Classification
advertisement

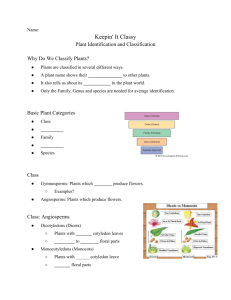
Name:_________________________________________________________________ Test Date:________________ Classification Test Study Guide ● Carolus Linnaeus is considered father of classification. He discovered a classification system called taxonomy. ● Classification – is the arrangement of organisms into orderly groups based on their similarities. 8 levels of classification in order: (from general to specific) domain → kingdom→ phylum → class → order → family → genus → species Daring King Phillip Crossed Over For Glittery Silver Domain- largest, most general group Species- most specific -contain one type of organism that can mate and produce fertile offspring “Order of Flow”: Domains can be broken into kingdoms, classes can be broken into orders There are three domains: 1. Bacteria- most types of bacteria (except those that live in extreme conditions) 2. Archaea- bacteria that live in extreme conditions 3. Eukarya- eukaryotic organisms There are six kingdoms: 1. Eubacteria- includes most types of bacteria (do not live in extreme conditions) 2. Archaebacteria- bacteria that live in extreme conditions, like in hot springs 3. Protista- single celled or simple multicellular organisms, some may have flagella (tail) 4. Fungi- obtain nutrients by absorbing them from their surroundings (molds, mushrooms) - Antibiotics, like Penicillin, are produced by using molds. 5. Plantae - includes all plants, perform photosynthesis 6. Animalia- move by themselves and have an advanced nervous system Examples: humans, corals, spiders, mice Scientific Names: ● The scientific name is written in Greek or Latin and is made up of a 2-part name consisting of genus (first) and species (second) names: Example: Homo sapiens- Human ↑ ↑ genus species Felis domesticus- house cat ↑ ↑ genus species ● When writing the scientific name the genus name should be capitalized and the species name lower case and the whole name should be underlined (if hand writing) or italicized (if typing). ● A specific organism may have many common names but only one scientific name. For example: trees in the genus Quercus are referred to commonly as “oaks,” but there are hundreds of trees in this genus. By just using the term “oak,” people avoid making a clear distinction, and this can be problematic. Canyon Oak (Quercus chrysolepis) Blue Oak (Quercus douglasii) California Black Oak, a Western U.S. tree species (Quercus kelloggii) Eastern Black Oak, an Eastern U.S. and Canadian tree species (Quercus velutina) Know How to Read a Dichotomous Key Dichotomous key-pairs of descriptive statements that help identify unknown organisms.