Unit: 4 Daily Agenda
advertisement

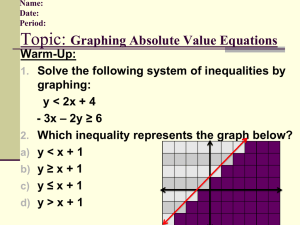
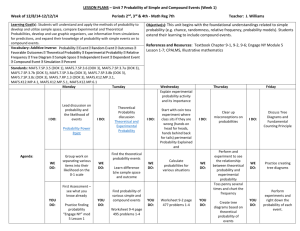
Unit : 4 M/J Grade 6 Mathematics st 1 , 2nd, 5th Florida Standard(s): Benchmarks, descriptions, DOK levels, standards unpacked (know/do) highlighted Unit Rate Including Percents Dates: 10/26 through 10/30/15 Week 1 of 2nd Nine Weeks MAFS.6.NS.2.3 (DOK 1): Fluently add, subtract, multiply, and divide multi-digit decimals using the standard algorithm for each operation. divide multi-digit decimals using the standard algorithm for each operation with speed and accuracy MAFS.6.NS.3.8 (DOK 2): Solve real-world and mathematical problems by graphing points in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane. Graph points in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane. real-world problems by graphing points in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane. MAFS.6.RP.1.2 (DOK 2): Understand the concept of a unit rate a/b associated with a ratio a:b with b ≠ 0, and use rate language in the context of a ratio relationship. For example, “This recipe has a ratio of 3 cups of flour to 4 cups of sugar, so there is 3/4 cup of flour for each cup of sugar.” “We paid $75 for 15 hamburgers, which is a rate of $5 per hamburger.” Identify and calculate a unit rate. Use appropriate math terminology as related to rate. the relationship between a ratio a:b and a unit rate a/b where b ≠0 MAFS.6.RP.1.3 (DOK 2): Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve realworld and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations. b. Solve unit rate problems including those involving unit pricing and constant speed. For example, if it took 7 hours to mow 4 lawns, then at that rate, how many lawns could be mowed in 35 hours? At what rate were lawns being mowed? c. Find a percent of a quantity as a rate per 100 (e.g., 30% of a quantity means 30/100 times the quantity); solve problems involving finding the whole, given a part and the percent. a table of equivalent ratios using whole numbers. Find the missing values in a table of equivalent ratios. Plot pairs of values that represent equivalent ratios on a coordinate plane. that a percent is a ratio of a number to 100. Find a percent of a number as a rate per 100. Use tables to compare proportional quantities. Apply the concept of unit rate to solve real-world problems involving unit pricing. Apply the concept of unit rate to solve real-world problems involving constant speed. ratio reasoning to convert measurement units in real-world and mathematical problems. ratio reasoning to convert measurement units by multiplying or dividing in real-world and mathematical problems. real-world and mathematical problems involving ratio and rate. Solve real-world problems involving finding the whole, given a part and a percent. Learning Goal: Students will understand ratio concepts and be able to use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world and mathematical problems using various models. Assessments Pre Assessment:5 question pre-test Formative Assessments: CPALMS, Exit Tickets, Journal Writing, Thinking Maps Summative Assessment: Quizzes, Tests, Work Text pages, IXL , Penda Learning Essential Question(s): Progress Monitoring/ Homework, Quiz, Spiral Notebook Checks, Journal Writing, Summative Assessment, Feedback Loop IXL, Penda Learning Higher Order Question(s) How do you identify the unit rate in a table, graph, and equation? Why is the unit rate instrumental when comparing rates? How does understanding rates help you solve percent problems? Key Vocabulary -axis -axis Monday, 10/26/15 Daily Objective BELL RINGER (5 Minutes) I DO: WE DO: YOU DO: Homework EXIT TICKET: (5 minutes) Unit: 4 Teacher Works, You Enjoy n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a Tuesday, 10/27, On Wed. schedule Daily Objective BELL RINGER ( 5 Minutes) I DO: Daily Agenda Unit: 4 Daily Agenda Rigor Level: 2 Rigor Level: 2 Deconstruct standards & understand Unit 4 (Rates, & % ) Expectations Create a tree map of Unit 4 Standards: Do / Know / Use Prior Knowledge Explain Unit 4 Standards, Explain Math “Allowance” WE DO: YOU DO: Homework Re-visit Social Contract, Deconstruct standards , Write Unit 4 goal Take pre-test and write brief summary on what it is you are expected to learn during this unit. Exit Ticket, if not completed (Teacher: Save Engage NY 6.1 Lesson 14 & 4 Quadrant Graphing Puzzle to Desktop) On a sheet of paper to turn in: What is your 2nd Nine Week’s grade Goal and HOW will you achieve it? EXIT TICKET: (5 minutes) Wednesday, 10/28 Unit: 4 Daily Agenda TC “Orange slice” TB= Text Book Daily Objective BELL RINGER ( 5 Minutes) I DO: WE DO: YOU DO: Know parts of a Coordinate Plane and plot ratios in all four quadrants Review dividing decimals: TC TB pg 132 ( 49, 51) Demo parts of a Coordinate Plane and plotting ratios TC Mini- Task : Plot Ratios on the Coordinate Plane TC TB pg 492-493 Create and label a Coordinate Plane on graphing board or graph paper; Plot Projected Ratios TC TB pg 494 (1-6) What is your plan to become or maintain proficiency on MAFS 6NS 2.3? Thursday, 10/29 Unit: 4 Daily Agenda Rigor Level: 2 Know parts of a Coordinate Plane and plot ratios in all four quadrants TC TB pg 494 (13-18) Check BR for accuracy, Explain directions and distribute “You Do” papers Review the way to write ordered pairs from a ratio Four Quadrant Graphing Puzzle & Engage NY 6.1 Lesson 14 Finish “You Do” Turn in “You Do” papers Friday, 10/30 Day B4 Halloween! Daily Objective BELL RINGER ( 5 Minutes) I DO: WE DO: You DO: Homework EXIT TICKET: (5 minutes) WT = Work Text Homework EXIT TICKET: (5 minutes) Daily Objective BELL RINGER (5 Minutes) I DO: WE DO: YOU DO: Homework EXIT TICKET: (5 minutes) Rigor Level: 2 Unit: 4 Daily Agenda Rigor Level: 2 Graph points in all four quadrants of the Coordinate Plane Skittles Ratio Math Give common numbers for all to use to fill out Skittles Ratio Activity Review direction Any Questions? Halloween Coordinate Graphing Be safe! Have fun! Eat lots of candy! Brush your teeth lots!! Rate yourself from the Rates Scale in your journal Note: Learning Scales and Accommodations are below. Rates Scale LEVEL STUDENTS WILL: Go beyond what was taught and make connections to the real world. 4 3 For example:Bring in something (picture, article, magazine, etc.) that relates this unit to the real world and write a paragraph explaining how they relate or how they are actually used. Solve real world problems - By graphing points in all 4 quadrants of the coordinate plane - Involving ratio and rate - Involving finding the whole, given a part and a percent. 2 Calculate a unit rate Find the percent of a number as a rate per 100 1 Graph points in all four quadrants on the coordinate plane Use appropriate math terminology as related to rate Analyze the relationship b/w a ratio and a unit rate 0 Even with help no success WICR Strategies used during each unit. Writing Writing activities that help students understand the content Inquiry Questioning strategies that help students understand the content Writing-to-Learn • summaries Process writing • using a rubric as evaluation On-demand/Timed writing • writing that is completed in class within a set amount of time • grade is evaluated using a rubric Cornell Notes • taking notes on the most important information • summarizing Higher level questioning in classes • Costa’s Level 1: Students find the answers right there in the text. Collaboration Working together with a partner or in a group of students to understand, to problem solve, or to complete a task/project Think Pair Share Sharing ideas with a partner or in a group Carousel/Gallery Walk • Costa’s Level 2: Students must figure out the answer from information in the text. • Costa’s Level 3: Students apply what they have learned or use what they Problem solving in groups Reading Any strategies in reading that help students understand Before reading activities • vocabulary activities • accessing prior knowledge • making predictions During reading activities • marking the text • Cornell notes • graphic organizers Projects in groups After reading strategies • summarizing • group projects • using the notes to study Reflective writing • students write about what they have learned and what they still need have learned to evaluate or create. Accommodations used daily on an individual basis in accordance with IEP and 504 plans and ELL Students Read directions for the student Check for understanding Allow to leave class for assistance Extra time for exams Daily agenda Allow student time to step out to de-escalate Testing in small groups Use of a planner/binder for organization English Language Dictionary Extended time on assignments =1 day Preferential seating Written direction given Break directions into chunks Read Aloud to Students Visual manipulatives Cooperative Learning, Vocabulary, Description, Introduction, . Student Friendly Mathematical Practice Statements MAFS.K12.MP.1.1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. • Make a plan! • Try different approaches when your problem is hard. • Solve your problem in more than one way. • Check whether your solution makes sense. MAFS.K12.MP.2.1 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. • Explain the meanings of the numbers, words, pictures, symbols, and objects you and others use MAFS.K12.MP.3.1 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. • Explain both what to do and why it works. • Work to make sense of others’ mathematical thinking. MAFS.K.12.MP.4.1 Model with mathematics. • Apply math to real-world situations. • Use models such as graphs, drawings, tables, symbols, numbers, and diagrams to solve problems. MAFS.K12.MP.5.1 Use appropriate tools strategically. • Choose appropriate tools for your problem. • Use mathematical tools correctly and efficiently. • Estimate and use what you know to check the answers you find using tools. MAFS.K12.MP.6.1 Attend to precision. • Communicate your mathematical thinking clearly and precisely. • Use the level of precision you need for your problem. • Be accurate when you count, measure, and calculate. MAFS.K12.MP.7.1 Look for and make use of structure. • Find, extend, analyze, and create patterns. • Use patterns and structures to solve problems. MAFS.K12.MP.8.1 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. • Use patterns and structures to create and explain rules and shortcuts. • Use properties, rules, and shortcuts to solve problems. • Reflect on your thinking before, during, and after you solve a problem.