OBEY THE LAW!!
advertisement

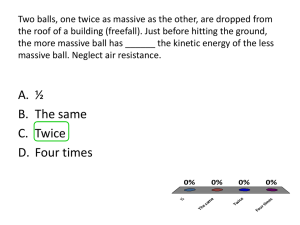
Group Member Names Period____ ________________________ ____________________________ __________________________ _____________________________ ________________________ OBEY THE LAW!! (The Law of Conservation of Energy) INTRODUCTION The LAW of Conservation of Energy states that energy can’t be created or destroyed – it can only be converted between types and forms of energy. The two types of energy are potential and kinetic. A car at the top of a hill has stored potential energy due to the attractive force of gravity. The amount of Potential energy (PE) it has depends on the height, it’s mass, and the force of gravity. This can be written as an equation: PE =mgh where, m =mass (in kg), g = 9.8 m/s2, and h = height it falls (in m). The units of energy are kg m2/s2 which is called a Joule (J). According to the law, all of this stored potential energy should be converted into the kinetic energy (KE) of motion. In other words, ALL the potential energy it had at the top should be completely converted into kinetic energy at the bottom of the hill. The amount of KE the car has depends on its speed at the bottom and it’s mass. The equation is: KE =1/2mvmax2 where, m =mass (in kg), and vmax is the maximum velocity at the bottom of the ramp (in m/s). The law tells us that for the car on the ramp PE = KE. In this lab you will calculate the PE of the car on a ramp at a certain height. You will find the KE of the car by measuring the maximum velocity of the car using the Labquest2. OBJECTIVES 1. Prove the Law of Conservation of Energy for a car on a ramp; 2. Become proficient in the metric system by using the mks (meters/kilograms/seconds) metric system to calculate energy in Joules; 3. Recognize the forms and types of energy. 4. Decompress and get back to normal after PACE and the winter vacation Group Member Names Period____ ________________________ ____________________________ __________________________ _____________________________ ________________________ MATERIALS LIST CPO Car on a Ramp apparatus Vernier Labquest2 Motion Detector Meter stick PROCEDURE Note: You will measure the motion of two different cars with different masses on two different car ramp stands. You will perform two runs for each stand and use your best run to include in the data table. For Each Car Ramp: 1. Connect the car ramp’s Motion Detector to the DIG/ 1 channel of your Labquest. Set the Motion Detector switch to the Car position. 2. Adjust the head of the detector so that it is pointing straight down the ramp 3. Set up the Labquest: Tap the number on the probe screen. Change units to meters; set the sample rate to 50 samples/sec; set the duration to 120 sec. 4. Place the car on the track at the bottom end stop. Click ► to begin data collection. You will hear a clicking sound from the Motion Detector. Wait about a second, then push the car slowly up to the top of the ramp, then let it go so it accelerates to the bottom of the ramp. Press ■ to stop the data collection. 5. Examine the position vs. time graph. Does the data look like you expect it to? Is it smooth and reliable? Repeat Step 4 if your position vs. time graph does not show an area of smoothly increasing position. Make sure the velocity graph shows a smooth bell curve. 6. Press the file cabinet to store your run. Repeat steps 1-5 until you have 2 good sets of data. 7. Record the maximum velocity value for your best run in the data table for each ramp. 8. Measure the mass of the car using a digital scale and record the value in the data table. 9. Measure the height the car fell: this is the difference between the height of the car at the top of the ramp and the height at the bottom of the ramp. Record this difference in the table. 10. Save your file using this naming format: Energy Lab 1 Lastname_Pn, where lastname is for the person signing out Labquest; and n = your period number. 11. Repeat all steps for the other ramp with a different mass. 12. Perform the energy calculations and fill in the data table for each ramp. Group Member Names Period____ ________________________ ____________________________ __________________________ _____________________________ ________________________ 13. Calculate the Energy loss: % Energy Loss = (PE-KE)/PE x100 (%) DATA Best Run Mass (kg) Height Fallen (m) PE (J) =mgh Vmax (m/s) KE (J) PE-KE Energy =1/2mvmax2 (J) Loss % Ramp 1 Ramp 2 POST LAB QUESTIONS 1. Was the LAW obeyed? 2. Explain why or why not? 3. List ALL the forms of energy that the PE was converted into, and describe how you observed each. 4. Which energy loss was most significant? How could you improve this experiment so that the LAW would be obeyed? Group Member Names Period____ ________________________ ____________________________ __________________________ _____________________________ ________________________ 5. Design your own experiment to prove the LAW of conservation of energy - can you think of one that might give you a better result than the car on a ramp? Describe how energy might be lost in your experiment. Draw a diagram of your set up ad give a brief procedure.