Astronomy Review
advertisement

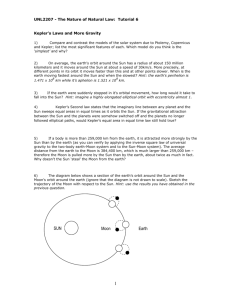
Astronomy Review Indicate areas of focus for test The Earth’s sun is an average-sized star. The Sun is more than a million times greater in volume than the Earth. Life on Earth is dependent on the energy produced by the Sun. Other stars are like the Sun but are so far away that they look like points of light. Distances between the stars are vast compared to distances within our solar system. Our solar system is quite small compared to the vastness that reaches out beyond Pluto. The Sun and planets that revolve around it are the major bodies in the solar system. Other members include comets, moons, and asteroids. Earth’s orbit is nearly circular. comet- a ball of ice and dust in orbit moon- the natural satellite of the earth, visible (chiefly at night) by reflected light from the sun. asteroid- objects revolving around the Sun that are too small to be considered planets Gravity is the force that keeps planets in orbit around the Sun and the Moon in orbit around the Earth. The amount of gravitational pull is determined by 2 factors: the mass of the objects the distance between them Objects in orbit in space remain in orbit because of inertia and the force of gravity Most objects in the solar system have a regular and predictable motion. These motions explain such phenomena as a day, a year, phases of the Moon, eclipses, tides, meteor showers, and comets. day- 24 hours caused by the rotation of the Earth year- 365 ¼ days caused by the Earth’s revolution around the Sun phases- different shapes of the moon as seen from Earth caused by the changes in the relative positions of the Earth, Sun, and Moon. eclipse - the partial or total blocking of an object by another o solar Moon blocks Sun o lunar Earth blocks Moon tides- the rise and fall of the level of water in the oceans caused by the Moon’s gravitational pull meteor showers- meteorites entering the Earth’s atmosphere causing streaks of light comets – become visible on Earth when their orbit brings them closer to the sun The latitude/longitude coordinate system and our system of time are based on celestial observations. Early Astronomers were able to look to the constellations to determine that the earth was moving at a predictable rate. Moons are seen by reflected light. Our Moon orbits Earth, while Earth orbits the Sun. The Moon’s phases as observed from Earth are the result of seeing different portions of the lighted area of the Moon’s surface. The phases repeat in a cyclic pattern in about one month. “d” dying (waning) “b” born (waxing) The apparent motions of the Sun, Moon, Planets, and stars across the sky can be explained by Earth’s rotation and revolution. Earth’s rotation causes the length of one day to be approximately 24 hours. This rotation also causes the Sun and Moon to appear to rise along the eastern horizon and to set along the western horizon. Earth’s revolution around the Sun defines the length of the year to be 365 1/4 days. rotation (rotate) - the spinning motion of a planet on its axis the earth rotates on its axis once every 24 hours, causing day and night revolution (revolve) – the movement of objects around another object orbit the path of an object as it revolves around another object in space the earth revolves around the sun once every 365 ¼ days (a year) causing seasons The tilt of Earth’s axis of rotation and the revolution of Earth around the sun cause seasons on Earth. The length of daylight varies depending on latitude and season. Summer Solstice (June 21)- the longest day of the year Winter Solstice (December 21)- the shortest day of the year Vernal Equinox (March 21)- equal day/night Autumnal Equinox (September 21)- equal day/night The shape of Earth, the other planets, and stars are nearly spherical.