college algebra handouts
advertisement
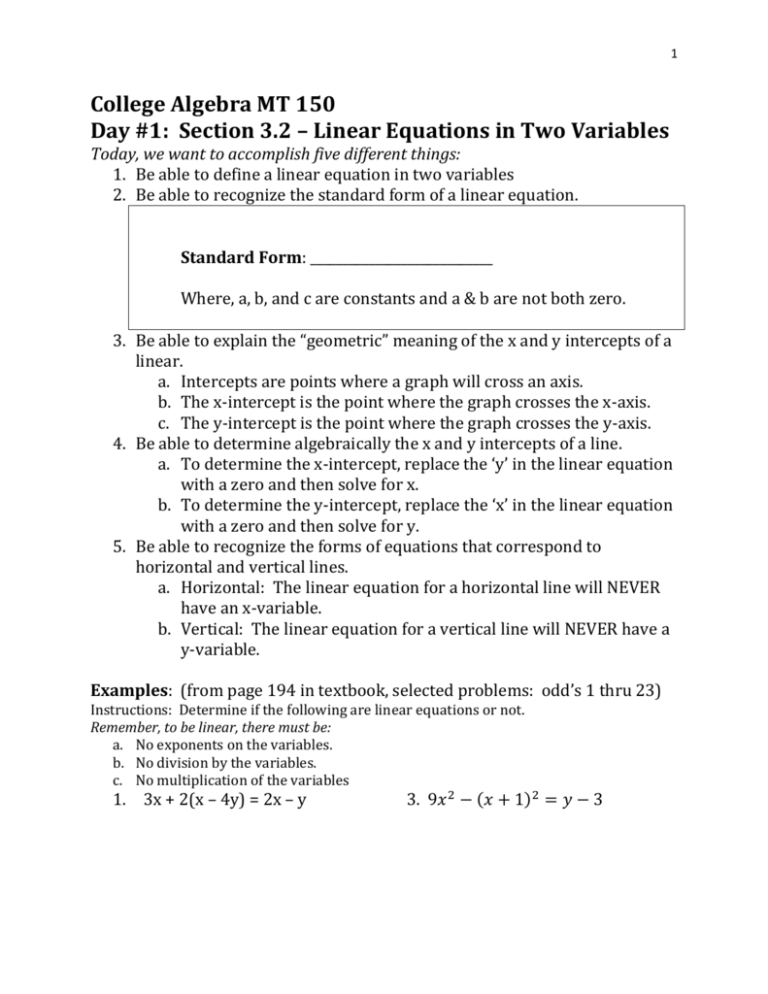
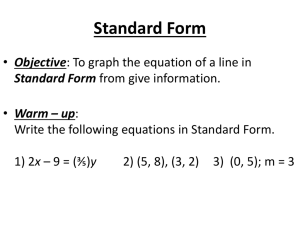
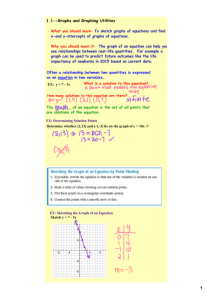
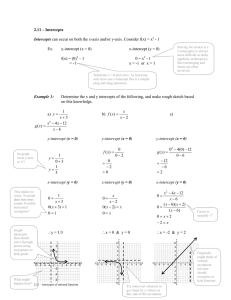
1 College Algebra MT 150 Day #1: Section 3.2 – Linear Equations in Two Variables Today, we want to accomplish five different things: 1. Be able to define a linear equation in two variables 2. Be able to recognize the standard form of a linear equation. Standard Form: ____________________________ Where, a, b, and c are constants and a & b are not both zero. 3. Be able to explain the “geometric” meaning of the x and y intercepts of a linear. a. Intercepts are points where a graph will cross an axis. b. The x-intercept is the point where the graph crosses the x-axis. c. The y-intercept is the point where the graph crosses the y-axis. 4. Be able to determine algebraically the x and y intercepts of a line. a. To determine the x-intercept, replace the ‘y’ in the linear equation with a zero and then solve for x. b. To determine the y-intercept, replace the ‘x’ in the linear equation with a zero and then solve for y. 5. Be able to recognize the forms of equations that correspond to horizontal and vertical lines. a. Horizontal: The linear equation for a horizontal line will NEVER have an x-variable. b. Vertical: The linear equation for a vertical line will NEVER have a y-variable. Examples: (from page 194 in textbook, selected problems: odd’s 1 thru 23) Instructions: Determine if the following are linear equations or not. Remember, to be linear, there must be: a. No exponents on the variables. b. No division by the variables. c. No multiplication of the variables 1. 3x + 2(x – 4y) = 2x – y 3. 9𝑥 2 − (𝑥 + 1)2 = 𝑦 − 3 2 6 5 5. 8 – 4xy = x – 2y 7. 9. 2y – (x + y) = y + 2 11. 𝑥 2 − (𝑥 − 1)2 = 𝑦 13. x(y + 1) = 16 – y( 1 – x) 19. x – 1 = 18. 𝑦 2 − 3𝑦 = (1 + 𝑦)2 − 2𝑥 20. 3x – 4 = 89(x – y) – y Determine the x and y intercepts. 25. 4x – 3y = 12 29. 3y = 9 (graph result) 𝑥 − =2 𝑦 2𝑦 𝑥 −𝑥 27. 5 – y = 10x 39. 3(x + y) + 1 = x – 5 (graph result) 3 Homework assignment (please complete on a separate sheet of paper): Textbook: p. 194 (2-24 even) Instructions: Determine if the following are linear equations or not. 2. 9x + 4(y – x) = 3 4. 3x + xy = 2y 6. 𝑥−𝑦 2 + 7𝑦 3 =5 10. (3 − 𝑦)2 − 𝑦 2 = 𝑥 + 2 14. 𝑥−3 2 = 4+𝑦 5 8. 3x – 3(x – 2y) = y + 1 12. (𝑥 + 𝑦)2 − (𝑥 − 𝑦)2 = 1 16. x – 3 = 4𝑥 + 17 5 18. 𝑦 2 − 3𝑦 = (1 + 𝑦)2 − 2𝑥 20. 3x – 4 = 89(x – y) – y 22. 𝑥 2 − 2𝑥 = 3 − 𝑥 2 + 𝑦 24. 16x = y(4 + (x – 3)) – xy Textbook: p. 195 (30-38 even) Instructions: Determine the x and y intercepts. 30. 2x – (x + y) = x + 1 32. y – x = x – y (graph this problem) 34. 2x – 3 = 1 – 4y (graph this problem) 36. 4 – 2y = -2 – 6x 38. 3y + x = 2x + 3y + 4