SYLLABUS
advertisement

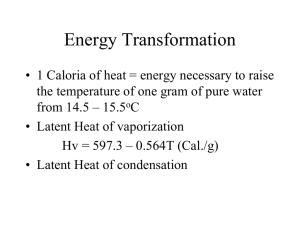
GEOL 3400 Water Resources INSTRUCTOR: Kelly Bringhurst OFFICE: Sc 206 Phone: 652-7768 Credits: 3 Email: kbringhurst@dixie.edu COURSE OBJECTIVES: Students will be expected to acquire a basic understanding of: 1. The hydrological cylce: where does the water come and where does it go? 2. The use of simple probability and statistics to describe geohydrologic phenomena. 3. The process of interception, evaporation and transpiration, whereby water is transferred from geosphere to atmosphere. The generation of runoff, factors controlling storage and transfer of water within the channels. 4. Flow through porous media and treatment of saturated flow with Darcy's law. 5. Well hydraulics, estimation of hydraulic conductivity from slug test. 6. Principles governing the flow in a unsaturated condition. 7. Contaminant migration in underground aquifer. 8. Water quality issues. REQUIRED TEXT: Fetter, 2003: Applied Hydrogeology, Prentice Hall. EXAMINATIONS: Three examinations will be given during this course. Information will be given in class regarding these. ASSIGNMENTS: There will be several assignments given during the semester. Some of these will be in class assignments that cannot be made up. Working together to help fellow students understand the material is encouraged, however each student is required to do their own work on the assignments. Assignments will not be accepted if it is found that the students have copied someone else’s work. CLASSROOM BEHAVIOR: Disrespect of others isn’t tolerated, this course is a learning environment. Please remember to respect other people. ATTENDANCE Daily attendance is expected. Class will begin promptly at the designated time. If you are unable to attend class for any reason, it is up to you to obtain the content of the lecture and any assignments from fellow students. Dixie College Policy explains in detail what needs to happen if you anticipate being absent from class because of a college-sponsored activity (athletic events, club activities, field trips for other classes, etc). Please read this information and follow the instructions carefully! GRADING: Grades will be based on the ratio of the number of points earned to the number of points possible. Percentage Letter Grade 100 - 94 A 93-90 A89 -87 B+ 86 -83 B 82-80 B79 -77 C+ 76 -73 C 72-70 C69 -67 D+ 66-63 D 62-60 Dbelow 60 F IMPORTANT LINKS: Reasonable Accommodation contact Disability Resource Center - dixie.edu/drcenter Testing Center location and hours- dixie.edu/testing Struggling? Contact the Tutoring Center - dixie.edu/tutoring Missing class for college activities, read Policy for Absences Related to College Functions Library, a good place to study, read and research - library.dixie.edu You not right good? Writing Center - dixie.edu/english/dsc_writing_center.php The classroom is a learning environment for everyone - Disruptive behavior policy Tempted to cheat? Copy this Academic dishonesty / Academic integrity policy Keep up on your Dmail account visit go.dixie.edu/dmail Outdoor Recreation and Adventure Center - http://www.dixie.edu/odr/index.php Course Topics: Chapter 1. Introduction Delineation of watershed, hydrological cycle, water as a resource, water supply. Chapter 2. Atmospheric aspects of hydrological cycle Weather and climate, humidity, latent heat of condensation, fusion and sublimation, and evapotranspiration Chapter 3. Precipitation and runoff Cloud, formation of precipitation, rise of the air mass, temporal and spatial distribution of precipitation, method of measuring the precipitation amount and effective precipitation depth in a watershed. Chapter 4. Stream flow Runoff, infiltration, effluent and influence streams, runoff, baseflow separation , stream flow velocity profile hydrograph and routing (rating) curves, stream ordering and bifurcation ratio. Chapter 5. Flood analysis Flood frequency duration, recurrence interval, flood attenuation and translation, hydraulic jump, Reynolds number and its relationship to turbulent and laminar, steady and uniform flow. Exam 1 Chapter 6. Groundwater Basics 1).Primary and secondary porosity, specific yield, perched water table, aquifer types. Hydraulic head and potential. Homogeneous, heterogeneous aquifers, intrinsic permeability and hydraulic conductivity. 2). Darcy’s law, groundwater discharge (Q=Kdh/L*A), Validity of Darcy’s law 3). Storativity, specific storage (Ss) specific yield (Sy) and storativity (S) 4) Major aquifers Chapter 7. Principles of Groundwater-Flow 1). Flow nets and conductivity ellipse, tangent law, steady and transient flow 2). Dupuit assumption. Chapter 8 (14,15,-16,17 in the text). Well Hydraulics. Pumping test and Theis type curve analysis, Well drawdown, cone of depression in confined and unconfined aquifers, step-drawdown and its purpose, Jacob method, distance drawdown method of conductivity and storativity Exam 2 Chapter 9. Leakly confined aquifer and slug test 1). Leaky confined aquifer, well screen, partial penetrating well. 2).Rising and falling head slug test, conductivity estimate from slug tests. Chapter 10. Multiple wells. Multiple wells and superposition principles 2). Image wells for barrier boundaries Image wells for recharge boundaries Chapter 11. Groundwater modeling 1). Model types and popular modeling programs. Finite difference and finite elements 2). Boundary conditions Chapter 12. Unsaturated flow 1). Capillary rise, soil characterisitic curve, hysteresis 2). Infiltration rate and tests, perc tests Chapter 13. Mass transport of solutes 1). Advection, dispersion and diffusion concepts 2). Types of common contaminants: Organic and Inorganic 3). Remediation Chapter 14. Water Law 1). Common laws and Legislative laws 2). Riparian Doctrine and Prior appropriate doctrine 3). Water Regulations. Final Exam