Triangles Classwork-Homework | 974.2KB
advertisement

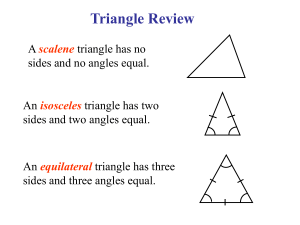
Triangles Chapter Problems Classify the Triangles by Sides or Angles Class Work In problems #1-10, choose the most appropriate description for the given triangle. (Equilateral, Scalene, Isosceles, Obtuse, Acute, Right, Equiangular) 1. Side lengths: 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm 2. Side lengths: 3 cm, 3 cm, 4 cm 3. Side lengths: 2 cm, 3 cm, 2 cm 4. Side lengths: 5 cm, 5 cm, 5 cm 5. Side lengths: 2 cm. 3 cm, 4 cm 6. Angle Measures: 30°, 60°, 90° 7. Angle Measures: 60°, 60°, 60° 8. Angle Measures: 92°, 37°, 51° 9. Angle Measures: 88°, 67°, 25° 10. Angle measures: 37°, 39°, 104° Complete the statement using ALWAYS, SOMETIMES, and NEVER. 11. An isosceles triangle is ___________ a scalene triangle. 12. An equilateral triangle is __________ an isosceles triangle. 13. An isosceles triangle is ___________ an equilateral triangle. 14. An acute triangle is ___________ an equiangular triangle. 15. An isosceles triangle is __________ a right triangle. For #16-20, classify the triangles by Sides & Angles 17. 16. 18. 64° 37° 22° 115° 58° 58° 106° 43° 37° 19. 20. 135° Geometry: Triangles ~1~ NJCTL.org Classify the Triangles by Sides or Angles Homework In problems #21-30, choose the most appropriate description for the given triangle. (Equilateral, Scalene, Isosceles, Obtuse, Acute, Right, Equiangular) 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. Side lengths: 5 cm, 6 cm, 7 cm Side lengths: 2 cm, 2 cm, 3 cm Side lengths: 3 cm, 3 cm, 3 cm Side lengths: 3 cm, 4 cm, 4 cm Side lengths: 4 cm, 3 cm, 2 cm Angle Measures: 60°, 60°, 60° Angle Measures: 60°, 30°, 90° Angle Measures: 33°, 52°, 95° Angle Measures: 37°, 43°, 100° Angle measures: 25°, 67°, 88° Complete the statement using ALWAYS, SOMETIMES, and NEVER. 31. A scalene triangle is ___________ an equilateral triangle. 32. An equilateral triangle is __________ an obtuse triangle. 33. An isosceles triangle is ___________ an acute triangle. 34. An equiangular triangle is ___________ a right triangle. 35. A right triangle is __________ an isosceles triangle. For #36-40, classify the triangles by Sides & Angles 38. 37. 36. 27° 36° 47° 108° 106° 36° 40. 39. 51° 46° 78° 46° 51° Geometry: Triangles ~2~ NJCTL.org Triangle Sum & Exterior Angle Theorems Class Work In the given triangles, solve for the missing variable(s). Geometry: Triangles ~3~ NJCTL.org Triangle Sum & Exterior Angle Theorems Homework In the given triangles, solve for the missing variable(s). Geometry: Triangles ~4~ NJCTL.org PARCC type question 66. Proof of Triangle Sum Theorem: Complete the proof by filling in the missing reasons with the “reasons bank” to the right. Some reasons may be used more than once, and some may not be used at all. D Given: j || k, ∠𝐷𝐵𝐸 is a straight angle Prove: 𝑚∠1 + 𝑚∠4 + 𝑚∠7 = 180° E B 3 4 2 1 C Statements 1. j || k ∠𝐷𝐵𝐸 is a straight angle 2. 𝑚∠𝐷𝐵𝐸 = 180° 3. 𝑚∠3 + 𝑚∠4 + 𝑚∠5 = 𝑚∠𝐷𝐵𝐸 4. 𝑚∠3 + 𝑚∠4 + 𝑚∠5 = 180° 5. ∠3 ≅ ∠1, ∠5 ≅ ∠7 6. 𝑚∠3 = 𝑚∠1, 𝑚∠5 = 𝑚∠7 7. 𝑚∠1 + 𝑚∠4 + 𝑚∠7 = 180° k 5 7 Reasons 1. 6 A Reasons Bank a) Angle Addition Postulate b) Substitution Property of Equality c) If 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the alternate interior angles are congruent. d) If 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the corresponding angles are congruent. e) Given f) Definition of congruent angles. g) Definition of a straight angle. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Inequalities in Triangles Class work For each triangle list the sides from greatest to smallest #67-69. 67. 68. 69. B H D 30° A C 65° F 24° 112° E G 76° I 75° For each triangle list the angles in order from greatest to smallest #70-72. 70. 71. 72. L M 5.7 O 4 Geometry: Triangles Q 6.75 2.5 K J 62 43 j 3.8 60 P N ~5~ 5.5 R NJCTL.org Will the three lengths given make a triangle? 73. 2, 3, and 4 74. 1, 3, and 4 75. 5, 6, and 7 76. 16, 8, and 7 77. 20, 10, and 10 78. 8x, 7x, and 14x Given the lengths of two sides of a triangle, what lengths could the third side, x, have? 79. 12 and 14 80. 15 and 6 81. 22 and 22 82. 9 and 12 83. 8y and 10y Inequalities in Triangles Homework For each triangle list the sides from greatest to smallest #84-86. 84. 85. 86. E B H 57° 41° 95° C D A F 63° 80° G 18° I For each triangle list the angles in order from greatest to smallest #87-89. 87. 88. 89. M K H 18 N 10 5 7 G 7 Geometry: Triangles 8 I J L 27 33 11 O ~6~ NJCTL.org List the sides in order from shortest to longest #90-91. 90. 91. H T 75° 40° 80° S 40° 80° V G 75° 70° 110° 40° U F I 60° J Will the three lengths given make a triangle? 92. 21, 34, and 49 93. 11, 31, and 44 94. 8, 6, and 5 95. 12, 5, and 7 96. 20, 30, and 11 97. 9x, 17x, and 26x Given the lengths of two sides of a triangle, what lengths could the third side, x, have? 98. 10 and 21 99. 19 and 8 100. 30 and 30 101. 5 and 15 102. 4y and 14y Similar Triangles Class work 103. Determine if the triangles are similar. If so, write a similarity statement & state the similarity postulate or theorem. a. A D E F b. C B c. G K J M P R H L Geometry: Triangles N ~7~ Q NJCTL.org PARCC type questions: Complete the proof by filling in the missing reasons with the “reasons bank” to the right. Some reasons may not be used at all. 104. Given: DH || FG Prove: ∆𝐷𝐸𝐻~∆𝐺𝐸𝐹 Reasons Bank F D a) If 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the alternate interior angles are congruent. b) If 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the corresponding angles are congruent. c) Given d) Vertical angles are congruent e) AA~ f) SAS~ g) SSS~ E G H Statements 1. DH || FG 2. ∠𝐷 ≅ ∠𝐺 3. ∠𝐷𝐸𝐻 ≅ ∠𝐺𝐸𝐹 4. ∆𝐷𝐸𝐻~∆𝐺𝐸𝐹 Reasons 1. 2. 3. 4. 105. Given: ÐR @ ÐA , PR = 9 , QR = 7.2 , AB = 4.8 , and AC = 6 Prove: ∆𝑄𝑃𝑅~∆𝐵𝐶𝐴 Reasons Bank Statements 1. ÐR @ ÐA , PR = 9 , QR = 7.2 , AB = 4.8 , and AC = 6 2. 𝑃𝑅 𝐶𝐴 𝑃𝑅 9 3 𝑄𝑅 7.2 3 = 6 = 2 , 𝐵𝐴 = 4.8 = 2 𝑄𝑅 Reasons 1. 2. 3. 3. 𝐶𝐴 = 𝐵𝐴 4. ∆𝑄𝑃𝑅~∆𝐵𝐶𝐴 106. a) If the scale factors are the same, then the sides are proportional. b) Given c) AA~ d) Calculating the scale factor between the sides of the triangles. e) SAS~ f) SSS~ 4. Given: ÐA @ ÐD , ÐB @ ÐE Prove: ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶~∆𝐷𝐸𝐹 E Reasons Bank B A C Statements 1. ÐA @ ÐD , ÐB @ ÐE 2. ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶~∆𝐷𝐸𝐹 Geometry: Triangles F D a) b) c) d) AA~ SAS~ SSS~ Given Reasons 1. 2. ~8~ NJCTL.org 107. AB BC CA DE EF FD Prove: ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶~∆𝐷𝐸𝐹 Given: Reasons Bank a) b) c) d) E B A C F D Statements AB BC CA 1. DE EF FD 2. ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶~∆𝐷𝐸𝐹 Reasons 1. 2. In problems 108-111, determine if DE || BC . 108. 110. PARCC type questions: Solve for y. 112. Geometry: Triangles AA~ SAS~ SSS~ Given 109. 111. 113. ~9~ NJCTL.org 114. 115. 116. 117. 118. 119. Geometry: Triangles ~10~ NJCTL.org PARCC type question: Complete the proof by filling in the missing reasons with the “reasons bank” to the right. Some reasons may not be used at all. 120. Prove the Side Splitter Theorem Reasons Bank Given BD ║ AE 𝐵𝐴 𝐷𝐸 Prove 𝐶𝐵 = 𝐶𝐷 a) If 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the alternate interior angles are congruent. b) If 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the corresponding angles are congruent. c) Given d) Reflexive Property of Congruence e) AA~ f) SAS~ g) If two triangles are similar, then their corresponding sides are proportional. h) SSS~ i) Substitution Property of Equality j) Subtraction Property of Equality k) Addition Property of Equality l) Segment Addition Postulate m) Addition Property of Fractions 2 1 2+1 3 (𝑒. 𝑔. 5 + 5 = 5 = 5) n) Simplifying the Equation C B D A E Statements 1. BD ║ AE 2. ∠𝐶 ≅ ∠𝐶 3. ∠𝐶𝐵𝐷 ≅ ∠𝐶𝐴𝐸 4. ∆𝐶𝐵𝐷~∆𝐶𝐴𝐸 𝐶𝐴 𝐶𝐸 5. = 𝐶𝐵 𝐶𝐷 6. CA = CB + BA CE = CD + DE 𝐶𝐵+𝐵𝐴 𝐶𝐷+𝐷𝐸 7. 𝐶𝐵 = 𝐶𝐷 8. 𝐶𝐵 𝐶𝐵 Reasons 1. 2. 3. 4. 𝐵𝐴 𝐶𝐷 5. 6. 7. 𝐷𝐸 + 𝐶𝐵 = 𝐶𝐷 + 𝐶𝐷 𝐵𝐴 𝐷𝐸 9. 9. 1 + 𝐶𝐵 = 1 + 𝐶𝐷 10. 𝐵𝐴 𝐶𝐵 = 8. 𝐷𝐸 𝐶𝐷 10. Similar Triangles Homework 121. Determine if the triangles are similar. If so, write a similarity statement & state the N similarity postulate or theorem. a. b. c. A L E H G K B D Geometry: Triangles C F J ~11~ M P NJCTL.org Q PARCC type questions: Complete the proof by filling in the missing reasons with the “reasons bank” to the right. Some reasons may not be used at all. 122. Given: BD || AE Reasons Bank Prove: ∆𝐴𝐶𝐸~∆𝐵𝐶𝐷 a) If 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the alternate interior angles are congruent. b) If 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the corresponding angles are congruent. Statements Reasons c) Given 1. 1. BD ║ AE d) Reflexive Property of Congruence 2. 2. ∠𝐶 ≅ ∠𝐶 e) AA~ 3. 3. ∠𝐶𝐷𝐵 ≅ ∠𝐶𝐸𝐴 f) SAS~ 4. 4. ∆𝐴𝐶𝐸~∆𝐵𝐶𝐷 g) SSS~ 123. Given: mÐP = 48°, mÐQ = 55° , mÐB = 55° , mÐC = 77° Prove: ∆𝑃𝑄𝑅~∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 Reasons Bank Statements 1. mÐP = 48°, mÐQ = 55° , mÐB = 55° , mÐC = 77° 2. 𝑚∠𝑅 = 77° 3. ∠𝑄 ≅ ∠𝐵, ∠𝑅 ≅ ∠𝐶 4. ∆𝑃𝑄𝑅~∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 a) b) c) d) e) f) Reasons 1. Triangle Sum Theorem Given AA~ SAS~ Definition of congruent angles SSS~ 2. 3. 4. Reasons Bank AB CA , ÐA @ ÐD DE FD Prove: ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶~∆𝐷𝐸𝐹 124. Given: a) b) c) d) E AA~ SAS~ SSS~ Given B A C Statements AB CA 1. , ÐA @ ÐD DE FD 2. ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶~∆𝐷𝐸𝐹 Geometry: Triangles F D Reasons 1. 2. ~12~ NJCTL.org In problems 125-128, determine if DE || BC . 125. 127. PARCC type questions: Solve for y. 129. 131. Geometry: Triangles 126. 128. 130. 132. ~13~ NJCTL.org 133. 134. 135. 136. PARCC type question: 137. Prove the Converse to the Side Splitter Theorem: Complete the proof by filling in the missing reasons with the “reasons bank” to the right. Some reasons may not be used at all. 𝐵𝐴 𝐷𝐸 Given 𝐶𝐵 = 𝐶𝐷 C Reasons Bank Prove BD ║ AE B A Statements 𝐵𝐴 𝐷𝐸 1. 𝐶𝐵 = 𝐶𝐷 𝐵𝐴 𝐷𝐸 D E Reasons 1. 2. 1 + 𝐶𝐵 = 1 + 𝐶𝐷 2. 3. 3. 𝐶𝐵 𝐵𝐴 𝐶𝐷 𝐷𝐸 + 𝐶𝐵 = 𝐶𝐷 + 𝐶𝐷 𝐶𝐵 𝐶𝐵+𝐵𝐴 𝐶𝐷+𝐷𝐸 = 𝐶𝐵 𝐶𝐷 4. 5. CA = CB + BA CE = CD + DE 𝐶𝐴 𝐶𝐸 6. 𝐶𝐵 = 𝐶𝐷 4. 7. ∠𝐶 ≅ ∠𝐶 8. ∆𝐶𝐵𝐷~∆𝐶𝐴𝐸 9. ∠𝐶𝐵𝐷 ≅ ∠𝐶𝐴𝐸 10. BD ║ AE 7. 8. 9. 10. Geometry: Triangles a) If 2 lines are cut by a transversal and the alternate interior angles are congruent, then the lines are parallel. b) If 2 lines are cut by a transversal and the corresponding angles are congruent, then the lines are parallel. c) Given d) Reflexive Property of Congruence e) AA~ f) SAS~ g) SSS~ h) If two triangles are similar, then the corresponding angles are congruent. i) Substitution Property of Equality j) Subtraction Property of Equality k) Addition Property of Equality l) Segment Addition Postulate m) Addition Property of Fractions 2 1 2+1 3 (𝑒. 𝑔. 5 + 5 = 5 = 5) n) Simplifying the Equation 5. 6. ~14~ NJCTL.org Applications Class work 138. You want to know the approximate height of your school building. You place a mirror on the ground and stand where you can see the top of the building in the mirror. How tall is your school? The mirror is 30 feet from the base of the school. You are 36 inches from the mirror and your eyes are 5 feet above the ground. Round your answer to the nearest whole number. 139. You want to know the approximate height of a very tall pine tree. You place a mirror on the ground and stand where you can see the top of the tree in the mirror. How tall is the tree? The mirror is 24 feet from the base of the tree. You are 24 inches from the mirror and your eyes are 6 feet above the ground. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 140. To find the distance d across a lake, you locate the points as shown. Find the value of d. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 120 ft d 15 ft 20 ft Applications Homework 141. You want to know the approximate height of your house. You place a mirror on the ground and stand where you can see the top of your house in the mirror. How tall is your house? The mirror is 25 feet from the base of your house. You are 60 inches from the mirror and your eyes are 5 feet 6 inches above the ground. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 142. You want to know the approximate height of a tall oak tree. You place a mirror on the ground and stand where you can see the top of the tree in the mirror. How tall is the tree? The mirror is 24 feet from the base of the tree. You are 36 inches from the mirror and your eyes are 5 feet above the ground. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. Geometry: Triangles ~15~ NJCTL.org 143. To find the distance d across a lake, you locate the points as shown. Find the value of d. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. 28 ft 15 ft 56 ft d Geometry: Triangles ~16~ NJCTL.org Triangles Review Multiple Choice 1. Identify the triangles by sides and angles a. scalene, acute b. isosceles, obtuse c. scalene, obtuse d. equilateral, equiangular 2. Angle measures of a triangle are given, find the value of x. a. 24 A triangle’s angles are: b. 28 m∠𝐴 = 2x - 1 c. 32 m∠𝐵 = x + 9 d. 30 m∠𝐶 = 3x + 4 3. Classify the triangle by sides and angles. a. scalene, obtuse b. isosceles, acute c. scalene, acute d. isosceles, obtuse 8 12 10 4. Using the figure at right, list the segments from least to greatest. ̅̅̅̅ , 𝐴𝐶 ̅̅̅̅ , 𝐵𝐶 ̅̅̅̅ , 𝐴𝐷 ̅̅̅̅, 𝐷𝐶 ̅̅̅̅ a. 𝐵𝐶 ̅̅̅̅ , ̅̅̅̅ b. ̅̅̅̅ 𝐴𝐵 , 𝐵𝐶 𝐴𝐶 , ̅̅̅̅ 𝐴𝐷 , ̅̅̅̅ 𝐷𝐶 ̅̅̅̅ ̅̅̅̅ ̅̅̅̅ ̅̅̅̅ ̅̅̅̅ c. 𝐴𝐷, 𝐷𝐶 , 𝐴𝐶 , 𝐴𝐵 , 𝐵𝐶 d. cannot be determined 5. Use the diagram to find the value of x. a. 130 b. 125 c. 120 d. 110 6. Which of the following values cannot be the third side of a triangle if two of the sides are 14 and 20? a. 18 b. 20 c. 32.5 d. 34 Geometry: Triangles ~17~ NJCTL.org 7. Decide whether the triangles are similar. If so, write a similarity statement. a. b. c. d. Yes, DABC : DDEF Yes, DABC : DDFE Yes, DABC : DFDE The triangles are not similar 8. Determine if the triangles are similar. If so, state the similarity postulate or theorem. a. b. c. d. Yes, by AA~ Yes, by SSS~ Yes, by SAS ~ The triangles are not similar 9. Determine if the triangles are similar. If so, state the similarity postulate or theorem. B a. b. c. d. C A Yes, by AA~ Yes, by SSS~ Yes, by SAS ~ The triangles are not similar D E 10. Solve for y a. b. c. d. 8 4.5 6 12 Geometry: Triangles ~18~ NJCTL.org 11. Solve for x F E 6 10 G 8 D a. b. c. d. H x 4 4.8 10 12.8 Short Constructed Response – Write the correct answer for each question. No partial credit will be given. 12. Find the values of x and z. x 2x-10 40 z 13. ∆𝐽𝐾𝐿~∆𝑁𝑃𝑀. Find the values if x & y K P 12 9 J L x 13.5 15 M Geometry: Triangles y ~19~ N NJCTL.org 14. To find the distance d across a stream, you locate the points as shown. Find the value of d. 200 ft d 21 ft 28 ft Extended Constructed Response – Write the correct answer for each question. Partial credit will be given. 15. Complete the proof by filling in the missing reasons with the “reasons bank” to the right. Some reasons may not be used at all. Given BD ║ AE Reasons Bank Prove ∆𝐵𝐶𝐷~∆𝐴𝐶𝐸 a) If 2 parallel lines are cut by a C transversal, then the alternate interior angles are congruent. b) If 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the corresponding angles are congruent. c) Reflexive Property of Congruence B D d) AA~ e) SAS~ f) Given A E g) SSS~ Statements Reasons 1. 1. BD ║ AE 2. 2. ∠𝐶 ≅ ∠𝐶 3. 3. ∠𝐶𝐵𝐷 ≅ ∠𝐶𝐴𝐸 4. 4. ∆𝐵𝐶𝐷~∆𝐴𝐶𝐸 Geometry: Triangles ~20~ NJCTL.org Answers 1. Scalene 2. Isosceles 3. Isosceles 4. Equilateral and isosceles 5. Scalene 6. Right 7. Equiangular & acute 8. Obtuse 9. Acute 10. Obtuse 11. Never 12. Always 13. Sometimes 14. Sometimes 15. Sometimes 16. Sides: Isosceles, Angles: Acute 17. Sides: Scalene, Angles: Obtuse 18. Sides: Isosceles, Angles: Obtuse 19. Sides: Scalene, Angles: Right 20. Sides: Isosceles, Angles: Obtuse 21. Scalene 22. Isosceles 23. Equilateral and isosceles 24. Isosceles 25. Scalene 26. Equiangular & acute 27. Right 28. Obtuse 29. Obtuse 30. Acute 31. Never 32. Never 33. Sometimes 34. Never 35. Sometimes 36. Sides: Scalene, Angles: Right 37. Sides: Scalene, Angles: Obtuse 38. Sides: Isosceles, Angles: Obtuse 39. Sides: Isosceles, Angles: Acute 40. Sides: Isosceles, Angles: Acute 41. X=58° 42. X=33° 43. X=23° 44. X=30° 45. X=79°, z=144°, y=55° 46. X=12 Geometry: Triangles 47. X=27 48. X=76°, y=104°, z=55° 49. j = 47, k = 180, m = 155, n = 25, p = 94, q = 61 50. r = 35, t = 145, u = 35, v = 90, w = 125 51. a = 54, b = 36, c = 36, d = 116, e = 152, f = 28, g = 98, h = 54 52. j = 128, k = 52, m = 52, n = 31, p = 149, q = 31, r = 49, t = 131 53. X=61° 54. X=31 55. X=37 56. X=27 57. X=32 58. X=96°, z=151°, y=68 59. X=66°, z=88°, y=79° 60. Z=90°, y=43°, x=71° 61. X=95°, y=51°, z=39° 62. a = 127, b = 90, c = 143, d = 37, e = 74, f = 111 63. g = 49, h = 117, j = 49, k = 76, m = 55 64. a = 143, b = 37, c = 37, d = 121, e = 158, f = 22, g = 108, h = 50 65. r = 90, t = 38, u = 38, v = 34, w = 146, x = 34, y = 30, z = 150 66. Statements Reasons 1. j || k 1. e ∠𝐷𝐵𝐸 is a straight angle 2. g 2. 𝑚∠𝐷𝐵𝐸 = 180° 3. a 3. 𝑚∠3 + 𝑚∠4 + 𝑚∠5 = 𝑚∠𝐷𝐵𝐸 4. b 4. 𝑚∠3 + 𝑚∠4 + 𝑚∠5 = 180° 5. c 5. ∠3 ≅ ∠1, ∠5 ≅ ∠7 6. f 6. 𝑚∠3 = 𝑚∠1, 𝑚∠5 = 𝑚∠7 7.b 7. 𝑚∠1 + 𝑚∠4 + 𝑚∠7 = 180° AC, BC, AB 68. DF, EF, DE 69. GI, HI, HG 67. ~21~ NJCTL.org 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. <K, <L, <J <N, <M, <O <P, <Q, <R yes no yes no no yes 2 < x < 26 9 < x < 21 0 < x < 44 3 < x < 21 2y < x < 18y 105. Statements 1. ÐR @ ÐA , PR = 9 , QR = 7.2 , AB = 4.8 , and AC = 6 2. 𝐶𝐴 𝑃𝑅 9 3 𝑄𝑅 7.2 3 = 6 = 2 , 𝐵𝐴 = 4.8 = 2 𝑄𝑅 106. Statements 1. ÐA @ ÐD , ÐB @ ÐE 2. DABC : DDEF 107. Statements AB BC CA 1. DE EF FD 2. DABC : DDEF 87. <H @ <I, <G 88. <K, <J, <L 89. <N, <M, <O 90. UV,TV,UT ,ST ,SU 2. d 3. a 4. e Reasons 1. d 2. a Reasons 1. d 2. c 108. yes 109. no 110. no 111. yes 112. 12 113. 11.36 52 114. 15 = 3.46̅ 115. 11.2 116. 4.5 117. 9.2 118. 18 119. 5 91. FJ,GF,GJ,GH, HJ, HI, JI 92. yes 93. no 94. yes 95. no 96. yes 97. no 98. 11< x < 31 99. 11 < x < 27 100. 0 < x < 60 101. 10 < x < 20 102. 10y < x < 18y 103. a. not similar b. yes ∆𝐺𝐻𝐽~∆𝐿𝐽𝐾 by SAS c. not similar 104. Statements Reasons 1. c 1. DH || FG 120. Statements 1. BD ║ AE 2. ∠𝐶 ≅ ∠𝐶 3. ∠𝐶𝐵𝐷 ≅ ∠𝐶𝐴𝐸 4. ∆𝐶𝐵𝐷~∆𝐶𝐴𝐸 2. a 3. d 4. e 𝐶𝐴 𝐶𝐸 5. 𝐶𝐵 = 𝐶𝐷 6. CA = CB + BA CE = CD + DE 𝐶𝐵+𝐵𝐴 𝐶𝐷+𝐷𝐸 7. = 8. Geometry: Triangles 𝑃𝑅 3. 𝐶𝐴 = 𝐵𝐴 4. DQPR : DBCA BC, AB, AC 85. EF, DE, DF 86. GI, HI,GH 2. ∠𝐷 ≅ ∠𝐺 3. ∠𝐷𝐸𝐻 ≅ ∠𝐺𝐸𝐹 4. DDEH : DGEF Reasons 1. b ~22~ 𝐶𝐵 𝐶𝐵 𝐵𝐴 + 𝐶𝐵 𝐶𝐵 = 𝐶𝐷 𝐶𝐷 𝐷𝐸 + 𝐶𝐷 𝐶𝐷 Reasons 1. c 2. d 3. b 4. e 5. g 6. l 7. i 8. m NJCTL.org 𝐵𝐴 𝐷𝐸 9. 1 + 𝐶𝐵 = 1 + 𝐶𝐷 10. 𝐵𝐴 𝐶𝐵 = 𝐷𝐸 𝐶𝐷 9. n 127. no 128. no 129. 10 130. 11.25 131. 10 132. 6 133. 4.5 134. 11.4 135. 8 136. 16.2 10. j 121. a. yes, ∆𝐴𝐵𝐷~∆𝐴𝐶𝐷 by AA~ or SAS~ b. not similar c. yes, ∆𝐾𝐿𝑀~∆𝑄𝑁𝑃 by SSS~ 122. Statements 1. BD ║ AE 2. ∠𝐶 ≅ ∠𝐶 3. ∠𝐶𝐷𝐵 ≅ ∠𝐶𝐸𝐴 4. ∆𝐶𝐵𝐷 ≅ ∆𝐶𝐴𝐸 123. Statements 1. mÐP = 48°, mÐQ = 55° , mÐB = 55° , mÐC = 77° 2. 𝑚∠𝑅 = 77° 3. ∠𝑄 ≅ ∠𝐵, ∠𝑅 ≅ ∠𝐶 4. DPQR : DABC 124. Statements AB CA 1. , ÐA @ ÐD DE FD 2. DABC : DDEF Reasons 1. c 2. d 3. b 4. e 137. Statements 𝐵𝐴 𝐷𝐸 1. 𝐶𝐵 = 𝐶𝐷 𝐵𝐴 Reasons 1. b 2. a 3. e 4. c Reasons 1. d 125. yes 126. yes 𝐷𝐸 2. 1 + 𝐶𝐵 = 1 + 𝐶𝐷 2. k 3. 3. n 𝐶𝐵 𝐵𝐴 𝐶𝐷 𝐷𝐸 + 𝐶𝐵 = 𝐶𝐷 + 𝐶𝐷 𝐶𝐵 𝐶𝐵+𝐵𝐴 𝐶𝐷+𝐷𝐸 = 𝐶𝐷 𝐶𝐵 4. 5. CA = CB + BA CE = CD + DE 𝐶𝐴 𝐶𝐸 6. 𝐶𝐵 = 𝐶𝐷 4. m 7. ∠𝐶 ≅ ∠𝐶 8. ∆𝐶𝐵𝐷~∆𝐶𝐴𝐸 9. ∠𝐶𝐵𝐷 ≅ ∠𝐶𝐴𝐸 10. BD ║ AE 7. d 8. f 9. h 10. b 138. 139. 140. 141. 142. 143. 2. b Reasons 1. c 5. l 6. i 50 feet 72 ft 90 ft 27.5 feet 40 ft 45 ft Unit Review Answer Key 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. c 9. a 10. a 11. d 12. x = 50 & z = 90 13. x = 18 & y = 22.5 14. 150 ft c b c b b d c Geometry: Triangles ~23~ NJCTL.org 15. Statements 1. BD ║ AE 2. ∠𝐶 ≅ ∠𝐶 3. ∠𝐶𝐵𝐷 ≅ ∠𝐶𝐴𝐸 4. ∆𝐵𝐶𝐷~∆𝐴𝐶𝐸 Geometry: Triangles Reasons 1. f 2. c 3. b 4. d ~24~ NJCTL.org