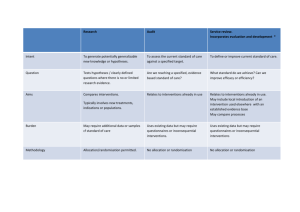
Table 1. Characteristics of the interventions CDPM practitioner
advertisement

Table 1. Characteristics of the interventions CDPM practitioner Theoretical training on: - Motivational interviewing training - Function of the respiratory system - Function of the cardiovascular system - Diabetes - Risk factors - Existing CDPM services Practical training: Three-week mentoring in specialized CDPM services facilities. Preliminary clinical The clinical evaluation of participants includes: evaluation Anthropometric characteristics Medical history Medication Functions (respiratory, cardiovascular, endocrine, gastro-intestinal) Lifestyle habits and risk factors Patient’s preoccupations and objectives Previous interventions (nutrition, physical activity, respiratory, smoking cessation), Recent changes (weight, alcohol consumption) Disciplines involved in The interventions, based on a referral from a family physician or nurse, are the intervention provided by professionals in the following disciplines: Clinical coordination Nursing Physical activity therapy Nutrition Respiratory therapy Smoking cessation therapy Implemented The interventions implemented are: interventions Self-management support Education on diseases (diabetes, COPD, asthma, cardiovascular) Education on risk factors (pre-diabetes, high blood pressure, dyslipidemias, obesity, physical inactivity, smoking) Counseling on medication Motivational interviewing Education about nutrition Education about physical activity Counseling on smoking cessation Tools and support Each intervention is supported by print and other material to ensure that patient material engagement is maintained even between the interventions. These include documents on: Chronic disease management Asthma, COPD Diabetes Cardiovascular Metabolic syndrome Hypo/hypertension Tools for smoking cessation Stress management Blood pressure monitoring journal Personal objectives journal Physical activity journal Communication & The CDPM practitioners in our study work within primary care settings which coordination enhances communication with primary care physicians, nurses and staff. The clinical coordinator ensures optimal communication and transition of care between the project team, the primary care professionals and specialized services. Special attention is given to the distinction of tasks fulfilled by project CDPM practitioners and tasks fulfilled by primary care nurses. Integration Prior to the implementation of interventions, a pre-implementation evaluation is conducted to identify the needs for CDPM services and the contextual factors of the participating PC clinics in the follow-up of CD patients. The preimplementation evaluation of the project promotes the sharing of a common positive vision of an intervention that focuses on prevention, earlier support for patients in the course of their disease, interprofessional collaboration, services integration, motivational interviewing and self-management support. Participating primary Participating primary care professional include: care professionals Family physicians (63) Nurses (5) Participating primary care settings: Four (4) clinics Four (4) family medicine groups Participating Participating specialists include: specialists Cardiologists Internal medicine specialists Endocrinologists Pneumologists