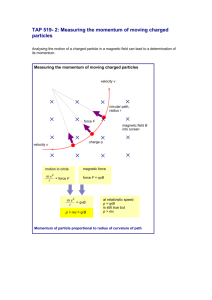
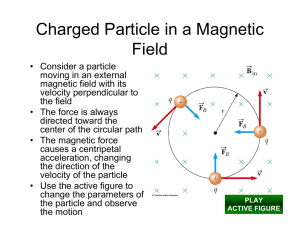
VOICE OVER FOR TLM for Project 5
advertisement
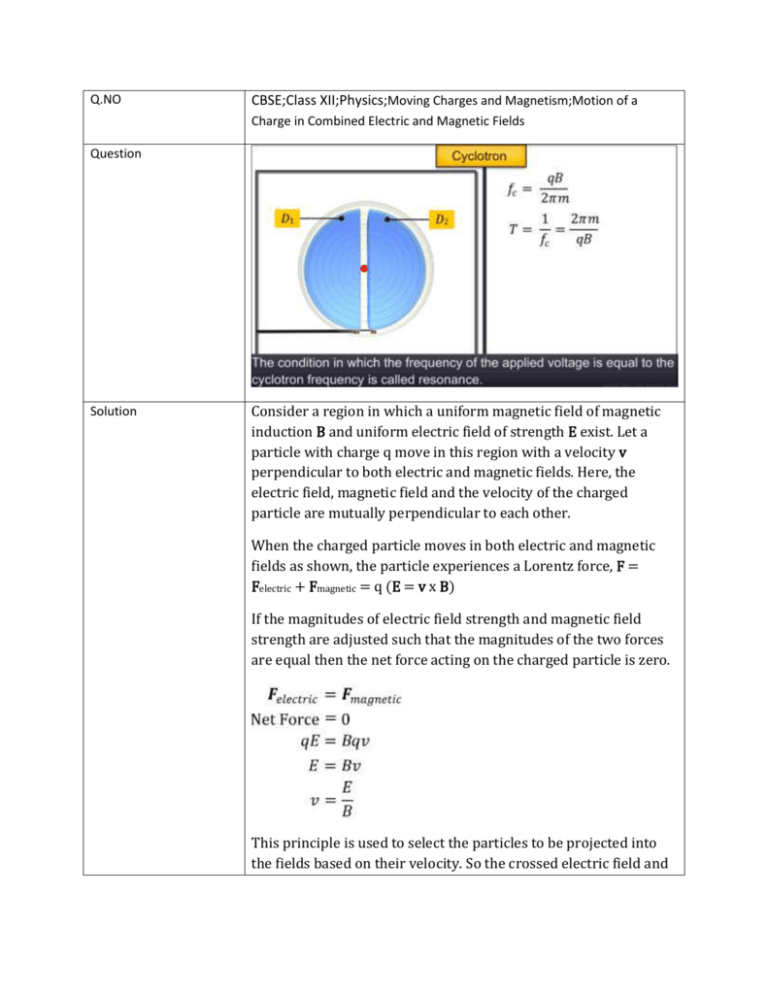
Q.NO CBSE;Class XII;Physics;Moving Charges and Magnetism;Motion of a Charge in Combined Electric and Magnetic Fields Question Solution Consider a region in which a uniform magnetic field of magnetic induction B and uniform electric field of strength E exist. Let a particle with charge q move in this region with a velocity v perpendicular to both electric and magnetic fields. Here, the electric field, magnetic field and the velocity of the charged particle are mutually perpendicular to each other. When the charged particle moves in both electric and magnetic fields as shown, the particle experiences a Lorentz force, F = Felectric + Fmagnetic = q (E = v x B) If the magnitudes of electric field strength and magnetic field strength are adjusted such that the magnitudes of the two forces are equal then the net force acting on the charged particle is zero. This principle is used to select the particles to be projected into the fields based on their velocity. So the crossed electric field and the magnetic fields are called velocity selectors. The particles, whose magnitude of velocity is equal to the ratio of E to B, pass through the combination of electric field and magnetic field without deviation and the remaining particles whose velocity is not equal to the ratio of E to B, deviate on either side of the electric field. This principle is used in the mass spectrometer and particle accelerators. The mass spectrometer is a device used to separate charged particles based on their charge to mass ratio. Particle accelerators are used to accelerate particles to very high energy. A cyclotron is a particle accelerator which accelerates a charged particle. It consists of two hollow, flat, semicircular metal disc-like containers called D1 and D2. These two Ds are separated by a narrow, parallel gap. These two Ds are connected to a highfrequency oscillator which produces an alternating voltage. This alternating voltage establishes an alternating electric field between the two Ds once from D1 to D2 and then from D2 to D1. This electric field between the Ds accelerates the charged particle when it passes through the gap between the Ds. When a charged particle enters a D, it moves in a circular path with constant speed because inside the D, it is influenced only by the magnetic field. Inside the D, the electric field is zero due to the shielding effect. The cyclotron frequency is independent of the speed of the charged particle and radius of the circular path. Cyclotrons are used to bombard nuclei with energetic particles by accelerating them in Cyclotrons, and to study nuclear reactions.