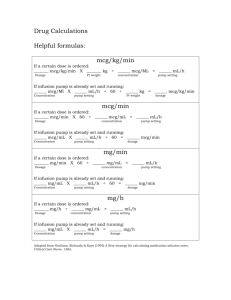
Donor Management Goal #2 - Organ Donation Alliance
advertisement

Gift of Life Michigan Donor Management Guidelines Donor Management Goal #1: Lung Recruitment Follow Pulmonary Management Guidelines (age 15 to 60): Attachment A including but not limited to: Medications o Narcan in conjunction with Norcuron o Norcuron prn for peak pressures >30 cm H2O o Albuterol and Atrovent via nebulizer or unit dose o Mucomyst nebulizer in conjunction with Albuterol for thick secretions o Solu-medrol Testing and Therapies o Chest x-ray o Bronchoscopy as soon as possible after brain death and consent o ABG’s baseline and on 100% q 4 hours o Bedside care including chest percussion therapy, turning, elevated HOB, etc (see Attachment A). o Ventilator Associated Pneumonia Protocol Donor Management Goal #2: Mean Arterial Pressure >60 Levothyroxine drip (T4) and Vasopressin per Hormonal Therapy Policy 5-09. Maintenance IV Fluid: Size/Age: Sodium Level: < 6 months ---<10 kg ---10-20 kg --->20 kg to age 15 ---15 and older <148 IV Fluid: IV should contain D10% D5/ 0.2 NS/ 20 mEq/L KCl D5/ 0.3 NS/ 20 mEq/L KCl D5/ 0.45 NS/ 20 mEq/KCl D5W/0.45 NS, NS, LR, (can add KCl as needed) 15 and older D5W, 0.45NS, (can add KCl as needed) >148 Hourly Maintenance Amounts: Adjust rate on a case by case basis based on fluid balance status Size: Calculation: <10 kg 100 mL/kg/24hours 10-20 kg (1000 mL + 50 mL/kg for each kg >10)/24 hours >20 kg (1500 mL + 20 mL/kg for each kg >20)/24 hours Adults (15 and 100 mL/hr adjusted to patient status and condition older) Page 1 2/6/2016 Hypovolemia: CVP < 6; PAWP <8 Bleeding/Coagulopathy: o Hematocrit < 30% or Hemoglobin <10 g/dL: Packed Red Blood Cells o PT >15 or INR > 1.5: Fresh Frozen Plasma o Platelets <100,000: Platelets o Fibrinogen <2.9 : Cryoprecipitate o Consult Medical Manager if diagnosed with Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) Consider ordering a functional HIT assay Avoid Heparin in management of donor Consider the use of Argatroban 15 minutes before crossclamp 350mcg/kg IV over 15 minutes Utilize routine cold flush of the allograft Age: PRBC’s FFP Platelets Cryo Pediatric 10-15 mL/kg 10-15mL/kg 10-20 mL/kg 5-10 mL/kg Adult 1-2 units 4 units 5 units 6 units Dehydration: o Adults: Fluid bolus o Pediatrics: 10-20 mL/kg NS or 5-10 mL/kg 0.2NS bolus 5% Albumin 5-10 mL/kg Diabetes Insipidus: urine output >4 mL/kg/hr o Manage electrolyte imbalances o Replace fluid loss as needed o Vasopressin or Desmopressin titrated to achieve u/o 1-3 mL/kg/hr A Creatinine Clearance is not required but may be requested by a transplant center: o Creatinine Clearance: volume of urine Urine Creatinine x min. of collection X 1.73 Serum Creatinine BSA Hypervolemia: CVP > 10; PAWP >12 Lasix, Bumex or Mannitol Consider decreasing hourly intake rate Donor Management Goal #3: Less than 2 Vasopressors Levothyroxine drip (T4) and Vasopressin per Hormonal Therapy Policy 5-09. Cardiac Algorithm: Attachment B: Attempt to wean vasopressors as able in the following order: 1. Neosynephrine 2. Epinephrine 3. Levophed 4. Dopamine Hypotension: MAP <60, CVP >6 Initiate T4 therapy Page 2 2/6/2016 If CVP <6: consider treatment for hypovolemia Add pressors in the following order: o Dopamine < 10 mcg/kg/min (consider tachycardia when starting) o Levophed o Neosynephrine Rule out causes of decreased preload, such as increased intra-thoracic pressure related to ventilator status. Consider pulmonary artery catheter to further assess hemodynamic status\ Hypertension: MAP >90, Wean vasopressors in the order listed above. CVP > 10: consider treatment for hypervolemia Assess for intolerance to T4 therapy (Policy 5-09) Rule-out temporary effects of brain stem herniation Hydralazine, Nitroprusside, or Nicardipine (avoid Beta-blockers if heart is being considered for transplant). Consider beta-blocker administration if heart has been ruled out. Arrhythmias: Correct Electrolytes Atrial fibrillation or flutter, SVT: o Diltiazem or cardioversion Lethal arrhythmias: o ACLS Protocol Low Ejection Fraction and/or Heart Failure: EF <45, CI < 2.2. See Cardiac Algorithm: Attachment B Consider effect ventilation settings has on cardiac output and preload. Consider use of Dopamine over other vasopressors Consider the use of Dobutamine or Primacor (Milrinone) Rule out coronary artery disease, cardiac contusion, myocardial stunning, etc. Donor Management Goal #4: pH 7.35-7.45 Baseline ABG and repeat every 4-6 hours Always treat pH, not CO2 Respiratory Acidosis/Alkalosis: Adjust minute ventilation (rate and or/volume) Metabolic Acidosis: o If Sodium is less than 140: Sodium Bicarbonate o If Sodium is greater than 140 and donor is making urine: Tromethamine (THAM) o If Sodium and Chloride are elevated and K is low or normal, consider using Potassium Acetate. Donor Management Goal #5: Final 100% FiO2 ABG= PO2 >300 or P/F ratio >3 Ventilator Settings: Volume Ventilation Page 3 2/6/2016 o Tidal Volume 10-12 mL/kg of Ideal Body Weight o Adjust rate for pH 7.35-7.45 o PEEP 5 cm H2O Pressure Ventilation o Consider if peak airway pressure is greater than 35 mm H2O o Adjust rate for pH 7.35-7.45 o PEEP 5 cm H2O Other setting changes to decrease peak pressure and minimize wasted ventilation: o Flow-decrease to 40-50 Liters/min o Inspiratory pause Pulmonary Edema, ARDS: Increase FiO2 and PEEP (maximum 10 cm H2O) Diuretics, avoid Colloids Consider proning Donor Management Goal #6: Sodium 135-155 Hypernatremia: Sodium >145 Change IV fluids (see maintenance IV fluid chart) Free water down NG o Adults: 200-400 mL every 4 hours o Pediatrics: 50-200 mL as tolerated Hyponatremia: Sodium <135 Change IV Fluids to 0.9%NS If <128, consider 3% NS (through central line) Hyperkalemia: Potassium > 4.5 Remove K from IV’s For pediatrics, consult with Medical Manager and/or Pediatric Intensivist. Consider use of following for adults to push K into cells: o D50 1 amp o Regular Insulin 15 units o Sodium Bicarbonate 1 amp o Calcium Gluconate 1 amp Consider Kaexylate down NG (consult with Medical Manager) If renal failure is present, consult with clinical resource and medical manager regarding dialysis. Page 4 2/6/2016 Hypokalemia: Potassium < 4.5 If K is consistently low, consider addition of KCl to primary IV fluid Be aware that Insulin and Albuterol push K into the cells Normal or High Low Phosphorus Metabolic Acidosis/ Phosphorus Hyperchloremia Pediatric KCl 0.5-1 mEq/kg KPhos 0.1-0.3 Kacetate 1-4 over 2 hours mmol/kg over 4-6 mEq/kg in 24 hours hours Adult KCl 20-60 mEq at 20 KPhos 10-15 mmol K actetate 40 mEq mEq an hour over 4-6 hours Hypocalcemia: Ionized Calcium < 1.13 Calcium Chloride or Calcium Gluconate Hypomagnesemia: < 2.0 Magnesium Sulfate Hyperglycemia: Blood Glucose >200 Maintain Blood Sugar between 70 and 200 Use Regular Insulin IV, monitor K Consider using donor hospital’s Critical Care Continuous Insulin Infusion Protocol (or see Insulin Continuous Infusion Guidelines below) Avoid D5W, if possible Check glucose as appropriate Insulin Continuous Infusion Guidelines: Initiate drip: Glucose 121-180 181-240 241-300 301-360 >360 Insulin 1-3 units/hr 2-3 units/hr 6 units IVP 8 units IVP 10 units IVP 4-5 units/hr 5-6 units/hr 6-8 units/hr Adjust According to Blood Glucose Levels every 1-2 hours Current Infusion: Current Infusion: Current Infusion: Glucose 1-5 units/hr 6-10 units/hr 11-16 units/hr 111-140 Increase by 0-1 Increase by 0-2 Increase by 0-3 unit/hr unit/hr unit/hr 141-180 Increase by 1-2 Increase by 1-3 Increase by 3-5 unit/hr unit/hr unit/hr 181-240 Increase by 1-2 Increase by 1-3 Increase by 4-6 unit/hr unit/hr unit/hr Page 5 2/6/2016 Current Infusion: >16 units/hr Call MM Call MM Call MM 240-300 301-360 >360 3 units IVP Increase by 2-3 unit/hr 4 units IVP Increase by 2-4 unit/hr 5 units IVP Increase by 2-4 unit/hr 5 units IVP Increase by 3-5 unit/hr 7 units IVP Increase by 3-5 unit/hr 9 units IVP Increase by 4-6 unit/hr 6 units IVP Increase by 4-6 unit/hr 8 units IVP Increase by 4-6 unit/hr 10 units IVP Increase by 5-7 unit/hr Call MM Call MM Call MM If blood glucose is below desired range: 80-110 No change 70-79 Decrease rate by 50% and recheck in 1 hour 60-69 Hold infusion for 1 hour and restart at 50% previous rate then recheck in 1 hour Less than 60 Discontinue infusion, consider giving D50 Hypoglycemia: Blood Glucose <50 Administer D50 If trouble controlling blood glucose, consider infusion of Dextrose in primary IV fluids, with Insulin infusion. *Alternative therapies and medications may be utilized with Medical Manager approval on a case by case basis.* Page 6 2/6/2016 Gift of Life Michigan Medication List Medication Albuterol Adult Dose Pediatric Dose <40kg or <16 years or 1.25-5 mg Q4 hours 2.5-5 mg Q4 hours Nebulizer or unit dose Amiodarone Life threatening arrhythmia: 150 mg IV bolus over 10 min; repeat if needed in 10 and 30 min; then 1mg/min for 6 hrs; then 0.5 mg/min for 18 hours. Pulse less V-fib or V-tach: 5mg/kg rapid IV bolus not to exceed 300 mg Perfusing Tachycardia: 5 mg/kg IV over 50 min; repeat twice up to total loading dose of 15 mg/kg Ancef 1 gm Q 8 hours IV Argatroban 350 mcg/kg IV over 15 min prior to cross-clamp 0.5 mg, typically given with Albuterol 0.5-1 gram IV 0.5-1 gram IV 600 mg Q8 hours IV 50-100 mg/kg/day IV split into 3 doses every 8 hours 350 mcg/kg IV over 15 min prior to cross-clamp 0.25, typically give with Albuterol Atrovent Nebulizer or unit dose Calcium Chloride Calcium Gluconate Clindamycin Desmopressin (DDAVP) Diltiazem (Cardizem) Dobutamine *consult MM Dopamine Epinephrine Furosemide (Lasix) Glucose 25% (D50) Hydrocortisone (Solu-Cortef) Hydralazine (Apresoline) Insulin- regular Lidocaine Levothyroxine 4-8 mcg/day IV in 2 divided doses 0.25 mg/kg IV bolus then 10-15 mg/hr 3-20 mcg/kg/min IV 10 mg/kg IV 100 mg/kg IV 25-50 mg/kg/day IV split into 4 doses every 6 hours 2-4 mcg/day IV in 2 divided doses 0.25 mg/kg IV over 2 min then 5-15 mg/hr 3-20 mcg/kg/min IV 3-20 mcg/kg/min IV 1-4 mcg/min IV 20-120 mg IV 1 amp (25 grams) 3-20 mcg/kg/min IV 0.05-0.3 mcg/kg/min IV 0.5-1 mg/kg IV 1-2 mL/kg IV 15 mg/kg Q6 hours 6 mg/kg IV Q6 hours 5-10 mg IV q 10-15 min (max of 10-15 mg Q4-6 hours 2-10 units/hr IV can be titrated higher to maintain blood glucose 70-200. 50-100 mg IV bolus; then 10-20 mcg/kg/min 20 mcg bolus; then 10-20 0.1-0.2 mg/kg/dose IV q 4-6 hours up to 1.7-3.5 mg/kg/day 0.05-0.2 unit/kg/hr IV, titrated for blood glucose 70-200. 1 mg/kg bolus IV; repeat in 15 min x2 then 20-50 mcg/kg/min Refer to Policy 5-09 Page 7 2/6/2016 Magnesium Sulfate mcg/hr 1-2 grams IV Mannitol 50-200 gm/24 hours IV in divided doses Methylprednisolone 15 mg/kg Q6 hours (Solu-Medrol) Mucomyst 3-5 mL of 20% solution or *Nebulizer only given 10 cc of 10% solution Q4 hours when combined with Albuterol Mucomyst *as needed to 25-50 mg/kg/dose IV diluted to 20% solution 0.25-0.5 g/kg IV every 4-6 hours 6 mg/kg Q6 hours 3-5 mL of 20% solution or 10 cc of 10% solution Q4 hours 600 mg PO pre-procedure ------------------------------------------- minimize contrast related renal toxicity Narcan *follow dose 8 mg IVP Not commonly given immediately with Norcuron Nicardipine Nitroprusside (Nipride) Norcuron (Vecuronium) Norepinephrine (Levophed) Potassium Acetate Potassium Chloride Potassium Phosphate Primacor (Milrinone) *Consult MM Saline 3% Sodium Bicarbonate THAM (Tromethamine Vasopressin 5-15 mg/hr until desired BP reached, then maintenance of 3 mg/hr 0.3-10 mcg/kg/min IV 10 mg IVP -----------------------------------------0.5-8 mcg/kg/min IV 0.08-0.1 mg/kg IV; then 0.05-0.1 mcg/kg/min maintenance 0.05-0.3 mcg/kg/min IV Initially 0.5-12 mcg/min 20-60 mEq 40 mEq/L IV 10-15 mmol IV 50 mcg/kg IV over 10 min 0.375-0.75 mcg/kg/min Mixed with 0.45 or 0.9 NS 40 mL/hr for 3 hours 1 amp or 50 mEq IV Base deficit x kg x 1.1= amount in mL of 0.3 molar solution 0.008-0.67 units/min 1-4 mEq/kg in 24 hours 0.5-0.1 mEq/kg over 2 hours 0.08-0.36 mmol/kg/dose over 46 hours 50 mcg/kg IV over 10 min 0.375-0.75 mcg/kg/min Mixed with 0.45 or 0.9 NS 5 mL/kg IV to raise Na by 4 mEq/L 1 mEq/kg/dose of 0.3 molar solution over 20-30 minutes 1mL/kg for each pH unit below 7.4 0.5-10 miliunits/kg/hr Page 8 2/6/2016 Pulmonary Management Guidelines Attachment A CRITERIA: This lung donor management routine will be considered on donors between the ages of 15-60 years old. Individuals > 60 or < 15 will be assessed on an individual basis. Medical history does NOT rule out lung donation. DCD Donors/No lung consent does not rule out utilization of pulmonary management guidelines. Bronchoscopy will be assessed on a case by case basis. For DCD Donation, certain aspects of guidelines will be utilized on a case by case basis. MEDICATIONS: 15 mg/kg Solu-medrol IVP at start of case as initial dose. Repeat with 15 mg/kg of Solu-medrol every 6 hours thereafter. If the patient is already on a T-4 drip, do not repeat the dose but follow with the 15 mg/kg dose 6 hours after the drip was hung. Ancef 1 gram Q 8 hours, if allergic to PCN, use Clindamycin 600 mg Q 8 hrs. Call Pharmacy after sputum gram stain result is returned to see if antibiotic adjustments need to be made. Narcan 8 mg IVP at BEGINNING of case combined with Norcuron 10 mg IVP. Narcan Rationale: Used in effort to prevent or minimize Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema Norcuron can be given before or after Narcan. Norcuron may be repeated prn. (Half-Life is 25-40 minutes) Norcuron rationale: Helps to decrease spinal reflexes and relaxes the diaphragm and other respiratory muscles to help ventilate. If Norcuron is not available consider: Pavulon 0.05- 0.2 mg/kg IV (half-life is approx 110 min),Nimbex 0.150.2 mg/kg IV (half-life is 20-45 min) Albuterol 2.5 mg or 5 mg and 0.5 mg Atrovent Q 4 hours. In-line nebulizer is first choice, if unavailable use unit/dose puff. Do not break ventilator circuit if possible; use a spring loaded nebulizer adaptor. Rationale: Every time you break the circuit de-recruiting of the lungs takes place. .Observe for Sinus Tachycardia. Mucomyst nebulizer, 3-5cc of 20% solution or 10cc of 10% solution Q 4 hours. Use ONLY in conjunction with Albuterol, never alone. Use only if patient has thick secretions. DIURETICS: Lasix 20-80 mg IV, Bumex 0.5-1 mg IVP Mannitol-Adult dose 300-400 mg/kg, usually given in conjunction with lasix Consider if PO2 is worsening and/or fluid balance is positive. Patient is hemodynamically stable ( minimal pressors) see Policy 5.6 VENTILATOR SETTINGS: Volume Ventilation (AC Mode) Suggested Tidal Volume (10-12cc/kg) ideal body weight. May go up to 15cc/kg. Ideal body weight calculations: Male:50 kg + 2.3 kg per in. >60 inches, Female:45 kg + 2.3 kg per in. > 60 inches Peak airway pressure should be kept < 35. (Reduce TV if > 35 or change to Pressure Control) Page 9 2/6/2016 Adjust A/C rate to deep PCO2 between 35-45 mmHg (as long as PH is 7.35-7.45) PEEP of +5-8 cm H2O FiO2 at 40% If ABGs are WNL, maintain current settings or increase volumes/and or rate to optimize donor management guidelines. I.E. PO2 > 300, P/F Ratio > 3. (P/F Ratio = maintenance FIO2 x 3). Slow flows to 40-50 lpm and/or increase inspiratory pause. RATIONALE: This decreases peak inspiratory pressure, minimizes “wasted ventilation” (time between exhalation and initiation of next breath), and increases mean airway pressure resulting in less trauma and increased oxygenation. All lung offers will be made on a PEEP of 5, according to UNOS Policy. Pressure Control Ventilation Maintain peak airway pressures of less than 35 cm H2O. Adjust rate to keep PCO2 between 35-45 mmHg. (even if TV drops <10 cc/kg) and as long as PH is between 7.35-7.45 PEEP +5-8 cm H2O MANEUVERS TO IMPROVE LUNG FUNCTION: Alveolar Recruitment Maneuver- Place vent in CPAP for 30 sec @ 40 cm of H20 Decrease peak flows to 40-50 lpm (slower inspirations) Rationale: Decreases lung damage and increase mean airway pressure which affects oxygenation. Alveolar Recruitment Maneuvers (ARM): CPAP 40 cm H20 for 30 Seconds o Do every 20 minutes x 3. o May be done at a lower pressure if vent is not able, or if the patient doesn’t tolerate 40 cm H20. o In order to RE-RECRUIT alveoli, perform once every time the circuit is broken, or patient is suctioned. o DO NOT PERFORM ARM IN THE PRESENCE OF: Severe Bronchospasm, Bullous emphysema, Untreated Pneumothorax, Unilateral Lung Disease (not suspected of being atelectasis), and Hemodynamic Instability. Use a PEEP valve when going to OR (set PEEP at +10 cm H20) Prone patient (If other treatments have failed and patient is hemodynamically stable)SJAA, WBRO, and Spectrum have proning beds available-contact resource manager Nitric Oxide @ 40 ppm may be indicated as salvage therapy to treat refractory hypoxia that may be due to high pulmonary vascular resistance. Contact resource manager. ARTERIAL BLOOD GASES: Baseline ABG on settings listed above Follow with O2 challenge on 100% FiO2 Repeat baseline ABG Q 4-6 hours Always treat PH, not CO2 Repeat O2 challenge within 2 hours of procurement surgery and prn Treat Metabolic Acidosis with NaHCO3 unless Sodium is >140. If Sodium is greater than 140, use THAM (acid-base buffer without sodium). Consult Pharmacist for dosing. PT MUST BE MAKING URINE PRIOR TO USING THAM. CHEST X-RAYS: Baseline CXR within 4 hours of consent Repeat CXR within 4 hours of procurement surgery Page 10 2/6/2016 BRONCHOSCOPY: As soon as possible after consent and brain death Evaluate the endo-bronchial tree, right and left side, for lesions, signs of infection, and overall condition of the endo-bronchial tissue Obtain bronchial washings for culture and gram stain USE VERY LITTLE SALINE DURING BRONCH. (10cc may be used to clear plug) BEDSIDE CARE: Chest PT Q 2-4 hours as indicated Q 1-2 hour tilting side to side- Rationale: Allows mobilization of secretions and opens atelectatic regions Q 2-4 hour ET Tube suctioning as indicated Place patient on specialty bed if possible. (Percussion and rotation) Oral care q 1-2 hours No ETT cuff leak-Ask RT to add 2-3 cc air to minimal occluding volume. Rationale: Reduces ventilator associated pneumonia HOB elevated at least 30 degrees- Rationale: Drops the diaphragm and reduces ventilator associated pneumonia and opens lungs. Deep glottic suctioning and oral care. Rationale: prevents aspiration. HEMODYNAMICS: Transduced central line/swan for CVP/PAP/PCWP monitoring. (Thoracic not femoral for adequate readings) Maintain CVP 6-8 mmHg Maintain PAWP 8-12 mmHg Page 11 2/6/2016 Cardiac Donor Management Guidelines Attachment B Obtain urine drug screen test if not previously done & patient admitted less than 36 Hormonal Therapy Regimen per protocol Place Pulmonary Artery Catheter Patient with history of smoking, drug abuse, HTN, cardiac disease, on more than 1 inotrope or requested by TC Goals: MAP > 60 mm Hg PCWP 8-12 mm Hg CVP 6-10 mm Hg C.I. > 2.5-3.5L/min-m2 Dopamine < 10 mcg/kg/min as indicated Hemodynamic Management Vasopressin 0.5-4 units/hr Pressors should be weaned in this order: Primacor < 0.75 mcg/kg/min Neosynephrine < 0.5 mcg/kg/min Epinephrine < 0.05 mcg/kg/min Levophed < 0.05 mcg/kg/min Dopamine < 5 mcg/kg/min Dobutamine < 5 mcg/kg/min as indicated Only Use Dobutamine w ith MM input Minimum: Adults patients Central line with CVP monitoring (thoracic pref erred, f emoral f or trends) Obtain Initial Echo r/o structural abnormalities (substantial LVH, valvular dysf unction, congenital lesions Obtain echo at lowest doses of inotropes and as long as time permits. LVEF > 45% LVEF < 45% Continue Hemodynamic Management Continue Hemodynamic Management Repeat echo warranted if cardiovascular improvement If no improvement contact RM/MM Solumedrol Adults: 15mg/kg Peds: 6mg/kg Using Dopamine/Nipride conjunctively and/or to increase C.O. & decrease PAWP Heart Catheterization Considerations: Males > 40, Females >45, Center Request, Cocaine Usage, Smoking History. Always get right & left sided catheterization & float SWAN or maintain SWAN May get approval from resource manager if pt meets above and cardiologist is in hospital ready to do cath ASAP. Approval by RM/MM Proceed with Thoracic Offers * NOTE: All Pressors/Ionotropes can cause significant hypotension or hypertension. Evaluate patient's hematocrit, ionized calcium, & volume status prior to administering. Loading doses are not alw ays recommended. Page 12 2/6/2016 Page 13 2/6/2016