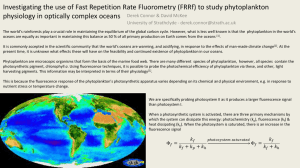
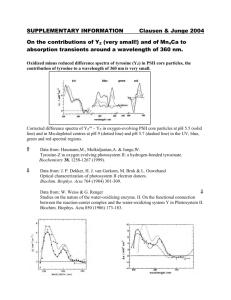
tpj12474-sup-0014-Legends
advertisement

Figure S1. Chloroplast localization and topology of TerC-GFP fusion protein. (a) Protoplasts were isolated from terc-1TerC-GFP. Chlorophyll fluorescence was excited at 450 – 490 nm and the emission was recorded at > 515 nm (Filterset 9, Carl Zeiss, http://microscopy.zeiss.com/microscopy/en_de/service-support/filtersetsdyes.html). GFP fluorescence was excited at 470 ± 40 nm and the emission was recorded at 525 ± 50 nm (Filterset 38 HE, Carl Zeiss). The overlay was constructed using the AxioVison software (Carl Zeiss, http://www.zeiss.de/). BF, bright field; Chl, chlorophyll fluorescence; GFP, GFP Fluorescence; ms, merged signal. (b) Extraction of thylakoid membranes of terc-1TerC-GFP and treatments with chaotropic salts or alkaline pH. Thylakoid membranes were resuspended at 0.5 mg chlorophyll/mL in 10 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, containing either 2 M NaCl, 0.1 M Na 2CO3, 2 M NaSCN, 0.1 M NaOH or no additive. After incubation for 30 min on ice, supernatants containing soluble proteins (s) or pelleted proteins (p) were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblots were performed using anti-GFP, anti-Lhcb1 and anti-PsaD. Note that GFP detected Terc-GFP behaved like the integral membrane protein Lhcb1. (c) Extraction of thylakoid membranes from wild-type, terc-1TerC-GFP, WTTerC-GFP and treatment with thermolysin. In intact thylakoids, only stroma-exposed polypetides are accessible to thermolysin. Note that GFP, but not PsaD and PsbO were accessible to the enzyme. Figure S2. Target for artificial micro RNA. Schematic drawing of TerC/At5g12130 with 14 exon (white boxes) and 13 introns (line) and the spliced mRNA. amiR-TerC targets nucleotide 657 to 677 of the endogenous mRNA. Stars denote two mismatches. Figure S3. Two-dimensional BN/SDS-PAGE of in vivo labeled thylakoid membrane complexes from WT and amiR-TerC. Thylakoid membranes (equivalent to 50 µg of chlorophyll) were solubilized with 1% [w/v] -DM and thylakoid membrane protein complexes fractionated by BN-PAGE. A 20-min pulse was followed by a chase for 60 min. Subunits of the thylakoid membrane complexes (PSII super, PSII dimer, PSII monomer, CP43-free PSII, RC) were fractionated on second dimension gels. PSII super, PSII dimer, PSII monomer, CP43-free PSII, RC and unassembled protein are denoted and the most strongly labeled thylakoid membrane proteins are indicated by arrowheads. Figure S4. Two-dimensional BN/SDS-PAGE of steady state levels of thylakoid membrane complexes. (a) Thylakoids were isolated from four-week-old wild-type, WTTerC-GFP, terc-1TerC-GFP, and amiR-TerC plants. Thylakoid membranes (50 µg of chlorophyll) were solubilized with 1% [w/v] -DM and thylakoid membrane protein complexes fractionated by BNPAGE. The position of protein complexes representing PSI monomers and PSII dimers, PSII monomers, CP43-free PSII complexes, trimeric and monomeric LHCII are indicated. Second dimension SDS gels were subjected to immunodetection with antibodies directed against PSII core subunit proteins. (b) Second dimension SDS gels were stained with colloidal Coomassie blue (G 250). The complexes PSII dimer, PSI monomer, PSII monomer, CP43-free PSII, LHCII trimer and LHCII monomer are indicated at the top of each gel and the four PSII core subunits are indicated by arrowheads. Figure S5. Split-Ubiquitin analysis of TerC full-length and mature protein. Semiquantitative analysis of interaction between TerC and thylakoid membrane proteins. Split ubiquitin assay for interaction of full-length TerC (TerC1-384) or mature TerC (TerC61-384) and selected PSII subunit proteins, PSII assembly factors, miscellaneous factors and PSI subunits. Growth of co-transfomed yeast cells on permission medium (-LT) was set to “+++” and visual inspection of growth on selective medium (-LTH) was set accordingly. Figure S6. Phylogenetic analysis The analysis involved 14 amino acid sequences: The amino acid sequences were GenBank NP_568257 (At5g12130) for Arabidopsis thaliana, XP_003536974 for Glycine max, AFW82790 for Zea mays, NP_001054496 (Os05g0121200) for Oryza sativa, XP_001761014 Chlamydomonas WP_010190840 Methanosaeta for Physcomitrella reinhardthii, for XP_003083381 Candidatus thermophile, patens, for Nitrosoarchaeum NP_952621 for XP_001700467 Ostreococcus limnia, Geobacter YP_843886 for tauri, for sulfurreducens, WP_004627106 for Clostridium termitidis, NP_927355 for Gloeobacter violaceus and NP_440265 (sll1022) for Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Blast search analysis was performed between At5g12130 and Synechocystis sp.PCC6803. The sequence of sll1022 possessed the highest query cover score (45%) with a sequence identity of 21% to At5g12130 on protein level and was therefore chosen for analysis. TerC of cyanobacterium Gloeobacter violaceus grouped together with bacterial homologs but not with Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Table S1. Photosynthetic Performance of amiR-TerC Lines. Mean values for five different measurements (± SD) per plant are shown. F0, minimum fluorescence yield based on leaf area; Fv/Fm, maximum quantum yield of PSII Table S2. Primers used in this study Table S3. Antibodies used in this study. Method S1. Fluorescence microscopy For fluorescence microscopy, leaves of soil-grown Arabidopsis lines were cut into small pieces and incubated in 20 mM KCl. 10 mM MES pH 5.7, 10 mM CaCl2, 0.5 M mannitol, 0.1% BSA, 0.1 g mL-1 macerozyme (Duchefa, http://www.duchefa.com) and 0.1 g mL-1 cellulase (Duchefa) in the dark for 3 h. The isolated protoplasts were collected by centrifugation at 50g for 5 min and washed in 20 mM KCl, 10 mM MES, pH 5.7, 10 mM CaCl2 and 0.5 M mannitol. Protoplasts were analysed using the Axio Imager fluorescence microscope with integrated ApoTom and the X-Cite 120 FL (Carl Zeiss, http://www.zeiss.de/) lighting system. GFP fluorescence was excited at 470 ± 40 nm and the emission was recorded at 525 ± 50 nm using the AxioVision software (Carl Zeiss). Method S2. Topology studies The topology of TerC-GFP was determined with salt and thermolysin treatments of thylakoid membranes of transformed Arabidopsis lines. Salt treatments were performed as described previously (Armbruster et al. 2010) using antibodies specific for GFP, Lhcb1 (Agrisera) and PsaD (Agrisera). For thermolysin treatments, isolated thylakoid membranes were resuspended in10 mM HEPES-KOH, pH 8.0 and 5 mM MgCl2 at a chlorophyll concentration of 250 µg mL-1. Thermolysin was used in a final concentration of 50 µg mL-1 and samples were incubated for 30 min on ice. The reaction was stopped by adding EDTA pH 8.0 and after centrifugation at 15.000g for 10 min at 4°C, proteins were solubilized in the presence of 2 % (w/v) SDS and subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibodies specific for GFP, PsaD and PsbO (Agrisera). Method S3. Two-dimensional BN/SDS-PAGE Leaves from soil-grown Arabidopsis lines were harvested and thylakoids were prepared. Thylakoid samples equivalent to 50 µg chlorophyll were solubilized in 750 mM -aminocaproic acid, 50 mM Bis-Tris, pH 7.0, 50 mM NaCl and 1.0 % [w/v] -DM for 10 min at 4°C. After precipitation of non soluble material (19.000g, 15 min, 4°C), the membrane complexes were separated using nondenaturing BN-PAGE at 4°C as described (Schägger et al., 1994). Afterwards, BN-PAGE lanes were excised, incubated in 0.125 M Tris, pH 6.8, 4% (w/v) SDS, 1 mM DTT for 20 min and layered onto 12% Tris-Tricine SDS acrylamide gels. Second dimension gels were either stained with colloidal Coomassie blue (G 250), used for immunoblot analysis or the radioactive signals detected using a phosphor imager. Method S4. Phylogentic analysis The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the program MEGA5 as described by Hall (2013). The tree with the highest log likelihood was chosen. A discrete Gamma distribution was used to model evolutionary rate differences among sites (5 categories (+G, parameter = 1.0449)). The tree was drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. The analysis involved 14 amino acid sequences. All positions with less than 95% site coverage were eliminated. That is, fewer than 5% alignment gaps, missing data, and ambiguous bases were allowed at any position. There were a total of 197 positions in the final dataset.