Genetics Notes
advertisement
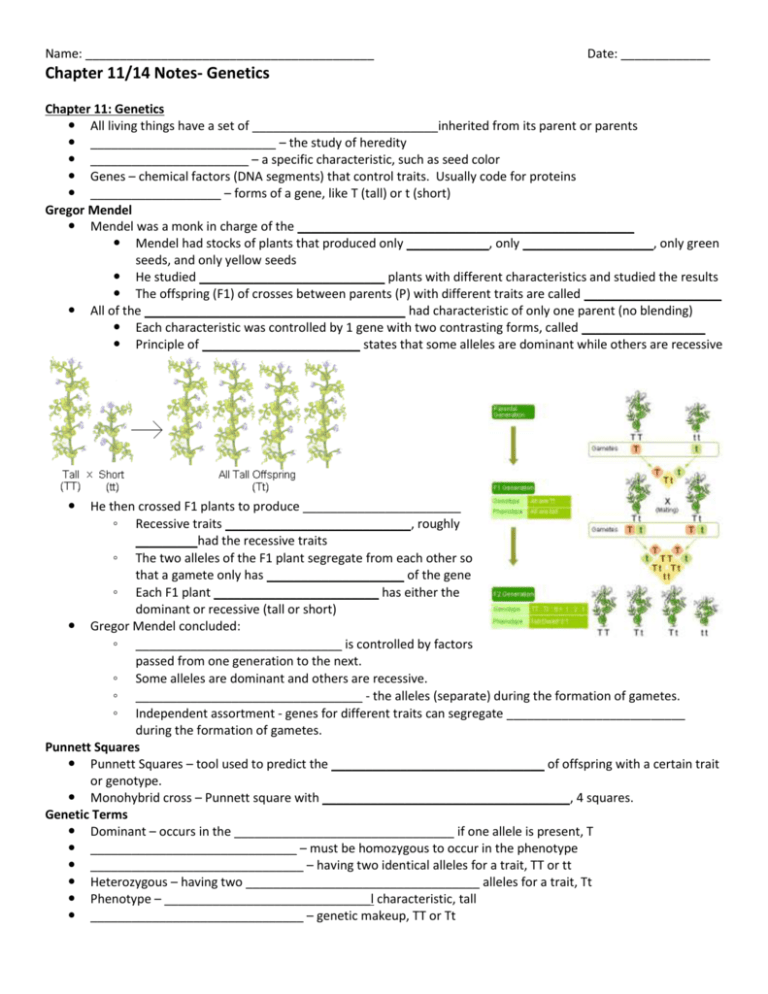
Name: __________________________________________ Date: _____________ Chapter 11/14 Notes- Genetics Chapter 11: Genetics All living things have a set of ___________________________inherited from its parent or parents ___________________________ – the study of heredity _______________________ – a specific characteristic, such as seed color Genes – chemical factors (DNA segments) that control traits. Usually code for proteins ___________________ – forms of a gene, like T (tall) or t (short) Gregor Mendel Mendel was a monk in charge of the _________________________________________________ Mendel had stocks of plants that produced only ____________, only ___________________, only green seeds, and only yellow seeds He studied ___________________________ plants with different characteristics and studied the results The offspring (F1) of crosses between parents (P) with different traits are called ____________________ All of the ______________________________________ had characteristic of only one parent (no blending) Each characteristic was controlled by 1 gene with two contrasting forms, called __________________ Principle of _______________________ states that some alleles are dominant while others are recessive He then crossed F1 plants to produce _______________________ ◦ Recessive traits ___________________________, roughly _________had the recessive traits ◦ The two alleles of the F1 plant segregate from each other so that a gamete only has ____________________ of the gene ◦ Each F1 plant ________________________ has either the dominant or recessive (tall or short) Gregor Mendel concluded: ◦ ______________________________ is controlled by factors passed from one generation to the next. ◦ Some alleles are dominant and others are recessive. ◦ _________________________________ - the alleles (separate) during the formation of gametes. ◦ Independent assortment - genes for different traits can segregate __________________________ during the formation of gametes. Punnett Squares Punnett Squares – tool used to predict the _______________________________ of offspring with a certain trait or genotype. Monohybrid cross – Punnett square with ____________________________________, 4 squares. Genetic Terms Dominant – occurs in the ________________________________ if one allele is present, T ______________________________ – must be homozygous to occur in the phenotype _______________________________ – having two identical alleles for a trait, TT or tt Heterozygous – having two __________________________________ alleles for a trait, Tt Phenotype – ______________________________l characteristic, tall _______________________________ – genetic makeup, TT or Tt Monohybrid Cross Dihybrid Cross Since alleles can segregate _______________________, the inheritance of one trait doesn’t affect the inheritance of another (seed color and seed shape) A dihybrid cross involves crossing two _____________________________traits of the F1 generation (both parents are heterozygous for both traits) Complex Forms of Inheritance Some alleles are neither dominant or recessive, and many traits are controlled by multiple alleles or multiple genes ________________________________ – both alleles are present in the phenotype, the black and white chicken, blood types Incomplete dominance – the alleles ________________________ to produce the phenotype, red + white = pink _______________________________________ – more than 2 alleles are possible choices, although only 2 can be used at a time, ex. ABO blood groups, rabbit coat color _____________________________________________________ – controlled by 2 or more genes, ex. skin color Sometimes expression is also affected by the environment; height and flower color of a sunflower are affected by genes and climate, soil, and water availability Sex-linked Genes that are located on sex chromosomes are said to be _________________________ genes ◦ Since males only have 1 X chromosome, all X-linked alleles are _____________________, even if recessive ◦ For females, a _________________________ allele must be with another recessive to be expressed ◦ _______________________________ and hemophilia are examples Chapter 14: Heredity Human Heredity A _________________________________ is a picture of chromosomes arranged in their pairs (46, 23 pairs in humans) _______________ _________________ All egg cells carry an X chromosome, half sperm cells carry an X, half a Y ◦ Leads to half combined becoming either XY, or XX ___________________________________ are non-sex chromosomes, labeled pairs 1-22 chromosomes ________________ chromosomes are the 23rd pair of chromosomes To study how traits are passed from generation to generation a _____________________________ chart is used ◦ Males are ___________________________ ◦ Females are ___________________________ ◦ _______________________ circle/squares have the trait ◦ Horizontal lines represent marriage ◦ Vertical lines connect parents to their ____________________________ White forelock (lock of hair just above the forehead) is dominant Many disorders are caused by an autosomal recessive allele (disease is only apparent in the _____________________________recessive condition) Some disorders are expressed with only one allele (dominant), which means the disease is apparent in the ______________________________ condition Some disorders are caused by a co-dominant alleles Disorder(s) Inheritance pattern Symptoms Cystic fibrosis Simple (autosomal) recessive Mucus in lungs, digestive tract, liver Sickle cell disease Sickle shaped red blood cells; joint pain, an Huntington’s disease Simple (autosomal) recessive (codominant on molecular level) Simple (autosomal) dominant Colorblindness Sex-linked recessive Mental deterioration and uncontrollable movements; onset -35-50 Difficulty discerning colors Hemophilia Sex-linked recessive Blood doesn’t clot correctly, missing Facto Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) Trisomy (3 chromosomes instead of 2) Mild to severe mental retardation ___________________________________________ leads to serious digestive problems ◦ Thick, heavy mucus clogs lungs and breathing passages ◦ Since it is recessive, must have 2 alleles to be affected _________________________________ disease leads to bent/twisted shape of RBCs (can clog in capillaries) ◦ Heterozygous individuals are generally healthy and more resistant to malaria Down syndrome (____________________________) ◦ Nondisjunction occurs when homologous chromosomes don’t separate during meiosis-leads to abnormal number of chromosomes ◦ ___________ copies of chromosome 21 ◦ Mild to severe mental disability, and higher susceptibility to many diseases Sex chromosome __________________________ ◦ Turner syndrome (X): sterile ◦ Klinefelter’s syndrome (XXY): generally sterile











