Abstract
advertisement

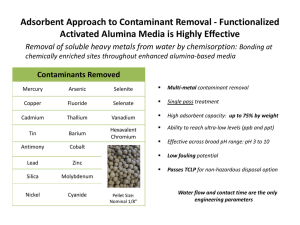
Third International Symposium On Environmental and Water Resources Engineering 2-3 June 2015, Tehran, Iran Decolorization of textile dyes mixture using heterogeneous Fenton process by nanostructured magnetite prepared with plasma َAlireza Khataee*, Salimeh Gohari * Research Laboratory of Advanced Water and Wastewater Treatment Processes, Department of Applied Chemistry, Faculty of Chemistry, University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran * a_khataee@tabrizu.ac.ir Abstract In this study, the degradation of mixture of three textile dyes (C.I. Basic Red 46 (BR46), Malachite Green (MG) and C.I. Basic Blue 3 (BB3)) was examined simultaneously through the heterogeneous Fenton process. The investigated catalyst was natural magnetite nanostructures (NMNs) prepared by modification of the natural magnetite microparticles by a novel glow discharge plasma (GDP) technology. A complete characterization such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Brunauer–Emmett– Teller (BET) analyses were performed to explain the physical and chemical properties of untreated- and GDP treated-magnetite particles. The multivariate curve resolution with alternating least squares (MCR-ALS) modeling was successfully utilized for multivariate calibration of the spectrophotometric data. In addition, by the use of this technique, the spectra and the concentration profiles of each dye were attained during the degradation process. A response surface methodology was utilized to investigate and model the influence of several factors on multiple responses such as BB3 removal (Y1), BR46 removal (Y2) and MG removal (Y3) in the simultaneous removal of these dyes. The results of the global desirability showed that 3.5 mg/L BR46, 3.5 mg/L MG, 3.5 mg/L BB3, 3 mmol/L H2O2 and a 90 min-reaction time were the optimum conditions. Key words: Fenton process; Glow discharge plasma; Magnetite nanostructures; Multi-response optimization; Multivariate curve resolution.