Road Map - OCPS TeacherPress
advertisement
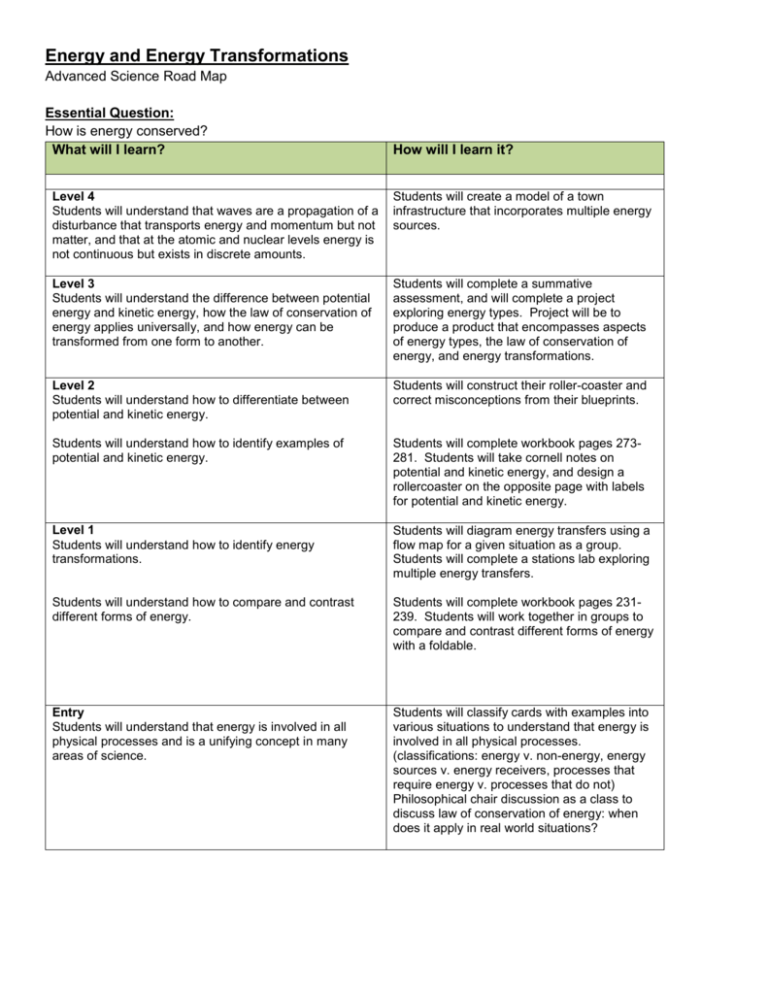
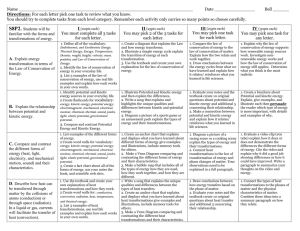
Energy and Energy Transformations Advanced Science Road Map Essential Question: How is energy conserved? What will I learn? How will I learn it? Level 4 Students will understand that waves are a propagation of a disturbance that transports energy and momentum but not matter, and that at the atomic and nuclear levels energy is not continuous but exists in discrete amounts. Students will create a model of a town infrastructure that incorporates multiple energy sources. Level 3 Students will understand the difference between potential energy and kinetic energy, how the law of conservation of energy applies universally, and how energy can be transformed from one form to another. Students will complete a summative assessment, and will complete a project exploring energy types. Project will be to produce a product that encompasses aspects of energy types, the law of conservation of energy, and energy transformations. Level 2 Students will understand how to differentiate between potential and kinetic energy. Students will construct their roller-coaster and correct misconceptions from their blueprints. Students will understand how to identify examples of potential and kinetic energy. Students will complete workbook pages 273281. Students will take cornell notes on potential and kinetic energy, and design a rollercoaster on the opposite page with labels for potential and kinetic energy. Level 1 Students will understand how to identify energy transformations. Students will diagram energy transfers using a flow map for a given situation as a group. Students will complete a stations lab exploring multiple energy transfers. Students will understand how to compare and contrast different forms of energy. Students will complete workbook pages 231239. Students will work together in groups to compare and contrast different forms of energy with a foldable. Entry Students will understand that energy is involved in all physical processes and is a unifying concept in many areas of science. Students will classify cards with examples into various situations to understand that energy is involved in all physical processes. (classifications: energy v. non-energy, energy sources v. energy receivers, processes that require energy v. processes that do not) Philosophical chair discussion as a class to discuss law of conservation of energy: when does it apply in real world situations? Standards: SC.6.P.11.1 Identify and differentiate between kinetic energy and potential energy. Describe and apply the law of conservation of energy to real world situations. SC.912.P.10.1 Energy is involved in all physical and chemical processes. It is conserved and can be transformed from one form to another and into work. Depth of Knowledge Questions: 1. How would you describe energy? 2. List several types of energy. 3. What is another way of describing potential energy? 4. What are two factors that determine and object’s potential energy? 5. What is another way of describing kinetic energy? 6. What are two objects that determine and object’s kinetic energy? 7. Define the law of conservation of matter. 8. What is efficiency? 9. Classify processes into types of energy. 10. How do you know that energy is being utilized? 11. What happens to energy when it is involved in a process? 12. Compare and contrast potential and kinetic energy. 13. How could you determine the efficiency of an appliance? Vocabulary: 1. energy 2. kinetic energy 3. potential energy 4. mechanical energy 5. law of conservation of energy 6. energy transformations 7. efficiency 8. chemical energy 9. electromagnetic energy 10. light energy 11. thermal energy 12. nuclear energy 13. sound energy 14. thermal energy