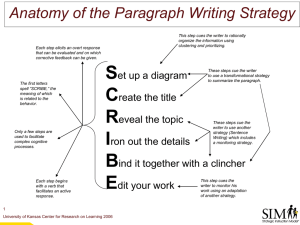
synthesized ed
advertisement

Ed.D. Qualifying Paper Evaluation Rubric The Qualifying Paper is a substantial review of approximately 50-60 focusing on a critical analysis of the literature on a topic. The review is both descriptive and evaluative of an area of inquiry of scholarly work done in the past. The review generally identifies some topic, theme, or point to emphasize that evolved as a result of readings. Occasionally a research question is proposed to guide the review. The review is a report of primary or original scholarship of mostly written documents. It is not merely a summary of the literature, but a thoughtful and comprehensive analysis and synthesis that places the topic in the context of work in the field. A good review results in a synthesis of the literature, formulating conclusions and recommendations and thus placing the topic in an updated context of established work in the discipline. Ideas and Content EE The topic is clearly defined; its development reflects knowledge of the issues in the area of study. a. Ideas are based on current or future leadership problems. b. Ideas are presented clearly and contribute to the development of the topic. c. The writing clearly and accurately reflects knowledge of the important issues in the area of study; the discussion of these reflects insight into them. d. Specific details support the central idea. ME The writer defines the topic, even though the development is still basic. a. Ideas are based on current or future leadership problems. b. Ideas are reasonably clear, though they may not be detailed, accurate, or expanded enough to show in-depth understanding or development. c. The writing draws on knowledge of the important issues in the area of study. However, these ideas are discussed in ways that make it difficult to assess their contribution to the development of the topic. d. It is easy to see where the writer is headed, though more information is needed to “fill in the blanks.” e. The writer generally stays on topic but does not develop a clear theme(s). DNME As yet, the paper has no clear sense of purpose or central theme. To extract meaning from the text, the reader must make inferences based on sketchy or missing details. The writing reflects more than one of the following problems. a. The writer is still in search of a topic or has not begun to define the topic in a meaningful way. b. Information is very limited or unclear; inaccuracies are apparent. c. The text may be repetitious or may read like a collection of disconnected random thoughts. d. Everything seems as important as everything else; the reader has a hard time sifting out what the writer is trying to say. Organization EE The organization parallels that outlined in Section 3 – Qualifying Paper of the Doctoral Student Handbook. The organization enhances the central idea(s) or theme(s). a. The introduction captures the reader’s interest; the conclusion leaves the reader with a sense of closure. -1- b. The order, structure, or presentation of information is cohesive, enabling the reader to move easily through the text. c. Thoughtful transitions clearly show how ideas connect. d. Details fit where they are placed; sequencing is logical and effective. e. Pacing is well controlled; the writer knows when to elaborate and when such elaboration becomes cumbersome. f. Organization flows smoothly; the reader hardly thinks about it. ME The organizational structure is strong enough to move the reader through the text without too much confusion. a. The introduction may not capture the reader’s interest; the conclusion may not tie-up loose ends. b. The order, structure, or presentation of information is at time disjointed. c. Transitions often work well; at other times connections between ideas seem fuzzy. d. Sequencing shows some logic, but it is not under control enough to consistently provide support for the ideas being developed. e. Pacing is fairly well controlled, though the writer sometimes lunges ahead too quickly or spends too much time on details that do not matter. f. The organization sometimes supports the main idea(s) or theme(s). At other times the reader feels an urge to add a transition or move things around. DNME The writing lacks a clear sense of direction. Ideas and details seem strung together in a loose or random fashion; there is no identifiable internal structure. The writing reflects more than one of the following problems. a. There is no introduction to set up what follows; no real conclusion is present to wrap things up. b. The connections between ideas are confusing or not even present. c. Sequencing needs work. d. Pacing feels awkward; the writer slows to a crawl when the reader wants to get on and vise-versa. Writing Style and Conventions EE The writer demonstrates a good grasp of standard writing conventions (e.g., spelling, punctuation, capitalization, grammar, usage, paragraphing, and APA formatting. These conventions are used effectively to enhance readability. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. ME APA formats and styling are correct; few if any errors exist. References are cited correctly in the text, reference list, and bibliography. Grammar and usage are correct and contribute to clarity and style. Punctuation and capitalization are correct. Paragraphing tends to be sound and reinforces the organizational structure. The writer manipulates conventions – especially grammar – for stylistic effect. Errors tend to be few in number; only minor editing is necessary. The writer shows reasonable control over a limited range of standard writing conventions. Conventions are sometimes handled well and enhance readability; at other times errors are distracting and impair readability. a. APA formatting and styling are usually correct. b. References are generally cited correctly, but some errors exist in the text, reference list, or bibliography. -2- c. Grammar and usage are usually correct; some decoding is needed to comprehend the paper. d. Internal punctuation (e.g., commas, apostrophes, semi-colons; dashes, colons, parentheses, quotation marks) is sometimes missing or wrong. This contributes to possible misunderstanding and stylistic concerns. e. Paragraphing is attempted but may run together or begin in the wrong places. f. The writing and errors in it detract from the writer’s style. g. Moderate editing is necessary to correct problems. DNME Errors in spelling, punctuation, capitalization, usage and grammar, and/or paragraphing repeatedly distract the reader and make the text difficult to read. The writing reflects one or more of the following problems. a. APA formats and style are frequently incorrect. b. References are frequently cited incorrectly in the text, reference list, or bibliography. c. Errors in grammar or usage are very noticeable and affect meaning and detract from the writer’s style. d. Paragraphing is missing, irregular, or so frequent that it has no relationship to the organizational structure of the text. e. The reader must read once to decode, then again for meaning. f. Extensive editing would is needed to correct problems. Critical Thinking EE Higher order thinking is consistently demonstrated through original, creative treatment of the topic. a. The reviewed literature fully covers the existing research base for the topic. b. Thoughtful consideration is given to others’ research; this research has been thoroughly analyzed and synthesized. c. Patterns related to existing research are clearly tied to the writer’s ideas and the research topic. d. A thorough analysis of supporting theorists’ works and ideas is discussed. ME Higher order thinking is present. a. Reviewed research generally covers the topic; gaps may be evident. b. Consideration is given to others’ research; this research is frequently reported rather than synthesized. c. Patterns related to existing research are identified but are not clearly tied to the writer’s ideas or the research topic. d. Supporting theory is presented but is not explicitly tied to the writer’s ideas. Gaps may be evident. DNME Higher order thinking is not present or present at a minimal level. One or more of the following problems are present. a. Reviewed research is minimal and does not cover the topic. b. Little or no consideration is given to others’ research. This research is consistently reported rather than synthesized. c. Arguments connecting existing research, theories, and the research topic have not been developed. d. Supporting theory is not adequately presented or not connected to the writer’s ideas. -3- Feedback for the Qualifying Paper Candidate’s Name: Committee Members: Date: Rating Dimension Ideas and Content Rating1 Comments2 Organization Conventions Critical Thinking Scoring Summary Scoring for Each Dimension □ Each dimension is rated ME or above. OR □ At least one dimension is rated below ME. OR □ Fewer than two dimensions are rated EE. Scoring for the Whole Paper □ A minimum of two dimensions are rated EE Acceptance □ The paper is accepted with commendation. □ The paper is accepted without revisions □ The paper is accepted with minor revisions □ The paper requires revisions before being accepted _______________________ Committee Advisor ________________________ Committee Member 1EE designates Exceeding Expectations, ME Meeting Expectations, and DNME Does Not Meet Expectations 2Any rating of DNME must include rater’s comments justifying the rating; examples from the paper exemplifying the concerns are encouraged. -4-