lab 13a
advertisement
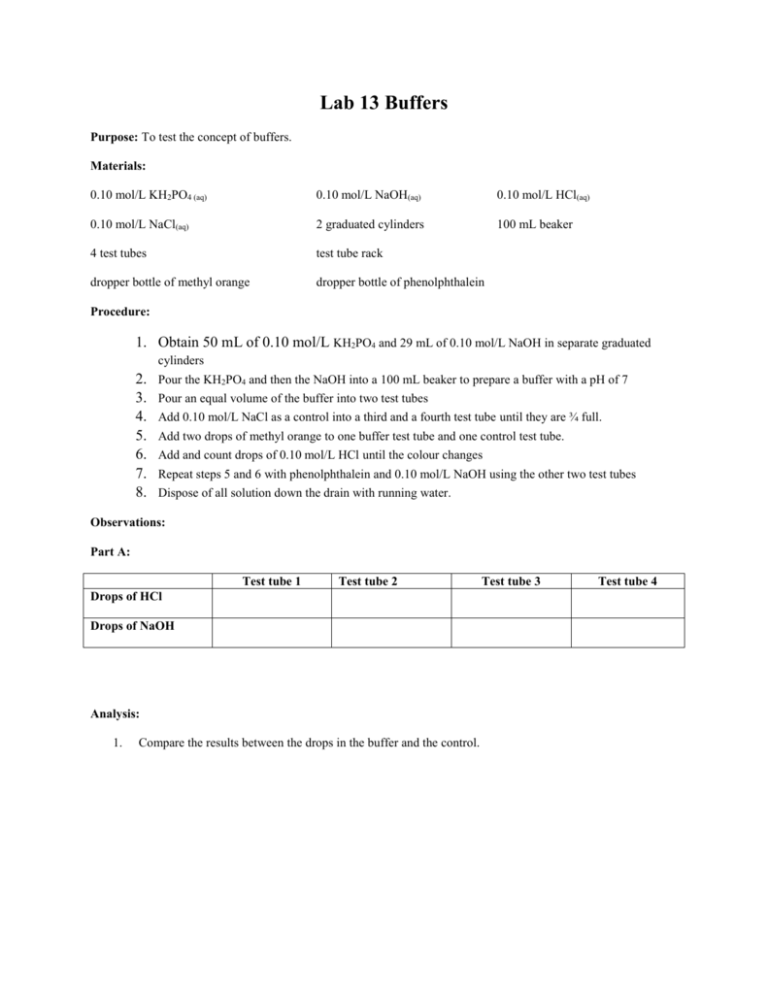
Lab 13 Buffers Purpose: To test the concept of buffers. Materials: 0.10 mol/L KH2PO4 (aq) 0.10 mol/L NaOH(aq) 0.10 mol/L HCl(aq) 0.10 mol/L NaCl(aq) 2 graduated cylinders 100 mL beaker 4 test tubes test tube rack dropper bottle of methyl orange dropper bottle of phenolphthalein Procedure: 1. Obtain 50 mL of 0.10 mol/L KH2PO4 and 29 mL of 0.10 mol/L NaOH in separate graduated cylinders 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Pour the KH2PO4 and then the NaOH into a 100 mL beaker to prepare a buffer with a pH of 7 Pour an equal volume of the buffer into two test tubes Add 0.10 mol/L NaCl as a control into a third and a fourth test tube until they are ¾ full. Add two drops of methyl orange to one buffer test tube and one control test tube. Add and count drops of 0.10 mol/L HCl until the colour changes Repeat steps 5 and 6 with phenolphthalein and 0.10 mol/L NaOH using the other two test tubes Dispose of all solution down the drain with running water. Observations: Part A: Test tube 1 Test tube 2 Drops of HCl Drops of NaOH Analysis: 1. Compare the results between the drops in the buffer and the control. Test tube 3 Test tube 4 2. Provide an explanation for the difference between acid required to change the indicator in the buffer and in the control. 3. Describe an application of a buffer solution. 4. How is buffering action displayed on a pH curve?