Genetics Test Check CLASS COPY. CLASS COPY. CLASS COPY
advertisement

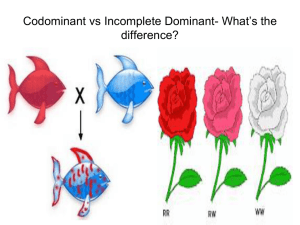
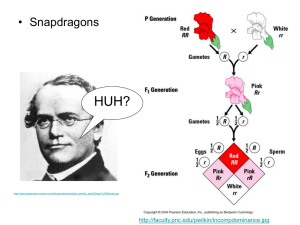
Genetics Test Check CLASS COPY. CLASS COPY. CLASS COPY. CLASS COPY. Note: STUDY ALL MATERIALSSSS! DO NOT JUST RELY ON THIS! MATCHING: Match the correct letter with each response. You will not use all answers. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Codominance Polygenic Incomplete dominance Sex-linked Simple(dominant controlled) a. There are only 2 phenotypes: dominant and recessive b. There are 3 phenotypes; the heterozygous is a blend of both. c. The trait is found either on the x or the y chromosome. d. There is more than 1 gene that controls a single trait. e. There are several traits controlled by only one gene. f. There are 3 phenotypes; the heterozygous shows each parent phenotype separately or a pattern. MULTIPLE CHOICE: Carefully read each prompt and then choose the BEST answer. Use the following to answer #6 and 7. Hemophiliacs have blood that does not coagulate well, and they often die at a young age. The disease allele is recessive and X-linked. 6. What type of inheritance is this? a. Simple dominance b. Incomplete c. Codominance d. Sex-linked e. None of the above 7. A hemophiliac male(affected) and a female who is a carrier for the disease(She does not have the disease but can pass it down) mate. Make a Punnett square. Which of the following is true based on your Punnett square? a. 100% of children can be hemophiliac(affected). b. 100% of females can be hemophiliac(affected). c. 100% of males would be hemophiliac(affected). d. Half of the females and half of the males could be hemophiliac(affected). e. 100% of children will be normal(unaffected). Use the following for #8 and 9: In dogs, D=pointed ears and d=round ears. A dog that is homozygous dominant for pointed ears breeds with a female dog that has round ears. 8. What type of inheritance is this? a. Simple dominance b. Incomplete c. Codominance d. Sex-linked e. None of the above 9. What are the chances of having a puppy with pointed ears? a. 0% b. 25% c. 50% d. 75% e. 100% Use the following for #10 and 11. In a certain animal, B=blue allele and Y=yellow allele. The heterozygous phenotype is green. 10. What type of inheritance is this? a. Simple dominance b. Incomplete c. Codominance d. Sex-linked e. None of the above 11. A blue and a green parent mate. What are the chances they will have a yellow baby? a. 0% b. 25% c. 50% d. 75% e. 100% Use the following for #12 and 13. In a certain animal, B=black and W=white. The heterozygous phenotype is black and white spots. 12. What type of inheritance is this? a. Simple dominance b. Incomplete c. Codominance d. Sex-linked e. None of the above 13. A spotted animal mates with another spotted animal. What are the chances of getting black offspring? a. 0% b. 25% c. 50% d. 75% e. 100% Use the following for #14 and 15. In dogs, D=pointed ears and d=round ears AND L=large paws and l=small paws. Assume that we are looking at the chance of having BOTH traits. 14. A heterozygous pointed ear/heterozygous large paw male mates with a homozygous pointed ear/homozygous small paw female. What is the female’s genotype? a. DdLl b. DDLL c. DDll d. ddll e. ddLL 15. Using the dihybrid cross method for both traits, make your Punnett square(s). What are they chances of having a pointed ear/small paw puppy? a. 2/16 b. 6/16 c. 8/16 d. 12/16 e. 16/16 Use the following for #16-18. A male that has blood type O mates with a female that has blood type A. 16. Type O is ___________ to type A. a. Dominant b. Incompletely dominant c. Codominant d. Recessive e. None of the above 17. Type A is _________ to type B. a. Dominant b. Incompletely dominant c. Codominant d. Recessive e. None of the above 18. The male and female mate and they have a type A child. What is the mother’s genotype that would ensure that the child is type A? a. b. c. d. e. IAIB IAIA A I Ai ii Genetics Test Check KEY Note: STUDY ALL MATERIALSSSS! DO NOT JUST RELY ON THIS! MATCHING: Match the correct letter with each response. You will not use all answers. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. F Codominance a. There are only 2 phenotypes: dominant and recessive D Polygenic b. There are 3 phenotypes; the heterozygous is a blend of both. B Incomplete dominance c. The trait is found either on the x or the y chromosome. C Sex-linked d. There is more than 1 gene that controls a single trait. A Simple(dominant controlled)e. There are several traits controlled by only one gene. f. There are 3 phenotypes; the heterozygous shows each parent phenotype separately or a pattern. MULTIPLE CHOICE: Carefully read each prompt and then choose the BEST answer. Use the following to answer #6 and 7. Hemophiliacs have blood that does not coagulate well, and they often die at a young age. The disease allele is recessive and X-linked. 6. D What type of inheritance is this? a. Simple dominance b. Incomplete c. Codominance d. Sex-linked e. None of the above 7. D A hemophiliac male(affected) and a female who is a carrier for the disease(She does not have the disease but can pass it down) mate. Make a Punnett square. Which of the following is true based on your Punnett square? a. 100% of children can be hemophiliac(affected). b. 100% of females can be hemophiliac(affected). c. 100% of males would be hemophiliac(affected). d. Half of the females and half of the males could be hemophiliac(affected). e. 100% of children will be normal(unaffected). Use the following for #8 and 9: In dogs, D=pointed ears and d=round ears. A dog that is homozygous dominant for pointed ears breeds with a female dog that has round ears. 8. A What type of inheritance is this? a. Simple dominance b. Incomplete c. Codominance d. Sex-linked e. None of the above 9. E What are the chances of having a puppy with pointed ears? a. 0% b. 25% c. 50% d. 75% e. 100% Use the following for #10 and 11. In a certain animal, B=blue allele and Y=yellow allele. The heterozygous phenotype is green. 10. B What type of inheritance is this? a. Simple dominance b. Incomplete c. Codominance d. Sex-linked e. None of the above 11. A A blue and a green parent mate. What are the chances they will have a yellow baby? B Y a. 0% BY b. 25% c. 50% BY d. 75% e. 100% Use the following for #12 and 13. In a certain animal, B=black and W=white. The heterozygous phenotype is black and white spots. 12. C What type of inheritance is this? a. Simple dominance b. Incomplete c. Codominance d. Sex-linked e. None of the above 13. B A spotted animal mates with another spotted animal. What are the chances of getting black offspring? a. 0% b. 25% c. 50% d. 75% e. 100% Use the following for #14 and 15. In dogs, D=pointed ears and d=round ears AND L=large paws and l=small paws. Assume that we are looking at the chance of having BOTH traits. 14. C A heterozygous pointed ear/heterozygous large paw male mates with a homozygous pointed ear/homozygous small paw female. What is the female’s genotype? a. DdLl Ear D d b. DDLL D DD Dd c. DDll D DD Dd d. ddll e. ddLL 15. C Using the dihybrid cross method for both traits, make your Punnett square(s). What are they chances of having a pointed ear/small paw puppy? (4/4 pointed x 2/4 small =8/16) a. 2/16 Paw L l l Ll ll b. 6/16 c. 8/16 l Ll ll d. 12/16 e. 16/16 Use the following for #16-18. A male that has blood type O mates with a female that has blood type A. 16. D Type O is ___________ to type A. a. Dominant b. Incompletely dominant c. Codominant d. Recessive e. None of the above 17. C Type A is _________ to type B. a. Dominant b. Incompletely dominant c. Codominant d. Recessive e. None of the above 18. B The male and female mate and they have a type A child. What is the mother’s genotype that would ensure the offspring was type A? a. b. c. d. e. IAIB IAIA(Mom has to have 2 A alleles to pass down to the child. If the mom was AO, the child could get the O and be OO(ii). ) A I Ai ii