PFC2 Chapter 23 Section 1 Guided Reading What is an
advertisement

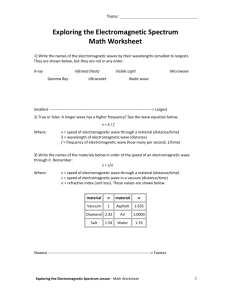
PFC2 Chapter 23 Section 1 Guided Reading 1. What is an electromagnetic wave? 2. How do radio towers make radio waves? 3. Which has more energy: an x-ray (higher frequency) or a microwave (lower frequency)? 4. What is the electromagnetic spectrum? 5. What fraction of a meter is 1 nanometer? 6. As the frequency of an electromagnetic wave increases, its wavelength _______________. 7. The energy of an electromagnetic wave is proportional to its _______________. 8. Why does light travel slower through glass than through a vacuum? 9. Write the equation for the index of refraction for a material as shown on page 547. 10. The frequency of an electromagnetic wave stays the same as it travels through a refractive material. What happens to the wavelength? 11. Fill in the type of low-energy electromagnetic wave next to its definition. a. wavelengths greater than 30 cm b. wavelengths between 30 cm and 1 mm c. wavelengths between 1 mm and 700 nm d. wavelengths between 700 nm and 400 nm 12. Fill in the type of high-energy electromagnetic wave next to its definition. a. wavelengths between 400 nm and 10 nm b. wavelengths between 10 nm and around 0.001 nm c. wavelengths less than ten-trillionths of a meter 13. Which type of electromagnetic wave is used by cell phone transmitters? 14. Which type of electromagnetic wave causes sunburn?