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Niche Exotic Species Succession Primary succession Secondary succession ______________________ A species that is not native to an area – has been brought in from a distant place. ______________________ A living part of an organism’s environment. ______________________ The role an organism has in its environment. ______________________ Type of succession that begins on soil after the destruction of an existing ecosystem. ______________________ The specific environment that provides the things an organism needs. ______________________ An environmental factor that prevents a population from increasing. ______________________ The study of how organisms interact with their environment. ______________________ Type of succession that begins with pioneer species growing on rock. ______________________ The series of predictable changes that occur in a community over time. ______________________ A non-living part of an organisms habitat. Populations Birth Rate Death Rate Population Density Carrying Capacity Competition Immigration Emigration 1. ______________________ Movement of individuals out of a population. 2. ______________________ The struggle between organisms to survive as they attempt to use the same limited resources. 3. ______________________ The number of births in a population in a certain amount of time. 4. ______________________ The number of individuals in an area of a specific size. 5. ______________________ The largest population that an area can support. 6. ______________________ The number of deaths in a population in a certain amount of time. 7. ______________________ Movement of individuals into a population. Energy Flow Food Chain Energy Pyramid Food Web Producer Decomposer Consumer Herbivore Carnivore Omnivore Scavenger 1. ______________________ An organism that obtains food by feeding on other organisms. 2. ______________________ An organism that can make its own food. 3. ______________________ An organism that breaks down other organisms and returns nutrients to the soil. 4. ______________________ The pattern of overlapping food chains in an ecosystem. 5. ______________________ A consumer that eats only animals. 6. ______________________ A consumer that eats plants and animals. 7. ______________________ A consumer that feeds on the bodies of dead animals. 8. ______________________ A diagram that shows the amount of energy (calories) that move from one feeding level to the next. 9. ______________________ A series of events in which one organism eats another and obtains energy. 10. ______________________ A consumer that eats only plants. Biomes from the Equator to the North Pole (from hot to cold climates) Desert Tropical Rain Forest Canopy Understory Grassland Biomes Savanna Temperate Deciduous Forest Deciduous Tree Tiaga Coniferous Tree Tundra Permafrost 1. ______________________ Soil that is frozen all year. 2. ______________________ An area that receives less than 25 cm of rain a year, is hot and has nutrient poor soil. 3. ______________________ Cold, dry biome, very short summers and only low growing vegetation. 4. ______________________ A forest with trees that lose their leaves. Georgia’s biome. 5. ______________________ A flat leaf tree that sheds its leaved every year. 6. ______________________ A leafy roof formed by tall trees. 7. ______________________ A grassland close to the equator. 8. ______________________ An area populated by grasses and grazing animals. 9. ______________________ A layer of shorter plants that grow in a rain forest. 10. ______________________ Coniferous trees, very cold winters and short summers. 11. ______________________ A tree that has cones and needle-shaped leaves. 12. ______________________ Rains every day. Diverse organisms. Has distinct Layers.