Middle School Research Paper Project: African American Heroes
advertisement

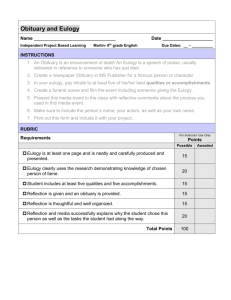
Unit Design For Middle School Research Project Developed by Gail Grimes and Heidi Thornthwaite Winans Academy of Performing Arts and Pontiac Academy for Excellence Understanding by Design Unit Design Worksheet Unit Title: Middle School Research Project Topic: African American Heroes Subject/Course: English Language Arts Grade(s): 8 Staff Name: Grimes / Thornthwaite Stage 1 - Desired Results Established Goals (Common Core State Standards): 1. W.8.2. Write informative/ explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant content. 2. W.8.7. Conduct short research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question), drawing on several sources and generating additional related, focused questions that allow for multiple avenues of exploration. 3. W.8.8. Gather relevant information from multiple print and digital sources, using search terms effectively; assess the credibility and accuracy of each source; and quote or paraphrase the data and conclusions of others while avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation. 4. W.8.9. Draw evidence from literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. 5. RI.8.1. Cite the textual evidence that most strongly supports an analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as inferences drawn from the text. 6. RI.8.8. Delineate and evaluate the argument and specific claims in a text, assessing whether the reasoning is sound and the evidence is relevant and sufficient; recognize when irrelevant evidence is introduced. 7. L.8.1. Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. 8. L.8.2. Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. Understandings: Students will understand that Essential Questions: 1. they must be able to effectively write research papers and realize these skills are transferrable into the real world. They will create research questions that demonstrate critical evaluation of multiple resources, perspectives, and arguments that culminate in a presented final project using the 1. How do writers vary their writing for different audiences and different purposes? 2. How does a writer create a research project to explore a topic? 3. How does a researcher evaluate and utilize credible sources? How does a researcher 1 writing process. properly summarize without plagiarizing? 2. they will need to look at multiple sources to find the most accurate and reliable information. 4. How do readers draw conclusions and infer meanings of text? 3. they must check the accuracy of information and be able to discern the relevant details while remaining unbiased. 5. Why is it important to be able to prove your argument? 6. How do readers determine if an author’s claims are sound and relevant? 4. they will need to provide proof to support an argument. 7. Why is it important to have correct conventions when speaking and writing? 5. they will need ample evidence to support their arguments and point of view in professional settings. 8. What role do grammar and mechanics play in crafting a solid piece of writing? 6. they need to know how to evaluate competing claims and advertisements in order to be intelligent consumers/citizens. 7. they must adjust their use of language to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes by using enunciation to emphasize key ideas and concepts when speaking. Students will know Students will be able to 1. how to effectively write research papers and realize these skills are transferrable into the real world. 1. write research papers and realize these skills are transferrable into the real world. 2. how to create research questions that demonstrate critical evaluation of multiple resources, perspectives, and arguments that culminate in a presented final project using the writing process. 2. create research questions that demonstrate critical evaluation of multiple resources, perspectives, and arguments that culminate in a presented final project using the writing process. 3. how to look at multiple sources to find the most accurate and reliable information. 3. conduct research using multiple sources to find the most accurate and reliable information. 4. how to check the accuracy of information and be able to discern the relevant details while remaining unbiased. 4. decipher relevant information and remain unbiased. 5. how to provide proof to support an argument. 6. provide ample evidence to support their arguments and point of view in professional settings. 5. provide adequate proof to support an argument. 6. how to use ample evidence to support their arguments and point of view in professional settings. 7. evaluate competing claims and advertisements in order to be productive researchers. 7. how to evaluate competing claims and advertisements. 8. how to adjust their use of language to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences. 8. adjust their use of language to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes to emphasize key ideas and concepts when speaking. 9. how to correctly use style conventions (MLA 9. demonstrate the correct use of style conventions 2 format) in a variety of grammatical structures. (MLA format) in a variety of grammatical structures. Unit Enduring Understanding: Unit Question: Research is the key to understanding and discovering the unknown. What are the processes for researching and writing about an unknown topic? Stage 2 - Assessment Evidence Performance Tasks: G: R: A: S: to write a comprehensive research paper historian/eulogist, award presenter teacher, peers, and parents delivering the eulogy of a chosen/assigned historical African American figure at their funeral should they have passed; if there are still living, you are to be the presenter at their life-time achievement award ceremony P: mock funeral, mock awards ceremony S: written report, spoken synopsis, rubric within written report Key Criteria: (Rubrics, etc.) RESEARCH PAPER (WRITTEN PORTION) RUBRIC: CATEGORY Exemplary Proficient Partially Proficient Not Proficient Research Questions 4 points Wrote thoughtful, creative, wellworded specific questions that were relevant to the assigned topic. 3 points Wrote well-worded, specific questions that were relevant to the assigned topic. 2 points Wrote questions which lacked focus, were poorly stated, and were not entirely relevant to the assigned topic. 1 point Wrote questions which lacked a specific focus, were poorly stated, and not relevant to the assigned topic. Selection of Sources 4 points Identified highly appropriate sources in a variety of formats (books, journals, electronic sources). 3 points Identified mostly appropriate sources in a variety of formats (books, journals, electronic 2 points Identified a few appropriate sources but made little attempt to balance format types. 1 point Identified no appropriate sources in any format. 3 sources). Note-taking & Keywords Organization and Synthesis Citations/ Sources 4 points Extracted relevant information. 3 points Extracted mostly relevant information. 2 points Extracted a lot of information which wasn’t relevant. 1 point Extracted irrelevant information. Brainstormed keywords, categories, and related terms that were effective in researching the questions. Selected mostly effective keywords to use in researching the questions. Selected some keywords that were not effective in researching the questions. Selected no effective keywords to use in researching the questions. Wrote notes including succinct key facts which directly answered all of the research questions and were written in the student's own words. Wrote notes which included facts that answered most of the research questions and were written in the student’s own words. Wrote notes which included irrelevant facts which did not answer the research questions. Some notes were copied directly from the original source. Wrote notes which included a majority of facts which did not answer the research questions. Most or all notes were copied wordfor-word from the original source. 4 points Presented content clearly and concisely with a logical progression of ideas and effective supporting evidence. 3 points Presented most of the content with a logical progression of ideas and supporting evidence. 2 points Presented content which failed to maintain a consistent focus, showed minimal organization and effort, and lacked an adequate amount of supporting evidence. 1 point Presented content which was unfocused, poorly organized, showed little thought or effort and lacked supporting evidence. Presented research findings through a eulogy or awards ceremony. Presentation was at least 5 minutes in length and had appropriate props including a visual representation. Presented research findings through a eulogy or awards ceremony. Presentation was under 5 minutes in length however presenter had appropriate props including a visual representation. Presented research findings through a eulogy or awards ceremony. Presentation was under 5 minutes in length and presenter had no appropriate props including a visual representation. Did not present (through a eulogy or awards ceremony) research findings to the class. 4 points Cited all sources of information accurately to demonstrate the credibility and authority of the 3 points Cited most sources of information in proper format and documented sources to enable accuracy checking. 2 points Cited most sources of information improperly and provided little or no supporting documentation to 1 point Created citations which were incomplete or inaccurate, and provided no way to check the validity of 4 information presented. Used information ethically all of the time. Used information ethically most of the time. check accuracy. the information gathered. Failed to use information ethically some of the time. Failed to use information ethically. FINAL SCORE: RESEARCH PRESENTATION OPTIONS RUBRICS: OPTION #1: Timeline 10 POINTS Student presents timeline dates and events to the class in over 4 minutes. 5 POINTS Student presents timeline dates and events to the class in under 4 minutes. O POINTS Student does not present their timeline to the class. Student has at least 15 pictures and events on their timeline. Student has less than 15 but more than 8 events and pictures on their timeline. Student has less than 8 pictures and events on their timeline. Student’s timeline is from birth to Student’s timeline is not in present (or death). chronological order or is missing major events. Student’s timeline does not make much sense chronologically and is missing most or all events. TOTAL POINTS: OPTION #2: Eulogy/Award 15 POINTS Student presents eulogy/award to the class in over 4 minutes. Student has a collage of pictures representing the person they have researched (at least 5 pictures) or one big picture (8x10). 7.5 POINTS Student presents eulogy/award to the class in under 4 minutes but over 2 minutes. THIS IS A 0 OR 15 POINT CATEGORY O POINTS Student presents eulogy/award to the class in under 2 minutes Student does not have any pictures or presentation materials. TOTAL POINTS: Other Evidence: BEFORE DURING AFTER Brainstorming: research topic ideas Summarizing: example paragraphs and articles Research Report: final product (rubric) Discuss: research process Paraphrasing: example paragraphs and articles Presentation: rubric based What Students Already Know: discussion Interactive Writing: modeling 5 Post Assessment Reflection: journal Think/Pair/Share: research topics writing information from sources Quick Writes: the writing process Conferencing: peer and teacher Provide Rubric: discuss expectations Note Cards: procedure and purpose Concept Map: KWL Checklists: ensuring status of tasks and completion Daily Assignments: questioning, work cited, peer editing, evaluating sources Describe the assessment/s and state the prompt if applicable. xF xS What type of scoring tools will be used for evaluation? x Analytic rubric x Holistic rubric □ Criterion rubric x Checklist □ Answer Key □ Other Student Self-Assessment and Reflection: See attachment one – Student Research Reflection See attachment two – Student Revision Checklist Stage 3 - Learning Plan Differentiated Instruction: C Level (40 points): 1. Vocabulary Journal of key terms from the unit (A-I) (10 points) 2. Vocabulary Journal of key terms from the unit (J-Z) (10 points) 3. Reflections Journal 1 and 2 (20 points) B Level (30 points): (Students need to pick one activity each from the following pairs: 1 & 2; 3 & 4; 5 & 6) 1. Students will complete a summarizing and paraphrasing activity practice worksheet (attachment #3). (10 points) 2. Students will complete activities regarding summarizing and paraphrasing online. http://www.tv411.org/reading/understanding-what-you-read/summarizing (10 points) 3. Provide evidence (bring examples into class) of a primary and secondary source. (10 points) 4. Explain in a three paragraph essay the difference between primary and secondary sources. (10 points) 6 5. Narrow down the focus of research paper (Attachment #4). (10 points) 6. Create a concept map and develop research questions (Attachment #5). (10 points) A Level (60 points): (Students must do 1 & 2, and have a choice between 3 & 4) 1. Unit Test (20 points) 2. Research Reflection (10 points) 3. Presentation - eulogy or lifetime achievement award according to rubric. (30 points) 4. Presentation - timeline according to rubric (30 points) Learning Activities: W Where are we going? To develop a deeper understanding of organizing and using information from multiple sources, including both primary and secondary sources, in order to create a research paper. Why? Because this empowers us to think, process, and provide support information as they undertake the multi-step process of writing a research paper. In addition, students can publish their work and orally present their topic to the class. Students will also learn how to use evidence to back judgments up, rather than simply repeating information from given resources. What is expected? This lesson can be used in any content area that requires student to write research papers. H Students will be hooked by using technology, including the internet to publish writing, to interact with others, and to collaborate with others. E Students will be equipped to develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising and editing, rewriting and trying a new approach. R Students will be asked to rethink and revise their research paper by providing multiple research checklists. (see Attachment #2) E Students will self-evaluate as they share rough drafts with peers with changes made after each review. If details do not support their thesis statement, they should revise their thesis statement or remove details that are outside the scope of their thesis. T Learning will be tailored by using the differentiated instruction above. O The unit will be organized so that key concepts build upon one another. Essential Vocabulary Accuracy - the condition or quality of being true, correct, or exact; freedom from error or defect; precision or exactness; correctness Additional - added; more; supplementary Analysis - a presentation, usually in writing, of the results of this process Argument - a discussion involving differing points of view; debate Avenues - a means of access or attainment Citation - the act of citing or quoting a reference to an authority or a precedent 7 Essential Vocabulary Claims - to assert or maintain as a fact Command - to direct with specific authority or prerogative; order Concluding - to bring to a decision or settlement; settle or arrange finally Concrete - pertaining to or concerned with realities or actual instances rather than abstractions; particular ( opposed to general) Conventions - a rule, method, or practice established by usage; custom: in writing, spelling, punctuation, subject-verb agreement, etc Convey - to communicate; impart; make known Credibility - the quality of being believable or worthy of trust Dash - the mark or sign (—) used to note an abrupt break or pause in a sentence or hesitation in an utterance Data - individual facts, statistics, or items of information Details - attention to or treatment of a subject in individual or minute parts Domain - a field of action, thought, influence, etc. Effectively - adequate to accomplish a purpose; producing the intended or expected result Ellipsis - the omission of one or more items from a construction in order to avoid repeating the identical or equivalent items that are in a preceding or following construction Evidence - that which tends to prove or disprove something; ground for belief; proof Explanatory - serving to explain Explicitly - fully and clearly expressed or demonstrated; leaving nothing merely implied; unequivocal Exploration - an act or instance of investigating; examination Focused - a central point, as of attraction, attention, or activity Formal - being in accordance with the usual requirements, customs, etc.; conventional Format - the organization, plan, style, or type of something Informational - knowledge gained through study, communication, research, instruction, etc.; factual data Informative - giving information; instructive Irrelevant - not relevant; not applicable or pertinent Literary - pertaining to authorship Multimedia - the combined use of several media, as sound and full-motion video in computer applications Plagiarism - an act or instance of using or closely imitating the language and thoughts of another author without authorization and the representation of that author's work as one's own, as by not crediting the original author Precise - being exactly that and neither more nor less Punctuation - the practice or system of using certain conventional marks or characters in writing or printing in order to separate elements and make the meaning clear, as in ending a sentence or separating clauses Reasoning - the process of forming conclusions, judgments, or inferences from facts or premises 8 Essential Vocabulary Reflection - a fixing of the thoughts on something; careful consideration Relevant - bearing upon or connected with the matter in hand; pertinent Selection - an act or instance of selecting or the state of being selected; choice Self-generated - made without the aid of an external agent; produced spontaneously Sources - a book, statement, person, etc., supplying information Specific - of a special or particular kind Standard - something considered by an authority or by general consent as a basis of comparison; an approved model Sufficient - adequate for the purpose; enough Textual - of or pertaining to a text Topic - the subject or theme of a discourse or of one of its parts Transitions - movement, passage, or change from one position, state, subject, concept, etc., to another; change Varied - characterized by or exhibiting variety; various; diverse; diversified; changed; altered Sequencing the Learning Monday Week 1 Intro to research process Show previous students’ completed research projects in order to write and organize a coherent report Tuesday Summarizing activity to avoid plagiarism Paraphrasing activity to avoid plagiarism Go over expectations along with rubrics Modeling and engaging in the process of summarizing and paraphrasing multiple resources Level C - 1 Level B – 1 or 2 Wednesday Thursday Friday Model using notecards Examine primary and secondary sources Overview of research process by modeling and examining the differences between research papers and reports Introduce bibliography Citing your sources within your report Extract information from sources in order to accurately find and utilize information Introduce MLA format, in-text citations, and quotation format Level C - 2 9 Level B – 3 or 4 Introduce, model, and guide students in creating an outline for their research report Week 2 Select and narrow a relevant research topic Demonstrate how to develop thesis statement Guide students to structure their thesis statement Week 3 Week 4 How to formulate research questions related to the topic/thesis statements Level B – 5 or 6 Continue researching using electronic sources to gather data and drafting paper Peer revising and editing of rough draft Work on presentation materials and anything else that needs to be done Work on presentation materials and anything else that needs to be done Level C – 3 (Journal 2) Begin researching using electronic sources to gather data and drafting paper Continue researching using electronic sources to gather data and drafting paper Continue researching using electronic sources to gather data and drafting paper Level C – 3 (Journal 1) Continue peer revising and editing of rough draft Demonstrate cover pages and table of contents Guide students to create cover pages and table of contents Present Research Projects - Present to class by choosing one of the two presentation options. Level A – 3 or 4 10 Continue to present research projects Create final drafts from corrections made through peer revising Research Project Reflection Unit Test Level A – 3 or 4 Level A – 1 & 2 ATTACHMENT #1 RESEARCH PROJECT REFLECTION DIRECTIONS: Answer the following questions in complete sentences. Explain your thoughts completely. 1. What is the purpose of completing a research project? 2. What are some things you learned about your research topic that surprised you? 3. If you could have changed your research topic to anything else, would you? Why or why not? 4. Did you work as hard as you could on your research project? Explain your answer. 11 5. What will you do differently the next time you have to complete a research project? 6. Did you learn anything from any of your classmates’ presentations? 7. What did you like the best about other classmates’ presentations? 8. If you were the teacher, what would you change about this assignment and why? 9. What grade would you give yourself if you could and why? 12 ATTACHMENT #2 NAME: RESEARCH PAPER PEER REVISION CHECKLIST NAME OF PERSON REVISING PAPER Paper is at least 5 pages in length I have used proofreader’s marks to revise any errors in this research paper. 1 2 3 4 5 COMMENTS: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 13 Paper is broken up into paragraphs and the paragraph order makes sense. If not, I have written suggestions to improve. Is there a thesis statement? Does the research support the thesis statement? Paper has a title that is not just the name of the research topic 14 ATTACHMENT #3 Name_________________________________________ PARAPHRASE PRACTICE WORKSHEET Directions: Read the original text below. Without plagiarizing, write a paraphrase on the lines for each of the original text passages. Be sure to give proper credit to the sources. Citation: Greening, Samantha M. “Natural Remedies for What Ails You.” Healthful Todays and Tomorrows 7 Apr. 2005: 18-21. Original Text: “Whether you have morning sickness, motion sickness, or nausea from chemotherapy or radiation therapy, help may be no farther than your refrigerator or kitchen pantry. There are several foods that can help the body mitigate mild to moderate nausea. Pectin is a dietary fiber that occurs naturally in plant cell walls. Fruits such as apples, peaches, plums, and currents are good sources of pectin, as are carrots and potatoes. Ginger, also known as ginger root, is another very powerful plant that works on the digestive tract. Ginger is found in ginger ale, gingersnaps, gingerbread, and certain Chinese dishes. So the next time your stomach is feeling queasy, try reaching for a can of ginger ale, or nibbling a gingersnap cookie, an apple, or a carrot.” ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Citation: Burgenni, Patrick K. “Teaching Finance: Whose Responsibility Is It?” U.S. Education News & Policy 13 Feb. 2006: 29-33. Original Text: “Who should teach children about personal finances? Ideally, it would be the child’s parent or guardian. However, many adults do not have the knowledge necessary to teach such concepts. This is evident by the staggering amount of credit card debt in the United States and the astounding number of adults who claim they cannot balance their own checkbook. Many argue that schools must step in and teach personal finance. Adding this requirement to the compulsory curriculum would require that more teachers be hired, which many school districts cannot afford, and would increase the credit requirement for graduation.” ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 15 ______________________________________________________________________ ATTACHMENT #4 Part 1: Fill in the blanks to develop your research problem/statement. 1. I am learning about (or studying/working on) 2. because I want to find out (who/what/where/when/whether/how/why) 3. in order to understand (how/why/what/whether) Example of completed research problem or statement: I am working on Lincoln’s beliefs about predestination in his early speeches because I want to find out how his belief in destiny and God’s will influenced his understanding of the causes of the Civil War, in order to help my reader understand how his religious beliefs may have influenced his military decisions. Write two possible research questions for your project below: Option 1 Option 2 16 ATTACHMENT #5 Concept map example Here is concept map on climate change. After completing the concept map and focusing the topic, this student developed the following research question: How does climate change impact polar bear habitat? DIRECTIONS: On the back of this paper, create a concept map on your research topic. Write your own focused research questions pertaining to your topic of choice. 17